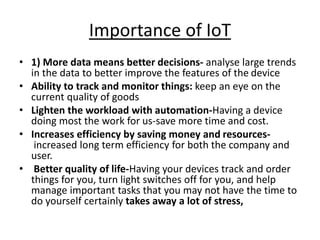
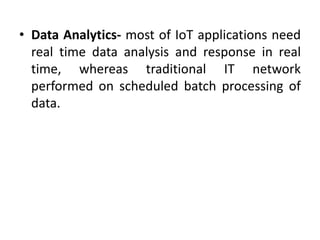
The document discusses Internet of Things (IoT) and its key aspects. It defines IoT as connecting physical objects through sensors and software to exchange data over the internet. IoT devices collect and share sensor data by connecting to gateways and the cloud to be analyzed with minimal human intervention. The document outlines technologies like sensors, connectivity, cloud computing and AI that enable IoT. It also discusses challenges of IoT like scalability, security, data analytics and interoperability.