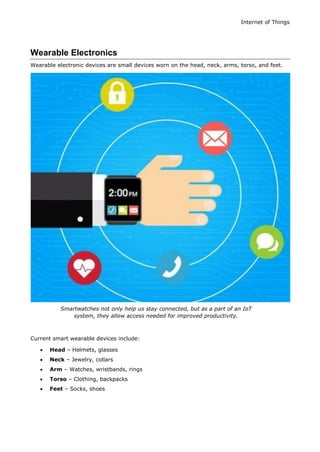
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Internet of Things (IoT), detailing its definition, key features, advantages, and challenges. It covers various applications of IoT across industries, emphasizing its role in enhancing automation, data collection, and operational efficiency. The report is intended for students seeking to gain intermediate knowledge of IoT concepts and systems.