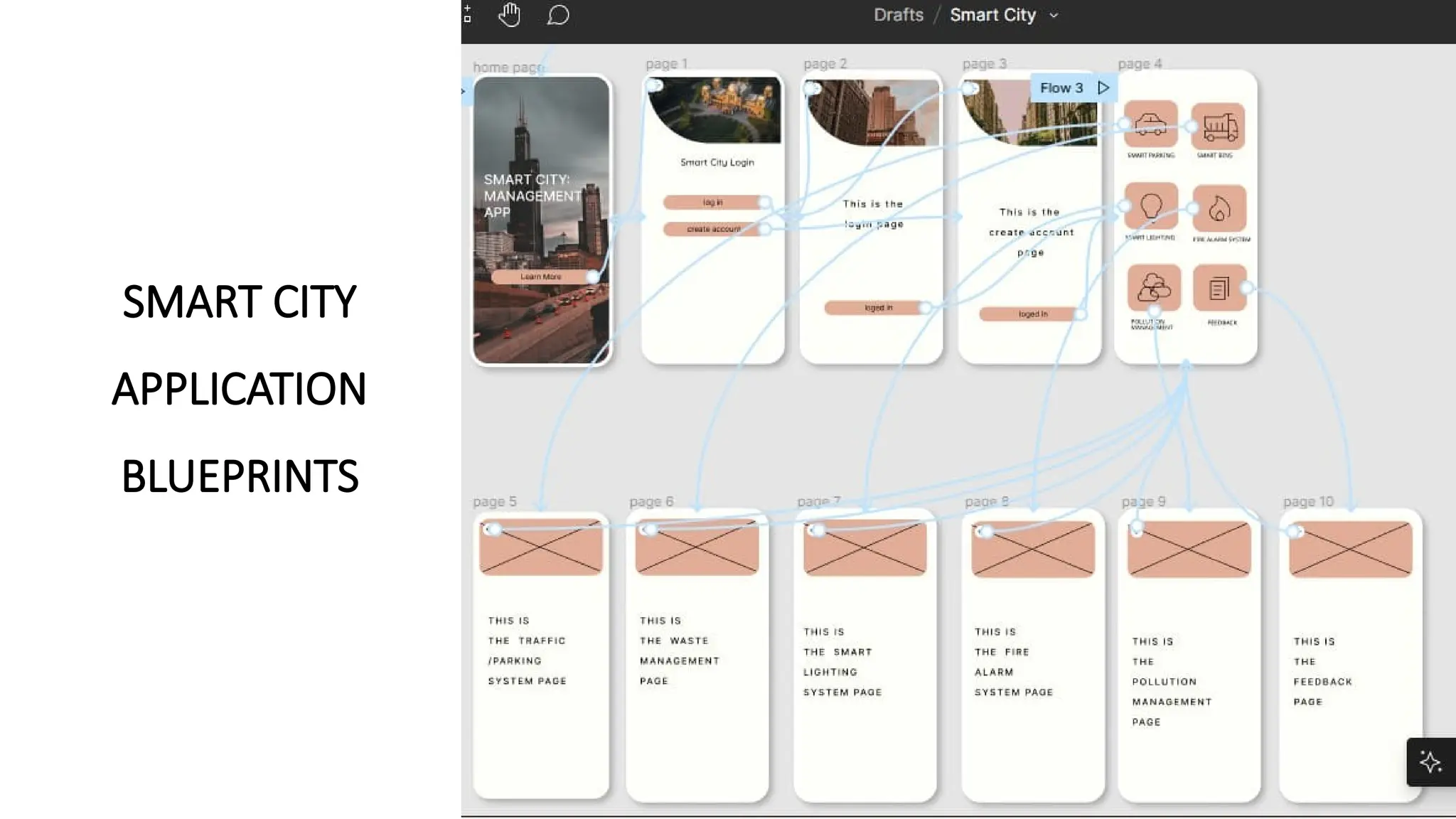
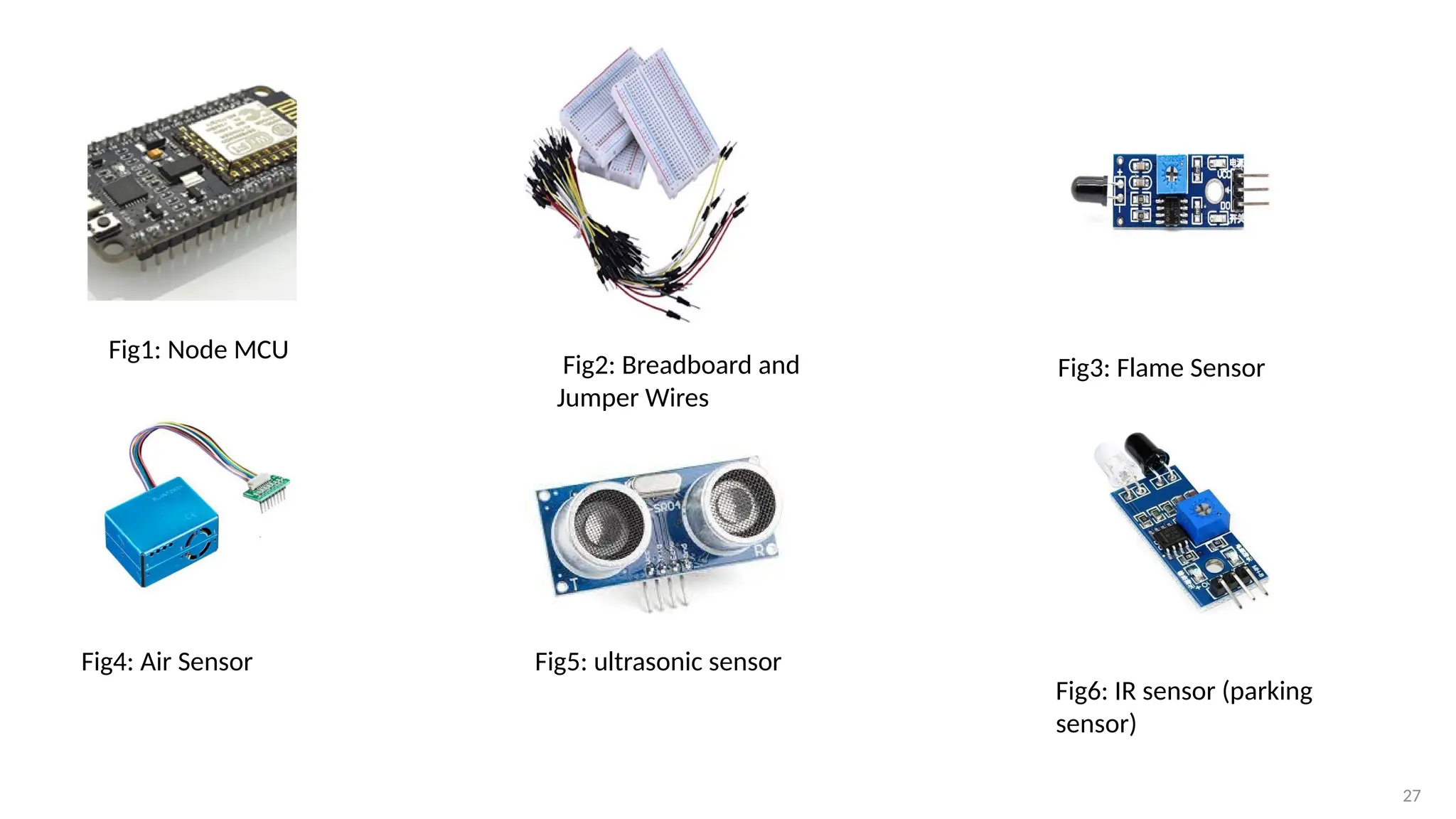
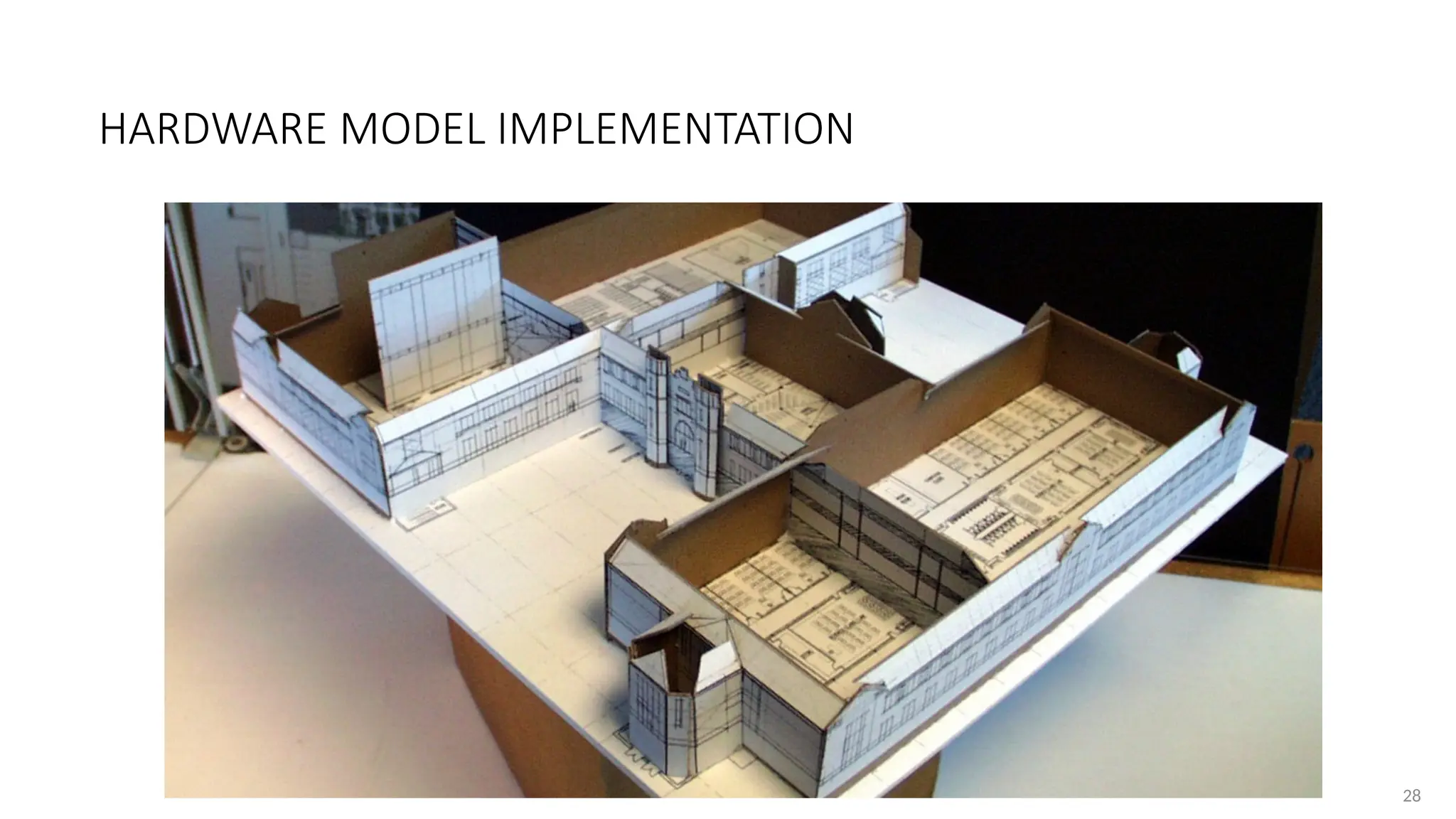
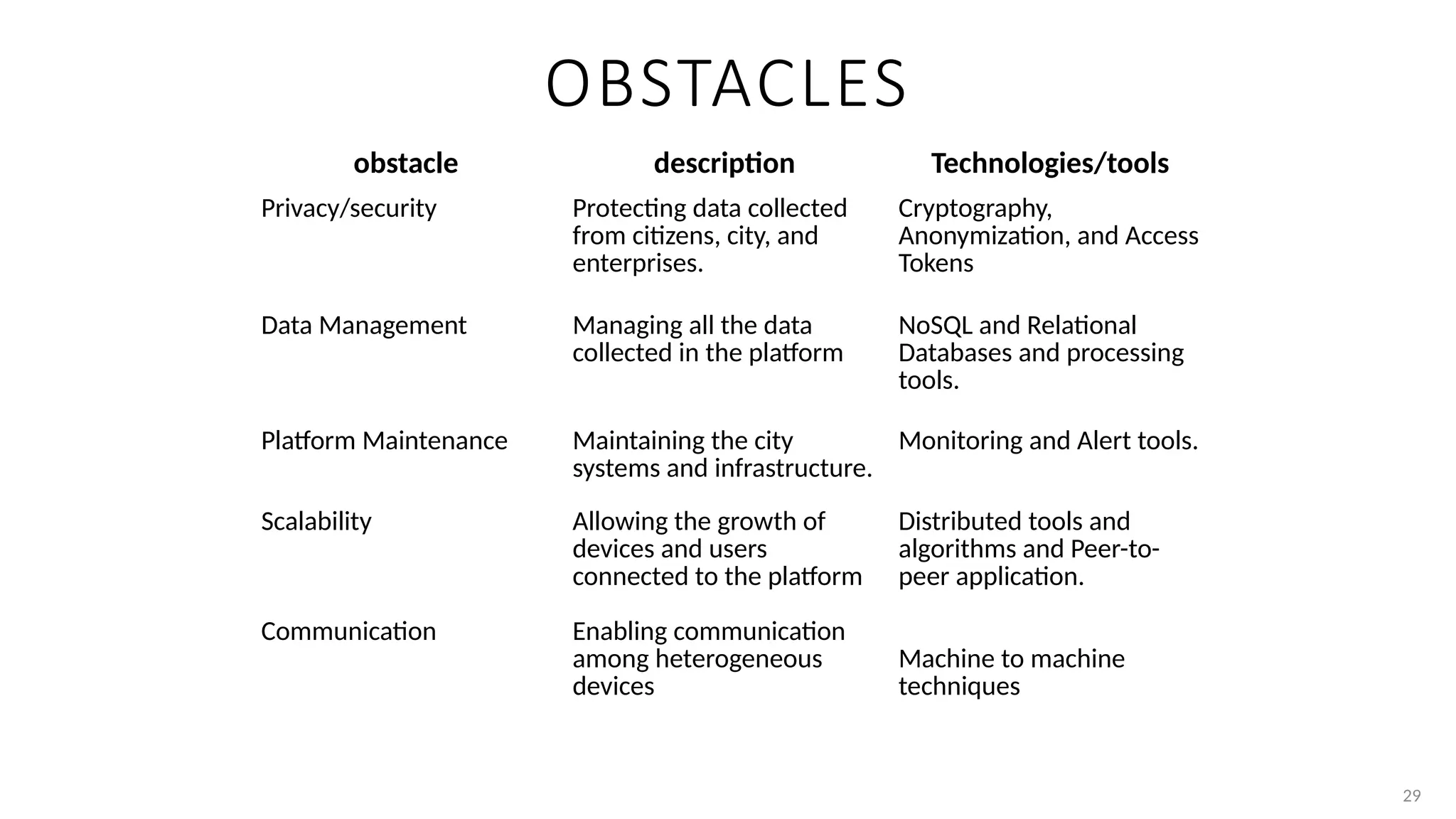
https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/chapter-1-ob-38248150/38248150https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/chapter-1-ob-38248150/38248150https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/chapter-1-ob-38248150/38248150https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/chapter-1-ob-38248150/38248150https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/chapter-1-ob-38248150/38248150
















![34
34
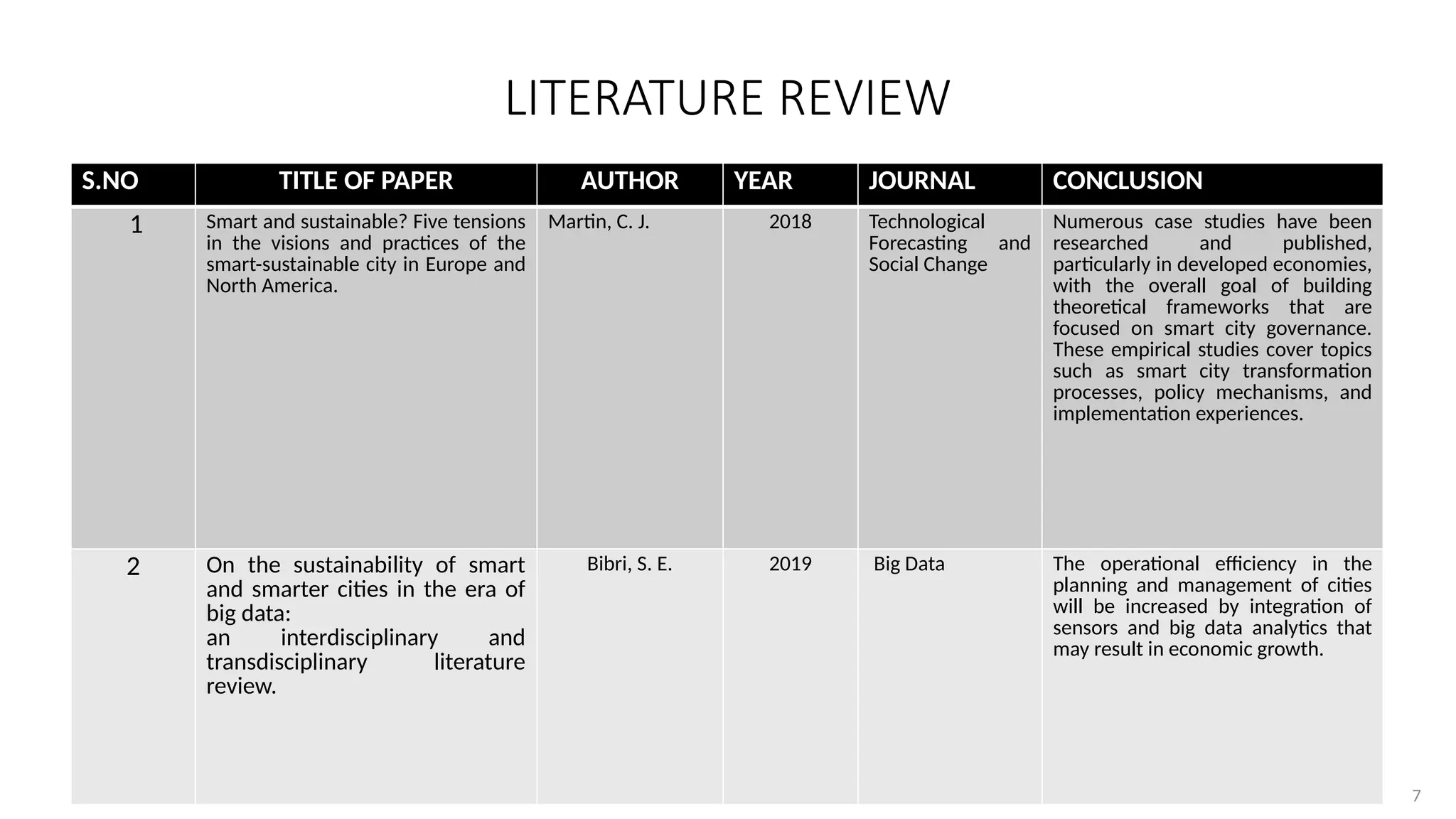
[1] Bibri, S. E. (2019). "On the sustainability of smart and smarter cities in the era of big data: an interdisciplinary
and transdisciplinary literature review." Journal of Big Data 6(1): 1-64.
[2] Ismagilova, Elvira, Laurie Hughes, Nripendra P Rana, and Yogesh K Dwivedi. "Security, Privacy and Risks within
Smart Cities: Literature Review and Development of a Smart City Interaction Framework." Information Systems
Frontiers (2020): 1-22.
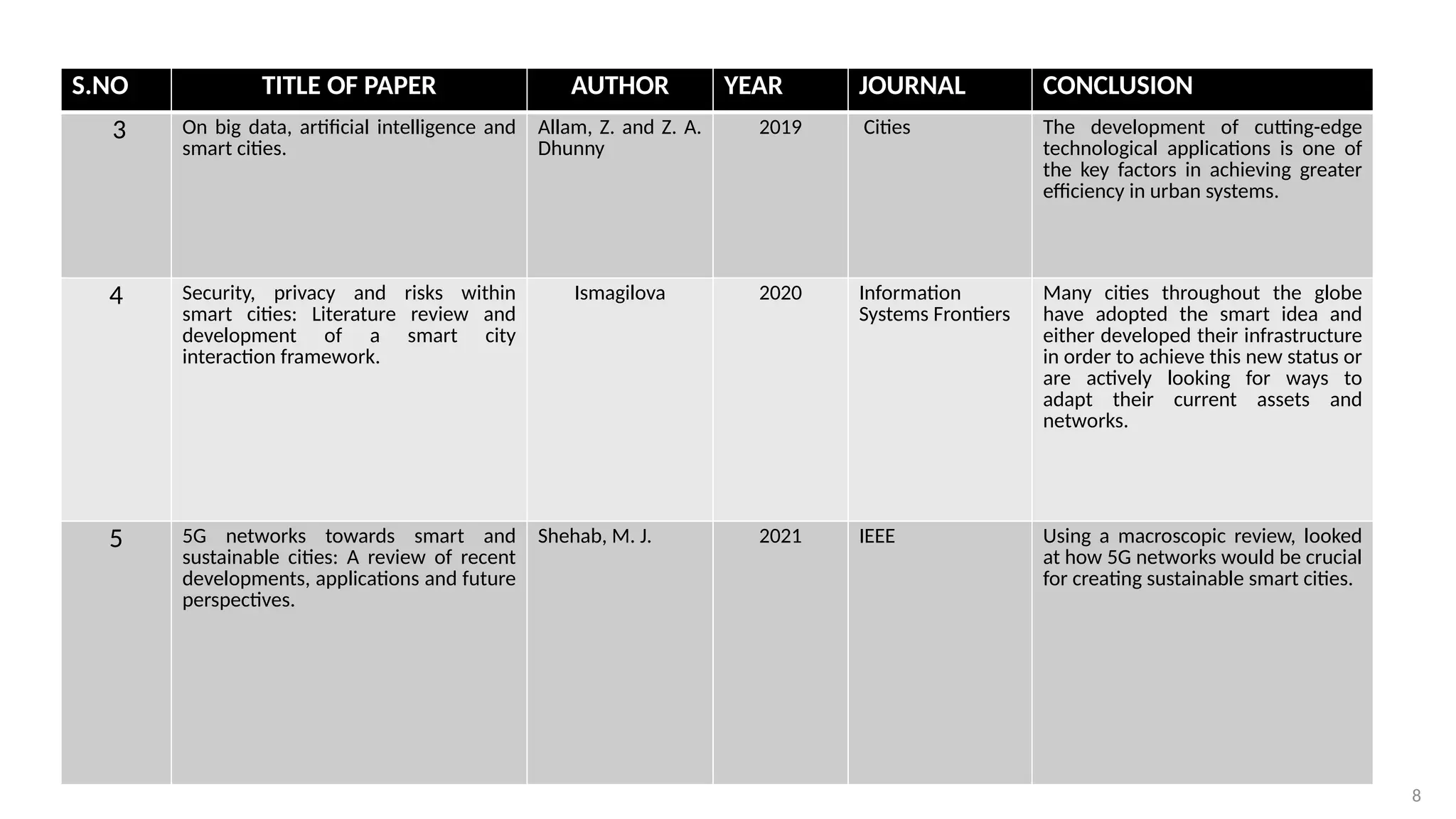
[3] Shehab, Muhammad J, Ihab Kassem, Adeeb A Kutty, Murat Kucukvar, Nuri Onat, and Tamer Khattab. "5g
Networks Towards Smart and Sustainable Cities: A Review of Recent Developments, Applications and Future
Perspectives." IEEE Access 10 (2021): 2987-3006.
[4] Allam, Zaheer, and Zaynah A Dhunny. "On Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Smart Cities." Cities 89 (2019): 80-
91.
[5] Martin, Chris J, James Evans, and Andrew Karvonen. "Smart and Sustainable? Five Tensions in the Visions and
Practices of the Smart-Sustainable City in Europe and North America." Technological Forecasting and Social Change
133 (2018): 269-78.
REFERENCES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/initialseminarfyp-250317180500-0b0301fe/75/https-www-slideshare-net-slideshow-chapter-1-ob-38248150-38248150https-www-slideshare-net-slideshow-chapter-1-ob-38248150-38248150-34-2048.jpg)