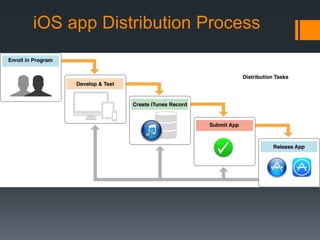
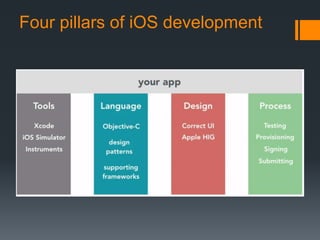
This document provides an overview of the iOS development process, from development in Xcode to distributing apps on the App Store. It discusses the core components of iOS like Xcode, Objective-C, UIKit and Cocoa Touch frameworks. The document explains how to set up the development environment, design app interfaces, code apps using Objective-C and common iOS design patterns. It also outlines the steps to test apps on real devices and submit apps to the App Store for distribution.












![Main Funciton –like C++
#import <whatever/what.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
//your code here*******
//you can have C code if you wish or Objective-C
return 0;
}
}
NOTE: Latest version of Objective-C uses Automatic
Reference Counting (kind of like automatic garbage collection)
----to handle getting rid of not needed items in memory (avoiding
memory leaks). YEAH! AUTOMATIC!
-----like Java this way
@autoreleasepool in a needed annotation around your main
block of code to “enable” this](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-140918012403-phpapp02/85/iOS-From-Development-to-Distribution-14-320.jpg)

![Declaring methods
C++ syntax
void function(int x, int y, int z);
Object.function(x, y, z);
Objective-C syntax
-(void)methodWithX : (int)x Y :(int)y andZ (int)z
[someObject methodWithX:1 Y:2 andZ:2];
-(return type) function_Apply function to Object name: (type) p1, (type) p2, ***;
passing parameters x,y,z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-140918012403-phpapp02/85/iOS-From-Development-to-Distribution-16-320.jpg)
![Messages ---really weird (new)
syntax
Almost every object manipulation is done by
sending objects a message
Two words within a set of brackets, the
object identifier and the message to send.
[Identifier message ]
Like C++ or Java’s Identifier.message()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-140918012403-phpapp02/85/iOS-From-Development-to-Distribution-17-320.jpg)
![Memory Allocation
Objects are created dynamically through the keyword, “alloc”
Objects are automatically deallocated in latest Objective-C
through automatic reference counting
Sample Allocation Of Object
AClass *object=[[AClass alloc]initWithSomeThing];
Constructor Does not exist in Objective C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-140918012403-phpapp02/85/iOS-From-Development-to-Distribution-18-320.jpg)

![NSString
NSString *theMessage = @”hello world”;
Number of characters in a string
NSUInteger charCount = [theMessage length];
Test if 2 strings equal
if([string_var_1 isEqual: string_var_2])
{ //code for equal case }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-140918012403-phpapp02/85/iOS-From-Development-to-Distribution-20-320.jpg)
![NSArray – holds fixed array of
points to objects
NSArray *thearray = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:o1,o2,o3,o4, nil];
//get element
[thearray objectAtIndex:0]; //element at index 0
Example
Note: you can not add or remove a pointer from an NSArray
---fixed once created
NSDate *now = [NSDate date];
NSDate *tomorrow = [now dateByAddingTImeInterval:24.0*60.0*60.0]; //add a day
NSDate *yesterday = [now dateByAddingTimeInterval:-24.0*60.0*60.0]; //minus a day
//array of Dates
NSArray *dateList = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:now, tomorrow, yesterday];
//get elements in array
NSDate *first = [dateList objectAtIndex:0];
Methods are:
count = gets number of items in array
objectAtIndex:i = returns element i of array (starting from 0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-140918012403-phpapp02/85/iOS-From-Development-to-Distribution-21-320.jpg)
![NSMutableArray – changeable array
of pointers to objects.
NSMutableArray *thearray = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:o1,o2,o3,o4, nil];
//get element
[thearray objectAtIndex:0]; //element at index 0
Note: you can add or remove a pointer from an NSMutableArray
Example
NSDate *now = [NSDate date];
NSDate *tomorrow = [now dateByAddingTImeInterval:24.0*60.0*60.0]; //add a day
NSDate *yesterday = [now dateByAddingTimeInterval:-24.0*60.0*60.0]; //minus a day
//array of Dates
NSMutableArray *dateList = [NSMutableArray array];
//set elements
[dateList addObject:now];
[dateList addObject:tomorrow];
[dateList addObject:yesterday];
Methods are:
array = gets empty NSMutableArray
addObject:obj = adds as next element the obj
to array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-140918012403-phpapp02/85/iOS-From-Development-to-Distribution-22-320.jpg)