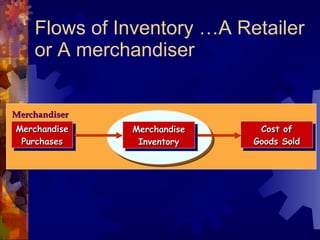
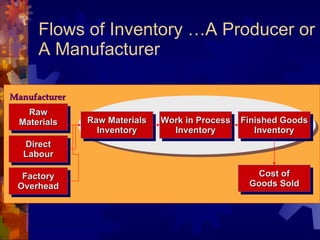
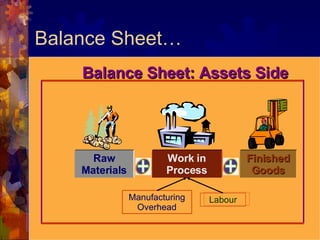
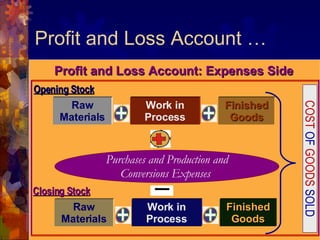
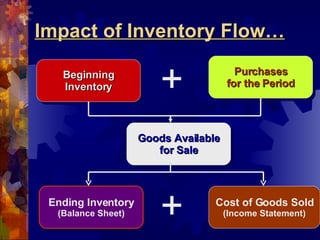
The document discusses accounting for inventory. It defines inventory as assets held for sale, in production, or as supplies. It describes different inventory types like raw materials and finished goods. Inventory systems can record transactions periodically or perpetually. Costs included in inventory are purchase costs, conversion costs, and other costs to bring inventory to its present state. Certain costs like administrative overhead are excluded.