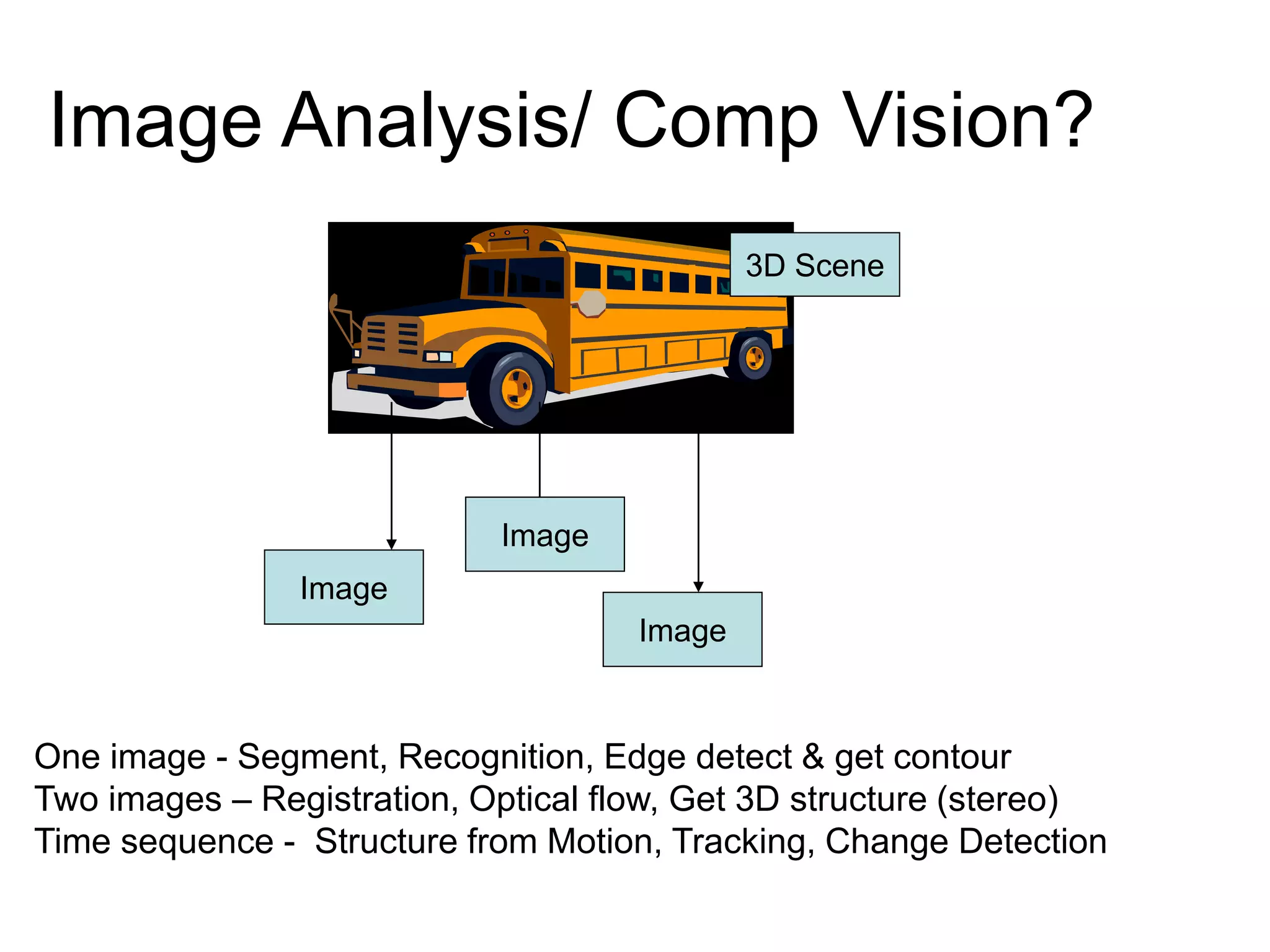
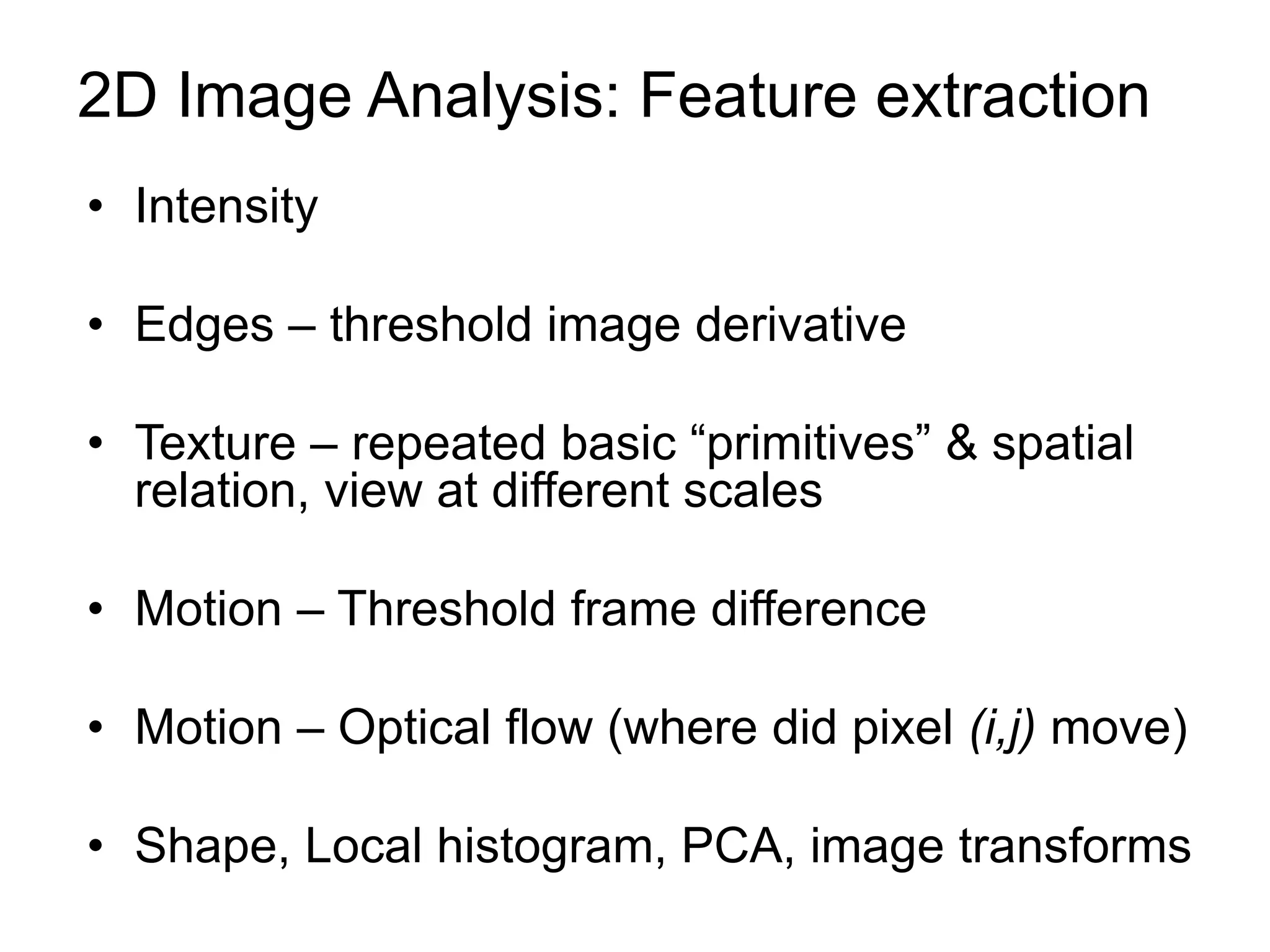
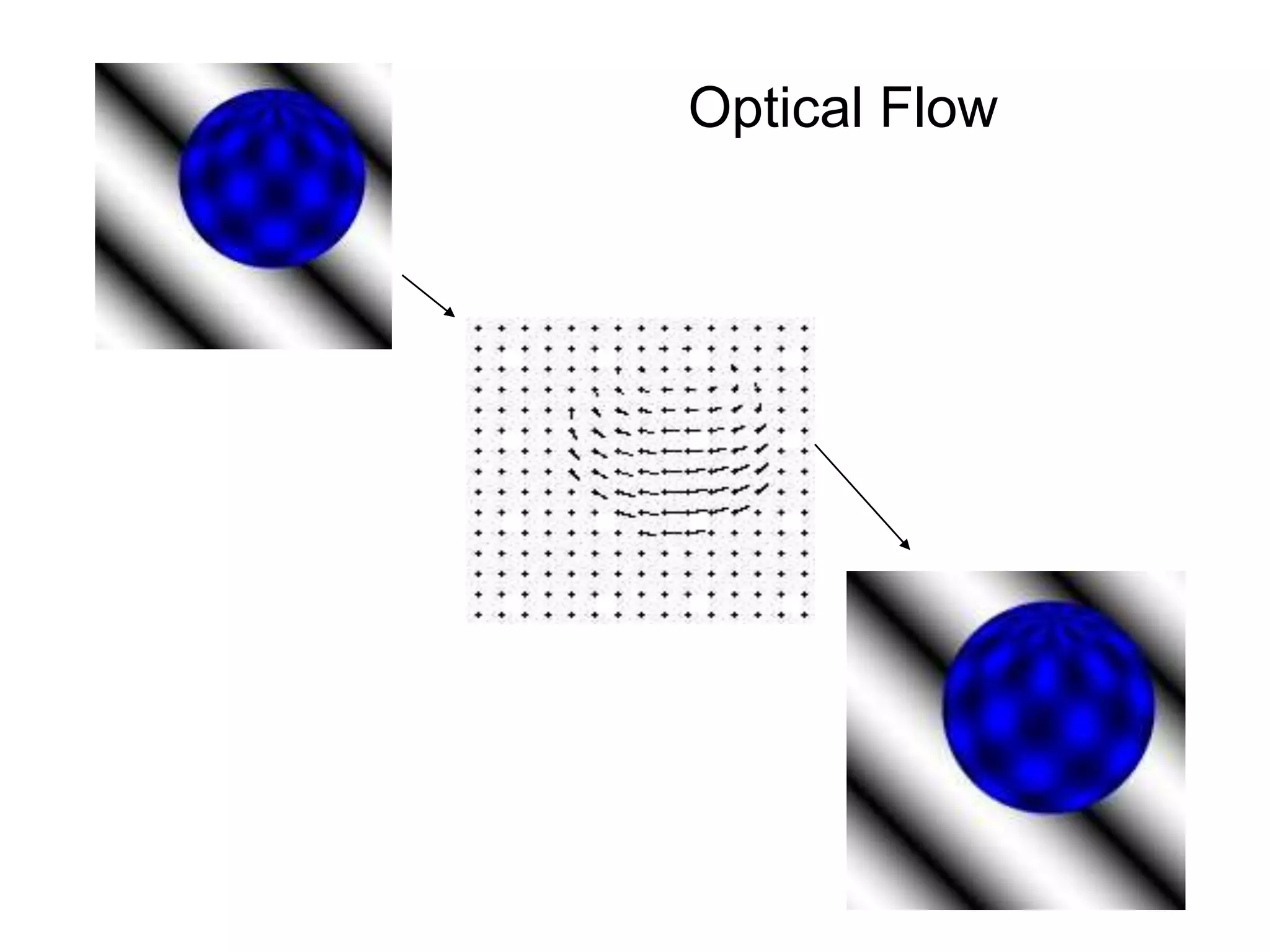
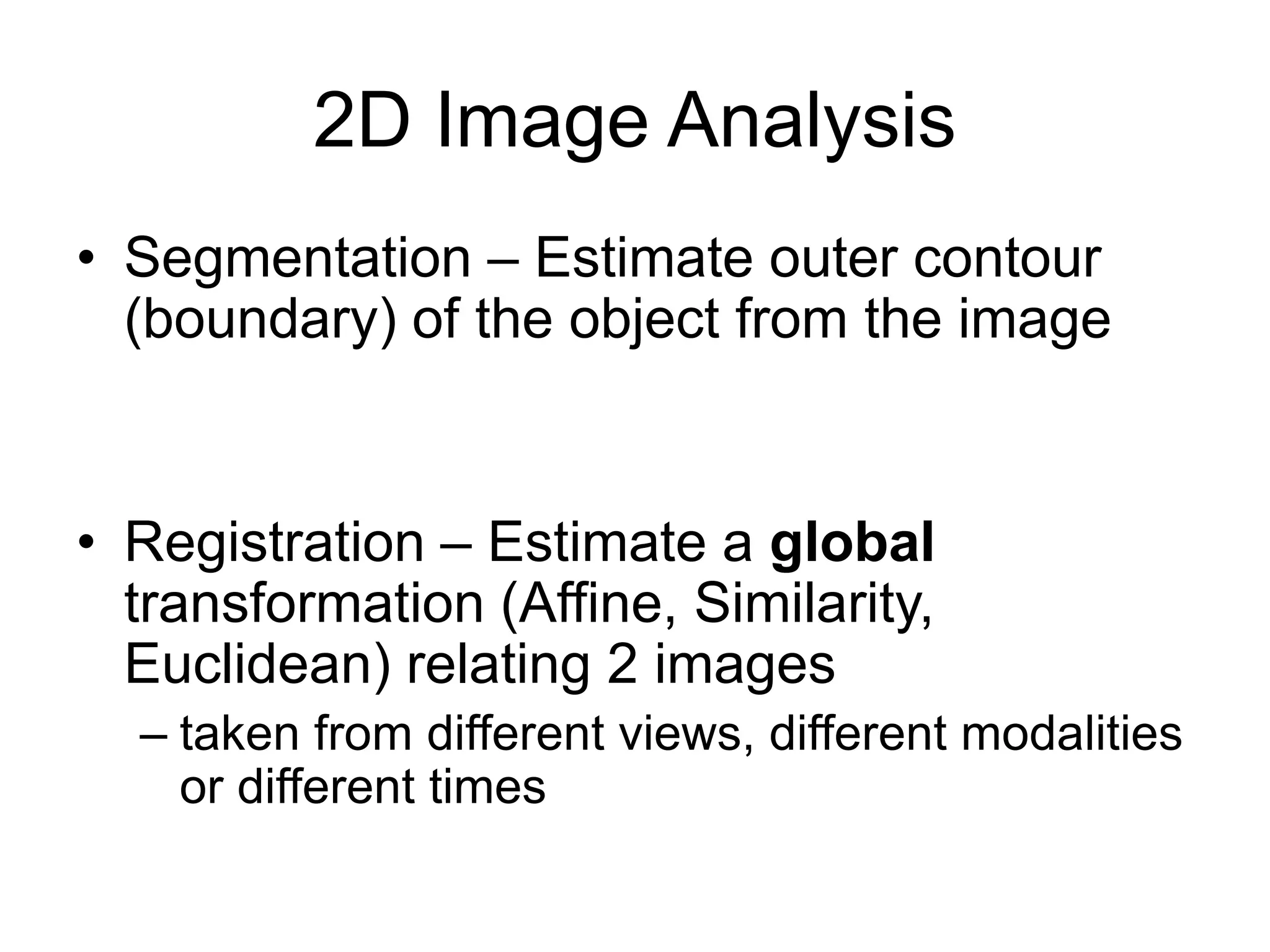
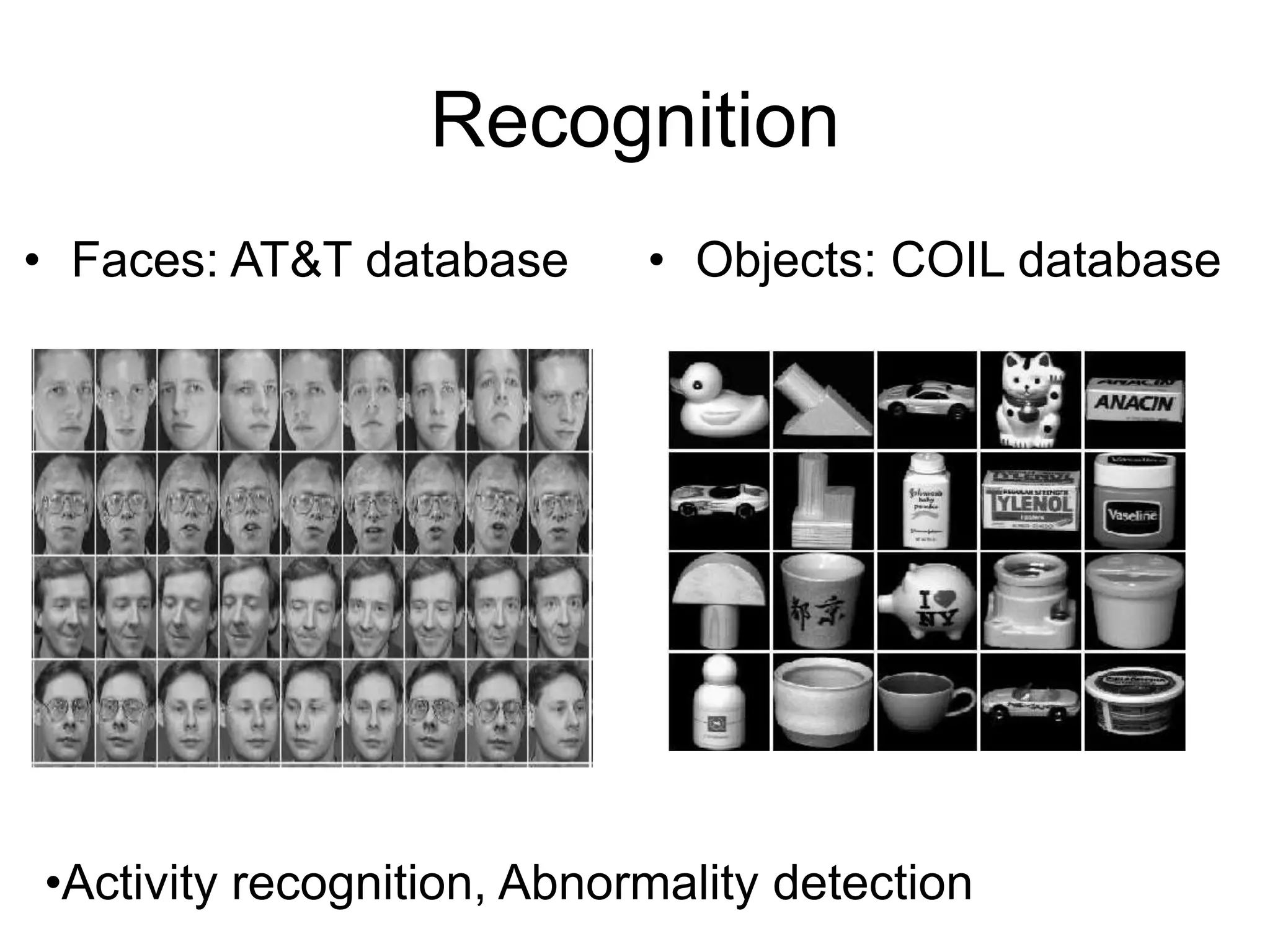
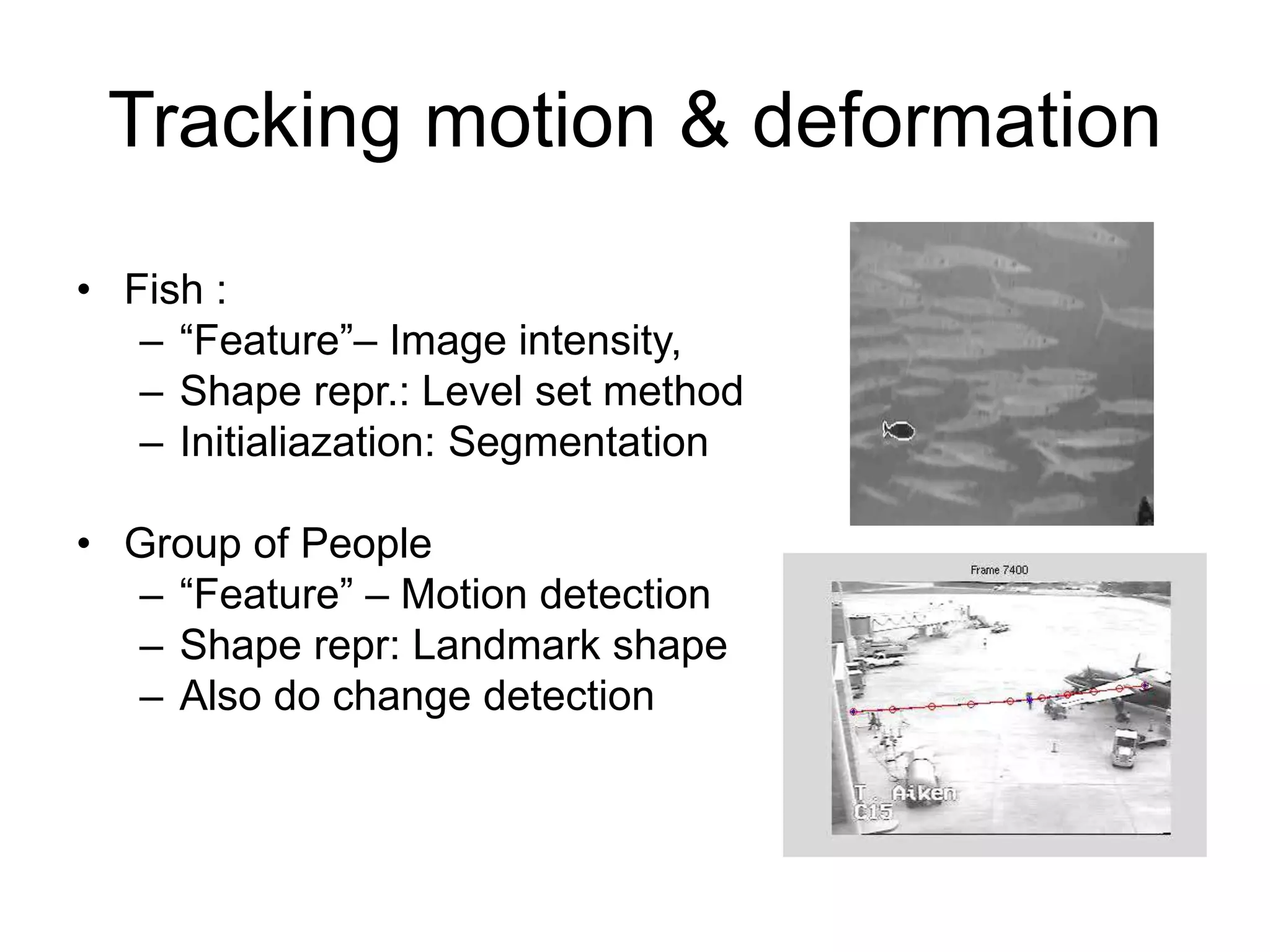
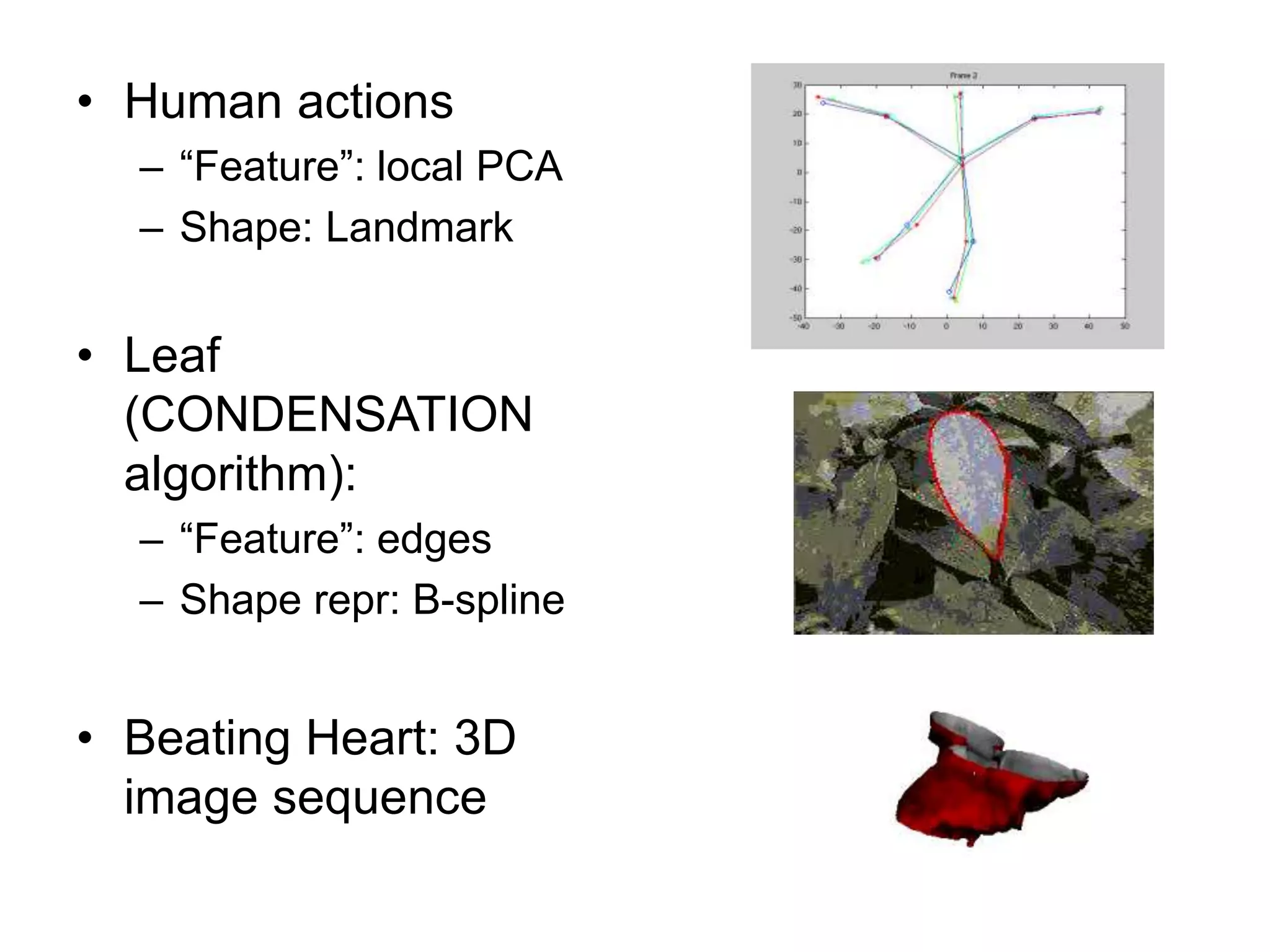
EE 520 is an image analysis and computer vision class that meets Monday, Wednesday, and Tuesday-Thursday. The class will be evaluated based on two projects worth 30% each and a midterm worth 40%. Projects will include a report, presentation, and MATLAB code. The class will cover topics like feature extraction, segmentation, registration, optical flow, shape representation, tracking, recognition, and inferring 3D structure from 2D images. Example applications include analyzing faces, objects, activities, leaf motion, and beating hearts.