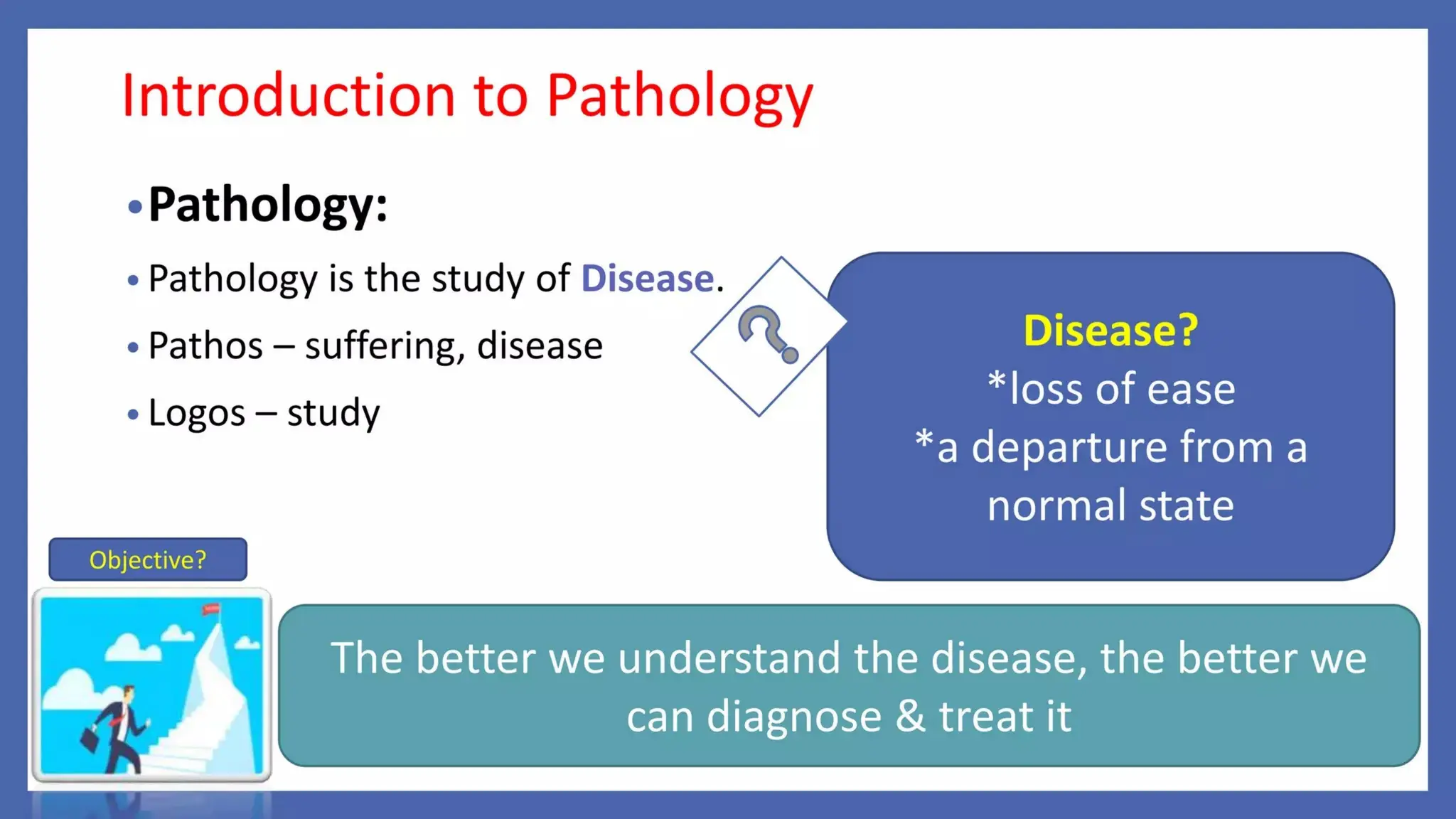
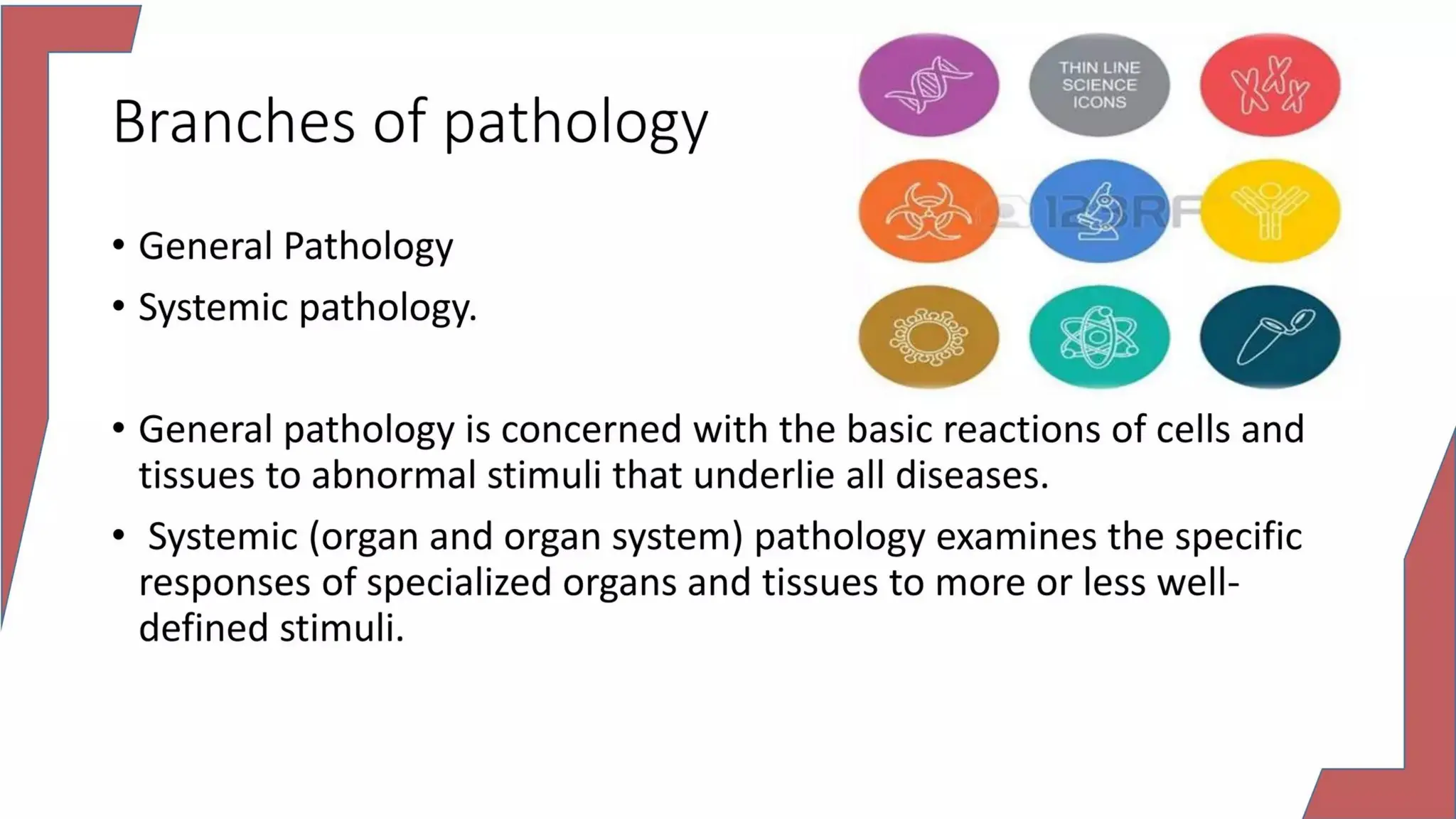
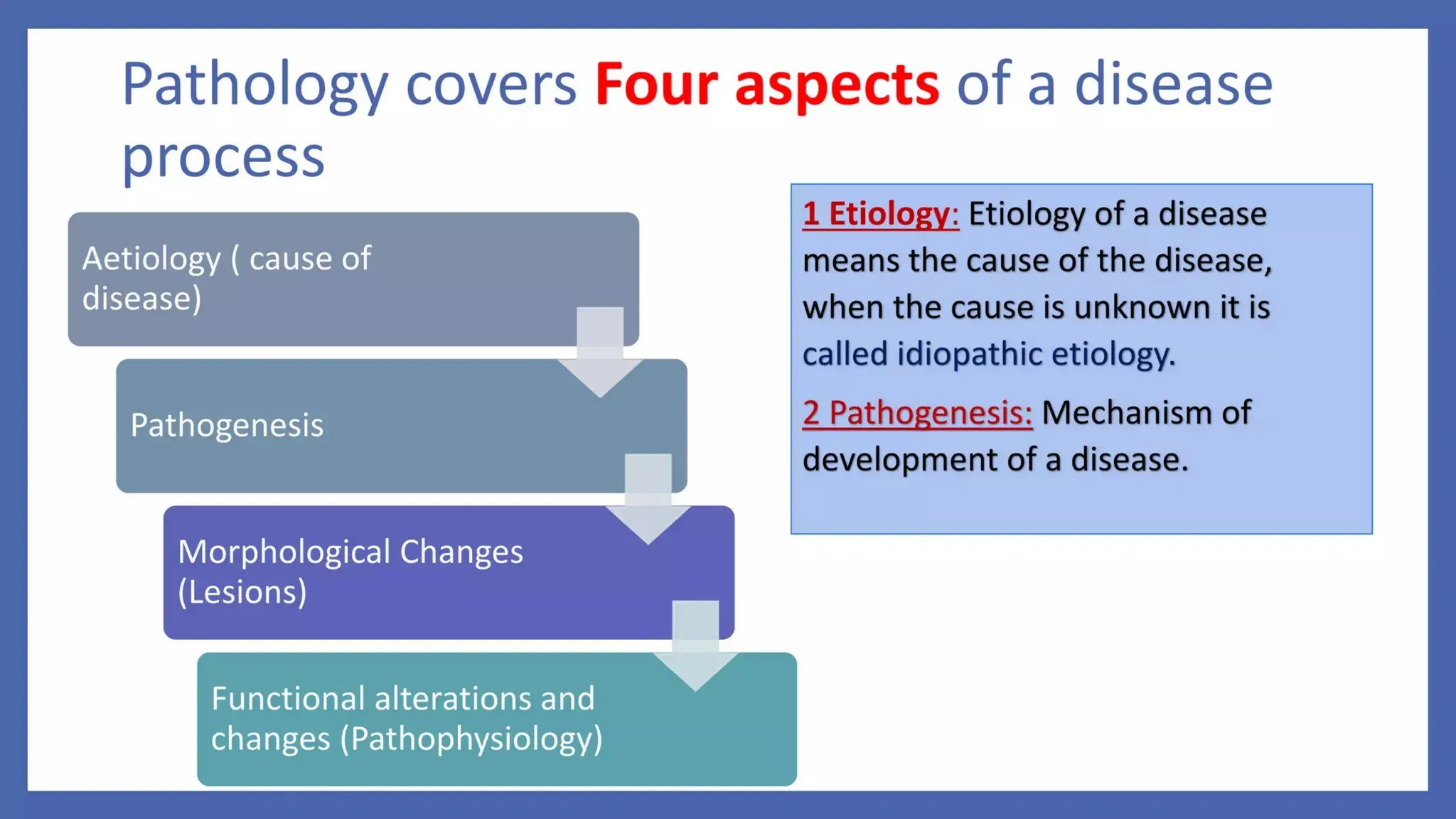
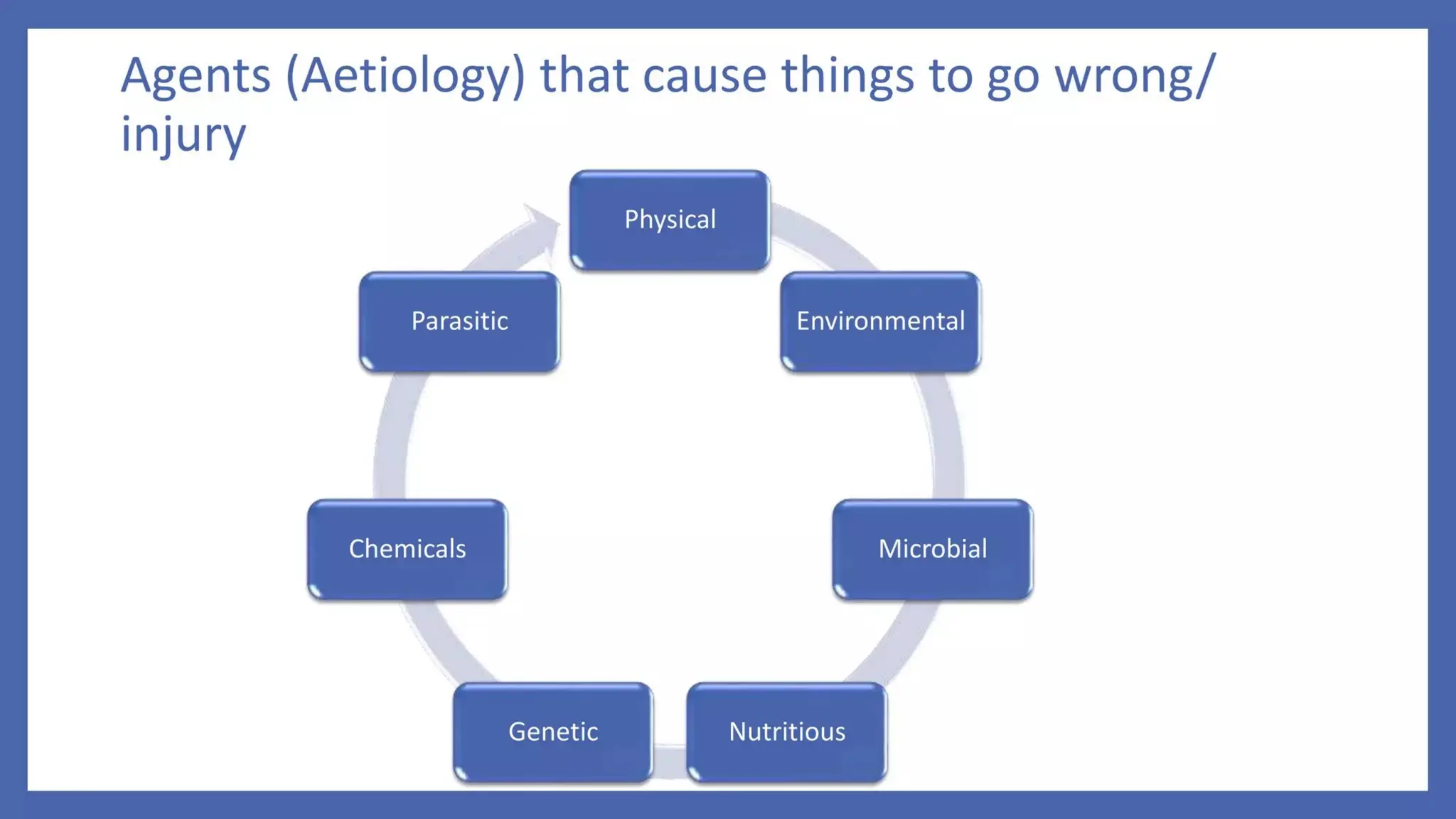
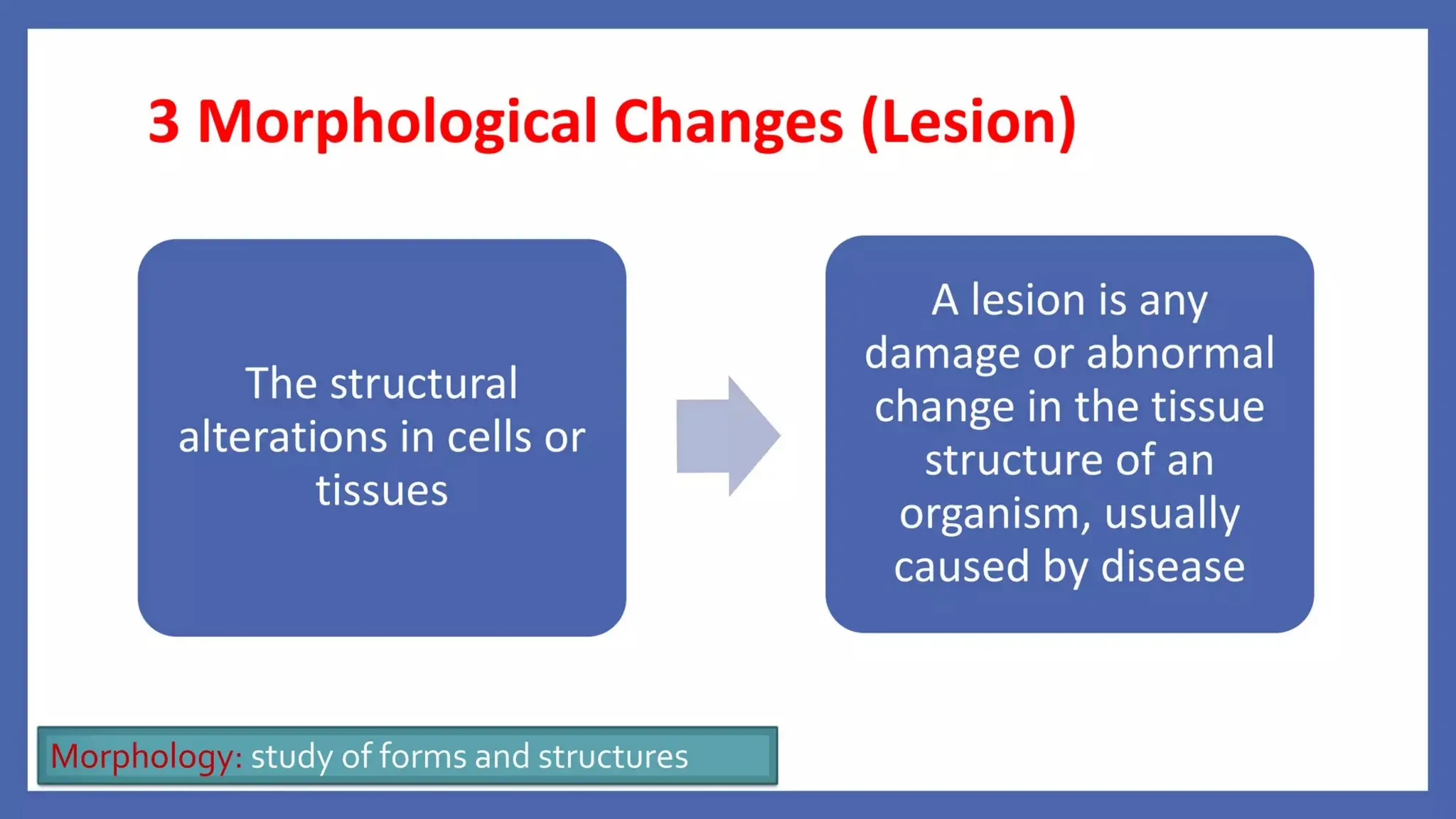
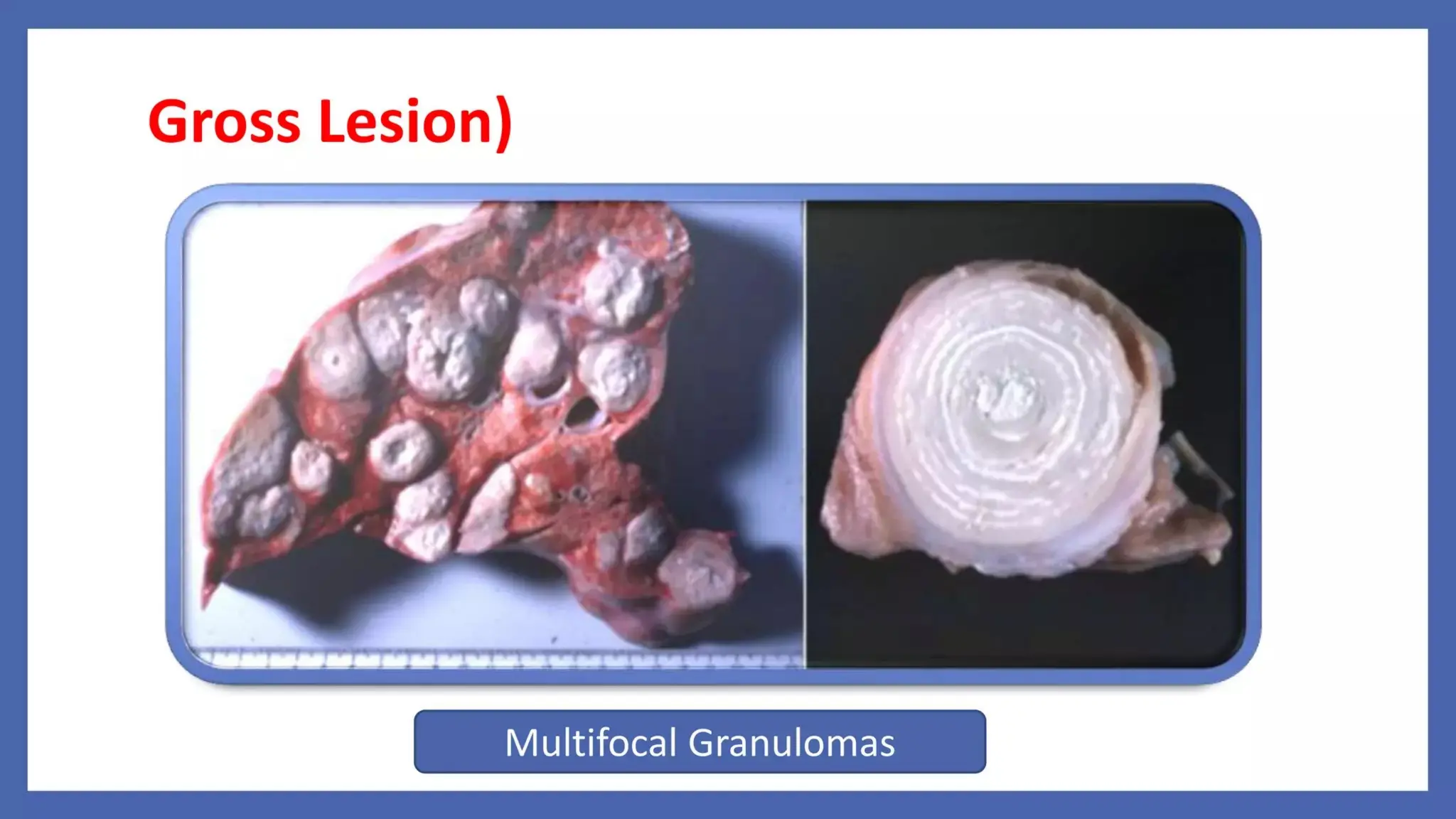
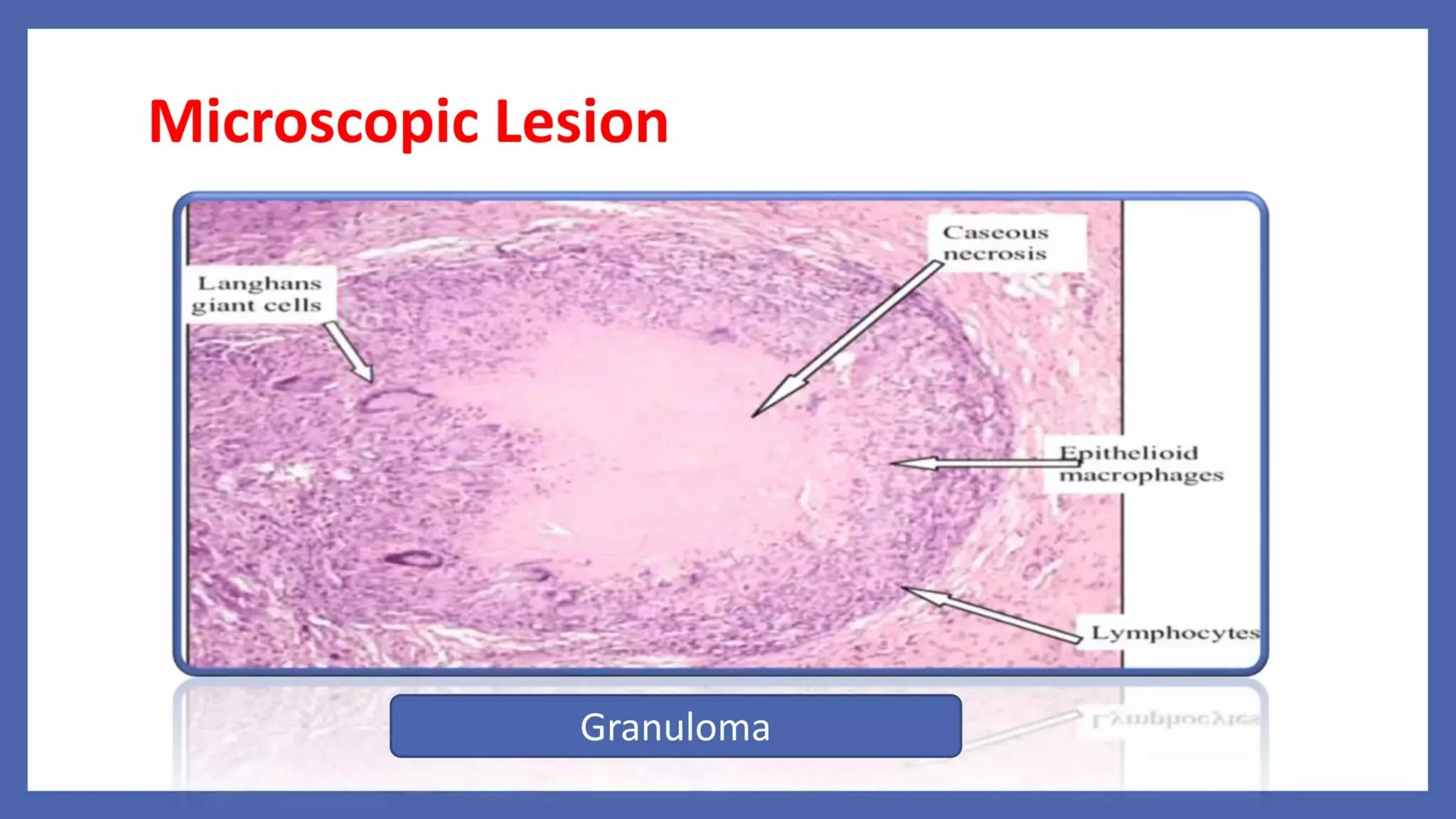
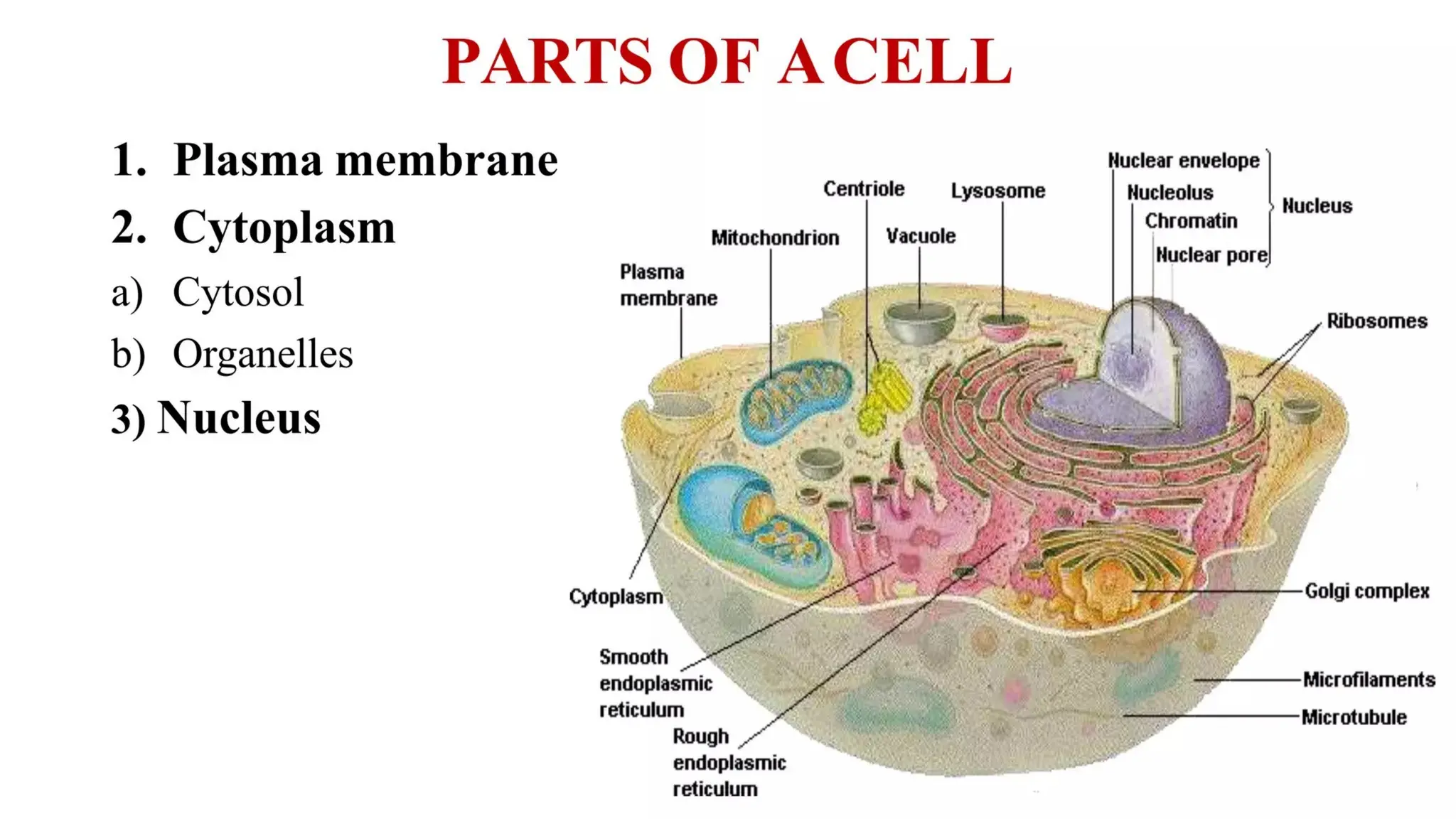
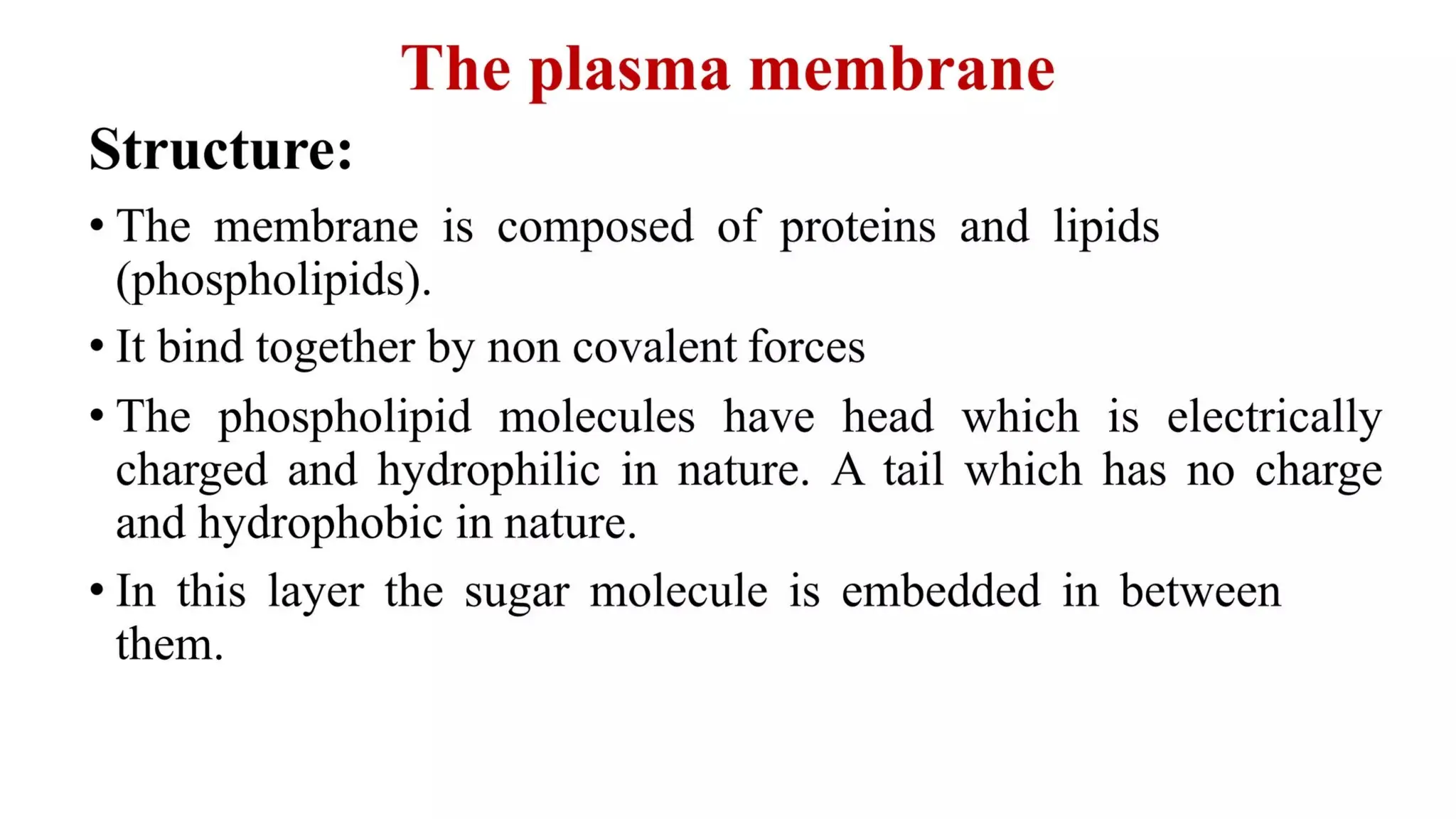
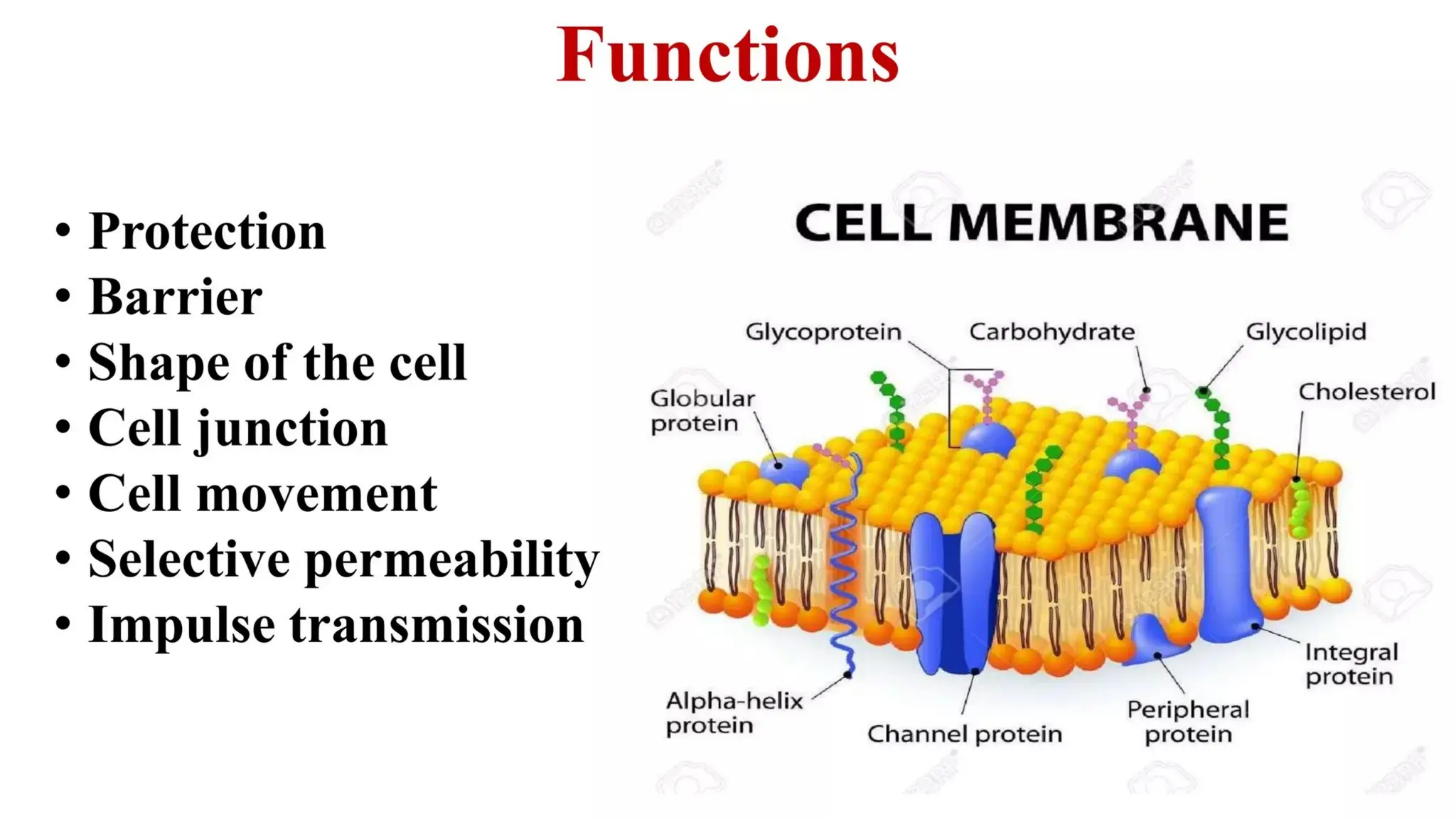
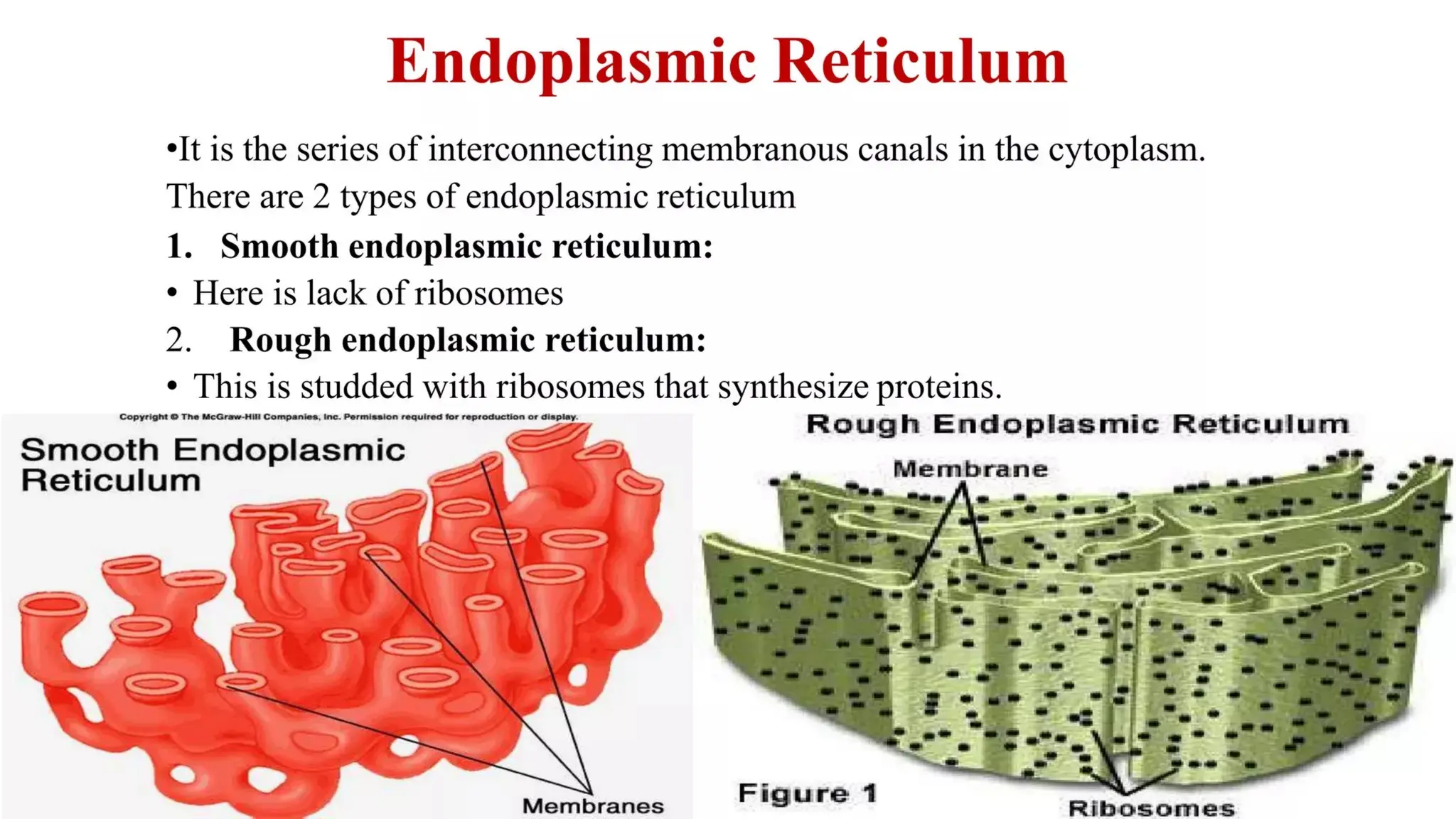
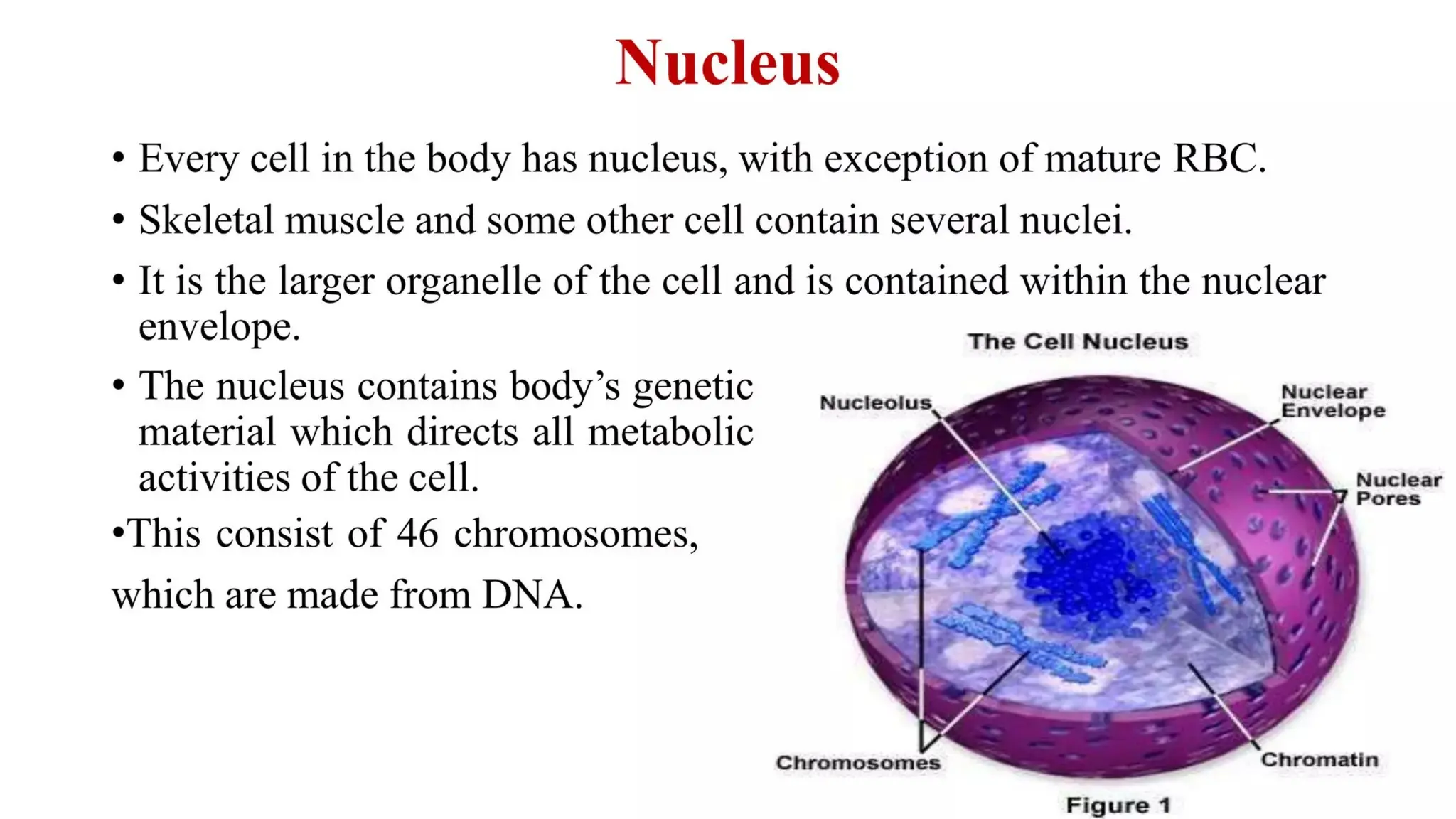
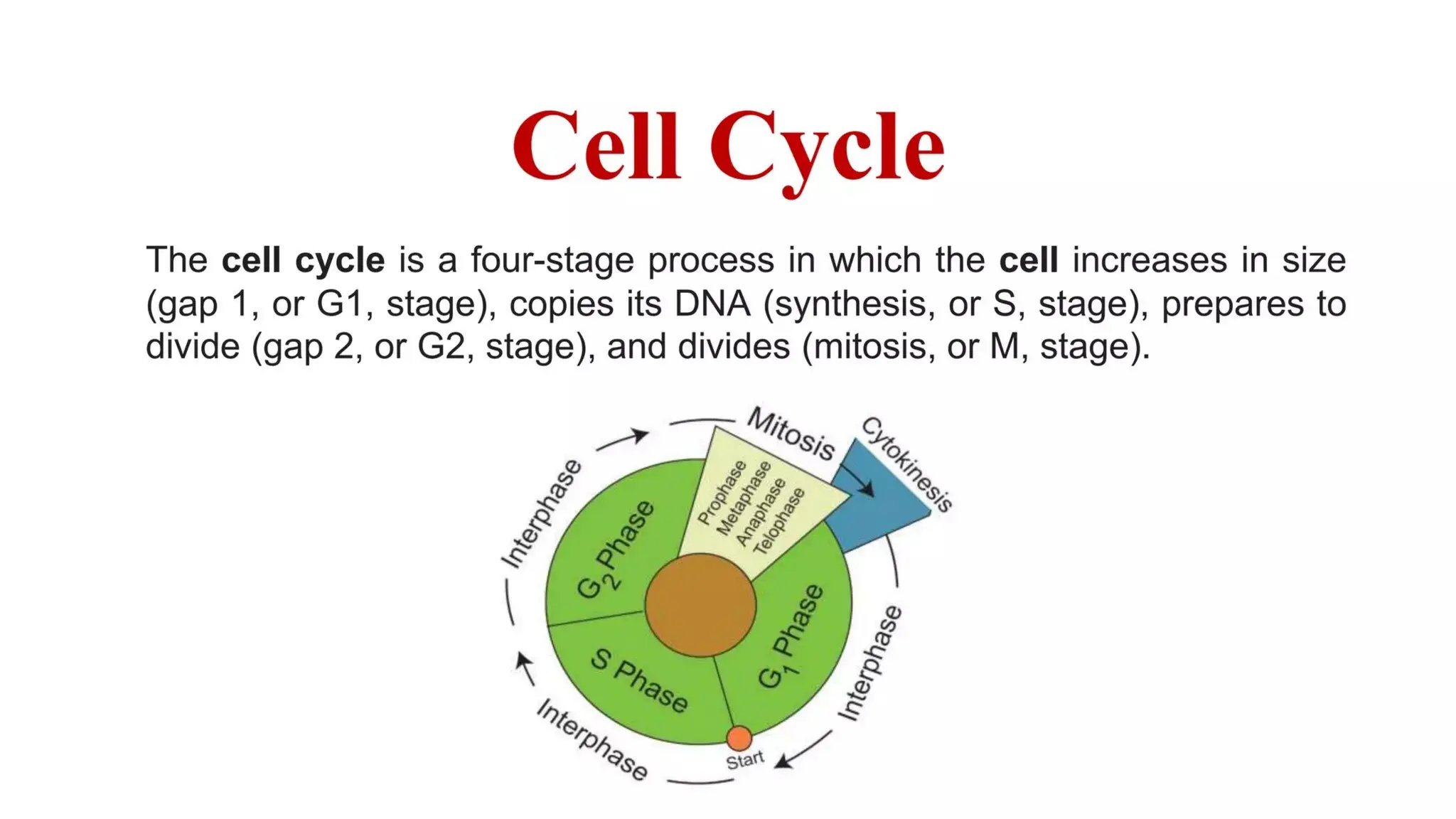
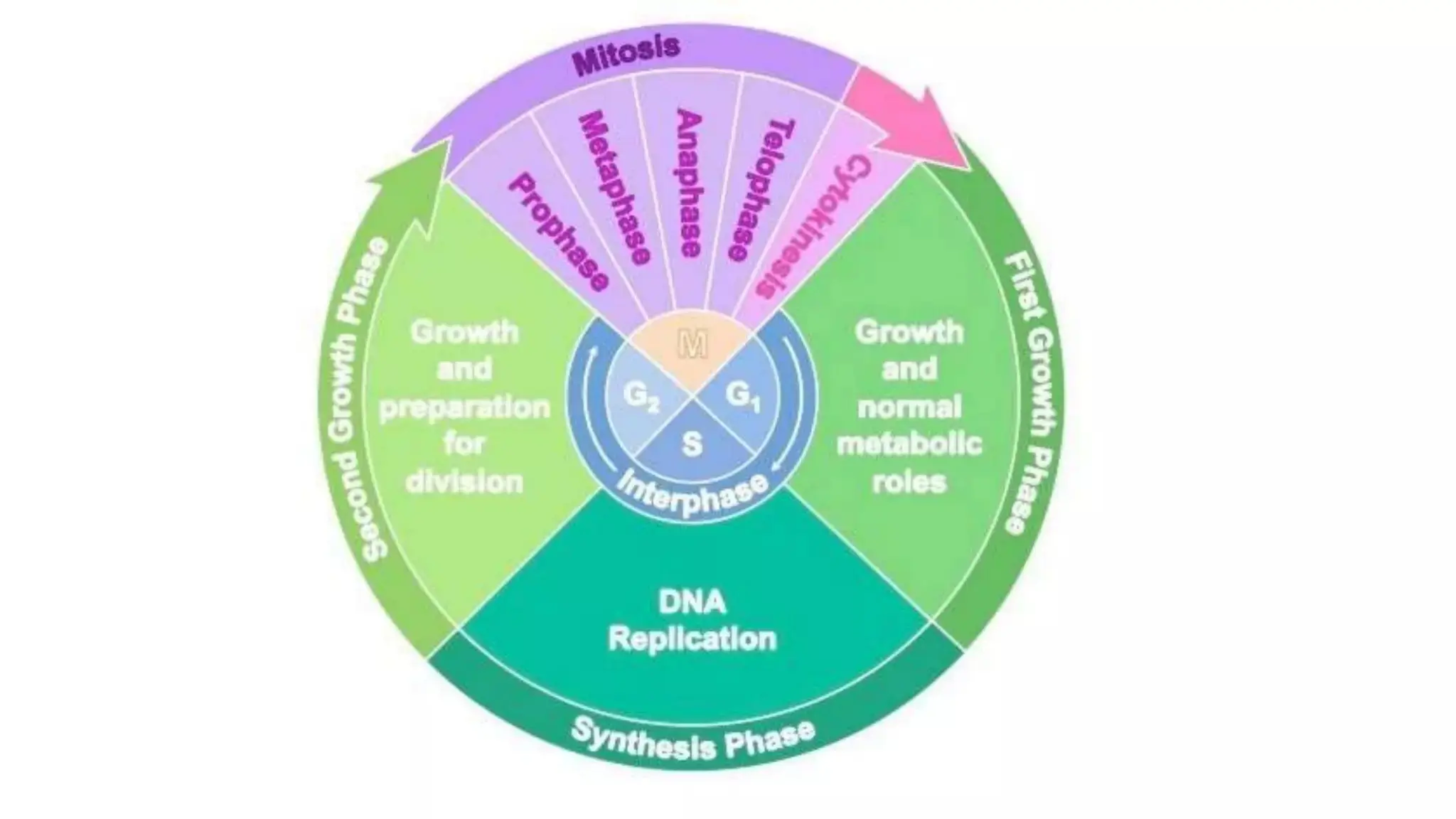
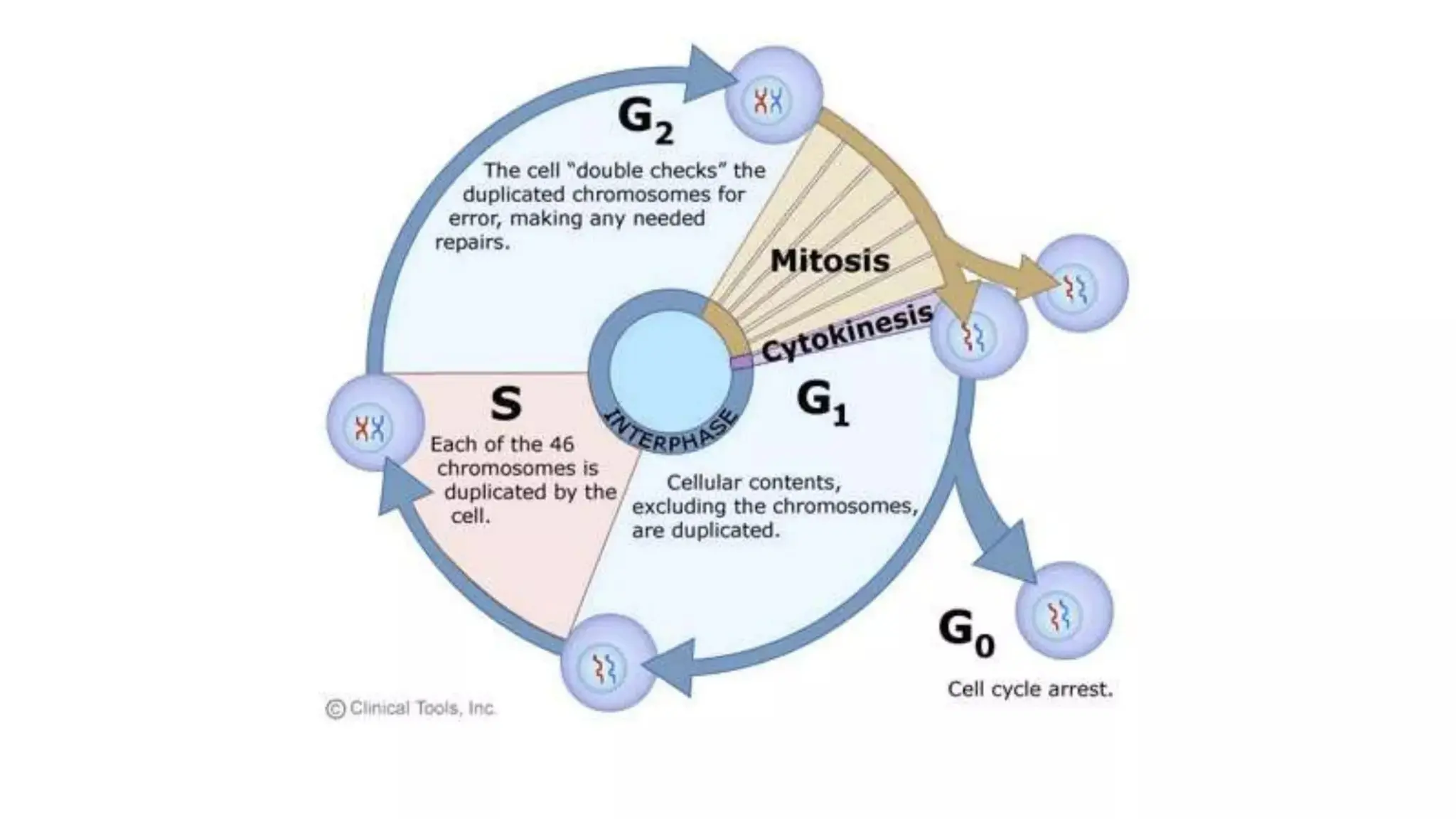
Pathology is a branch of medical science that studies the causes, nature, and effects of diseases through various methods such as anatomic, clinical, and forensic pathology. Key components include histopathology, microbiology, and molecular pathology, which facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Forensic pathology applies these principles to legal cases, determining causes of death and aiding in investigations.