This document provides an overview of computer technology, including:
1) A definition of a computer as an electronic device that can accept data as input, process it, and produce output.
2) An introduction to key concepts like data, information, input, output, storage, users, hardware, and software.
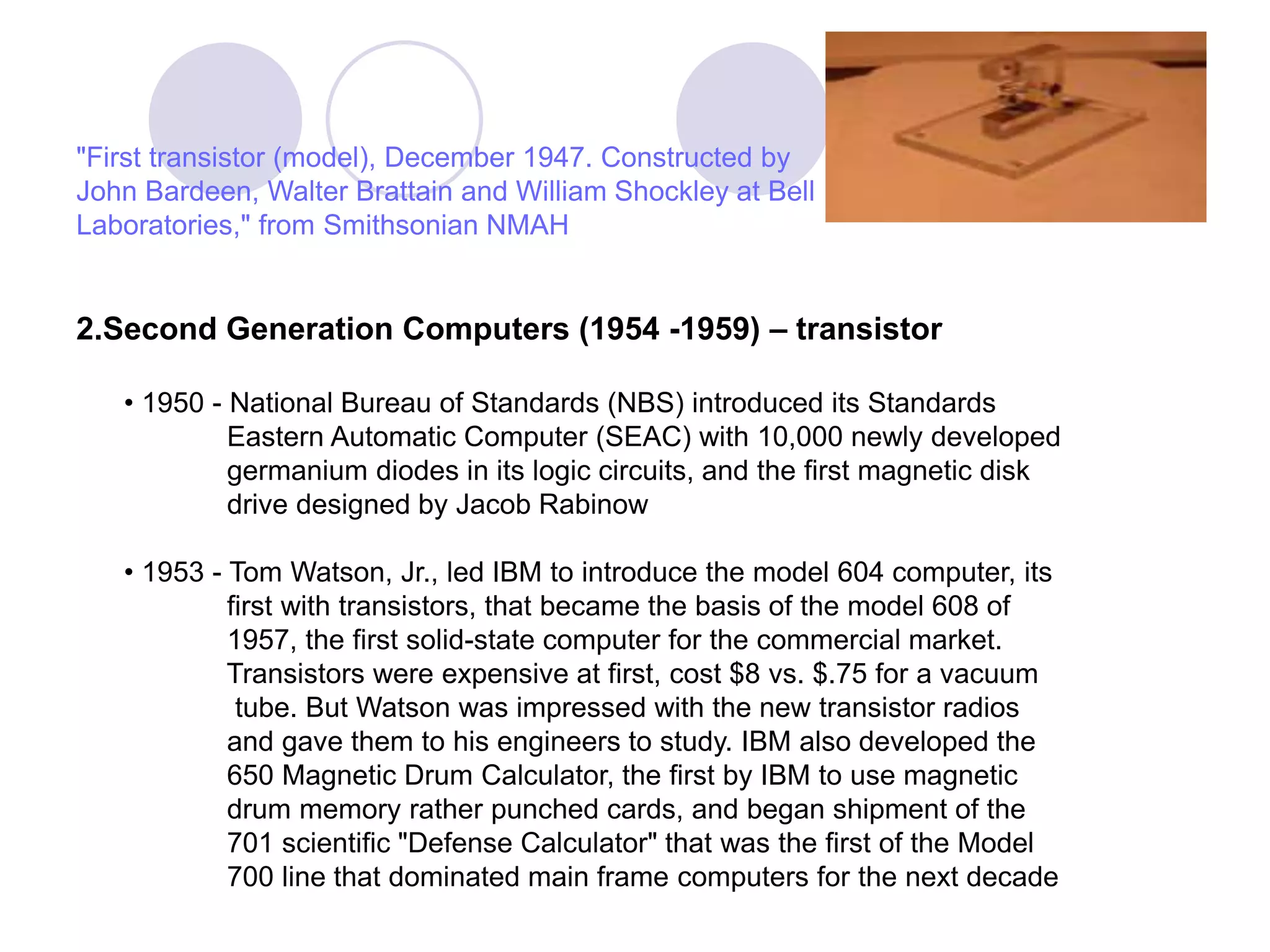
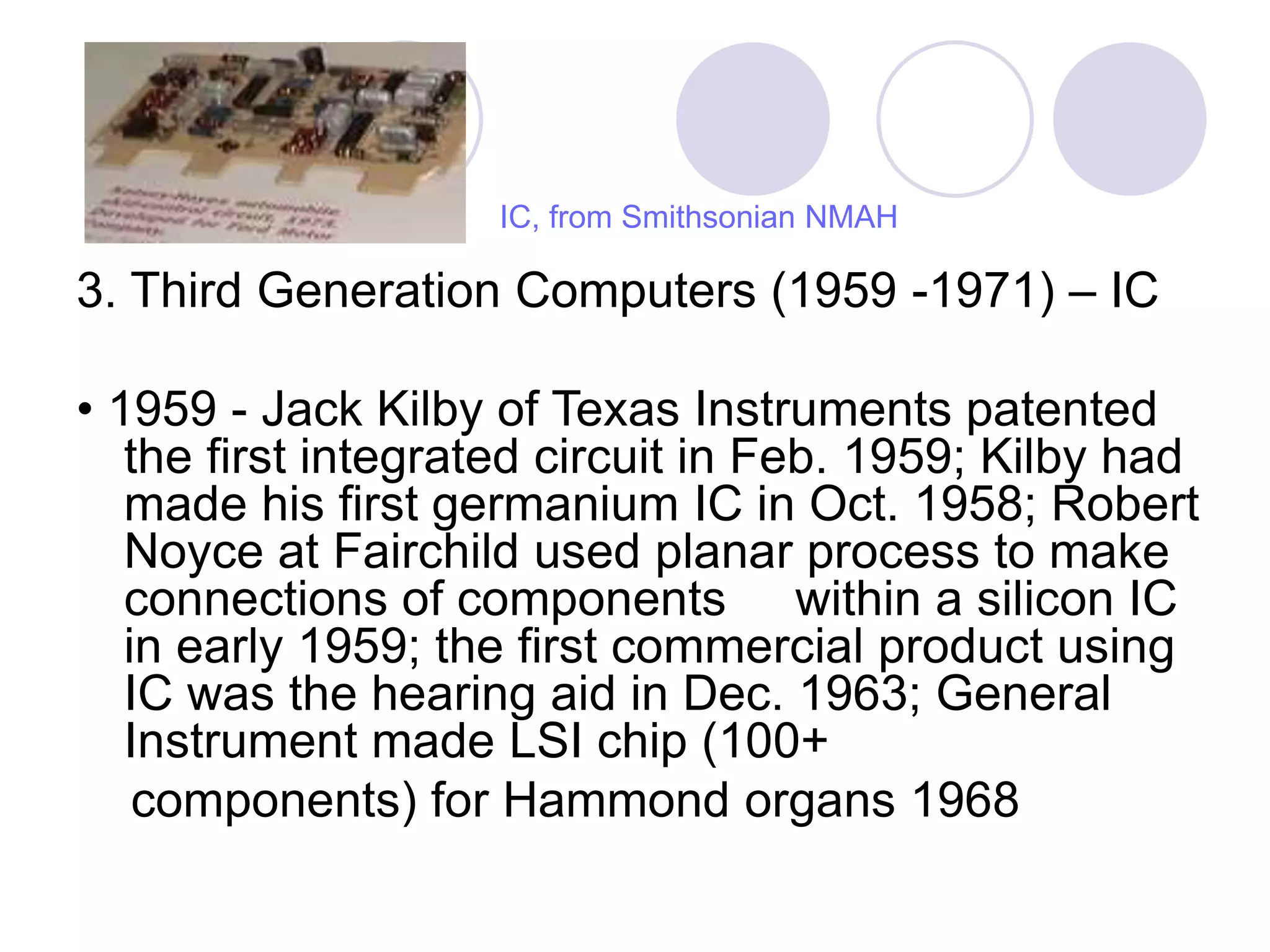
3) A brief history of computer evolution from the vacuum tube era to modern computers based on integrated circuits and microprocessors.
4) An overview of the four main types of computers - supercomputers, mainframes, minicomputers, and microcomputers.