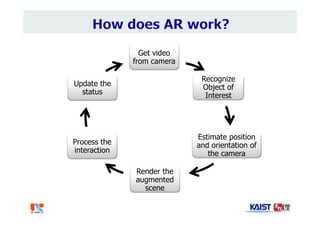
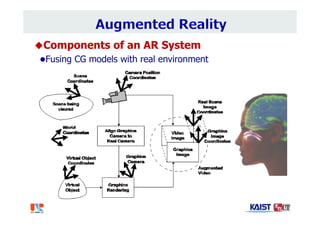
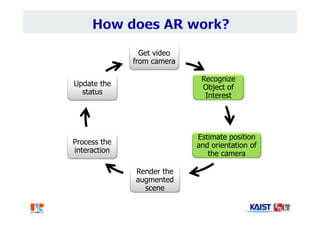
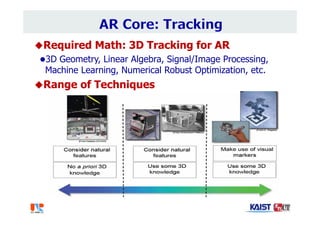
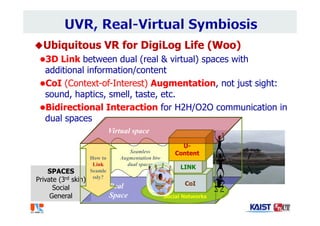
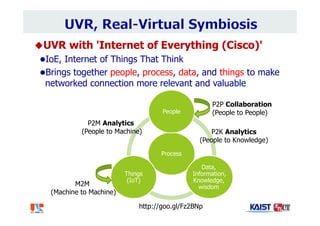
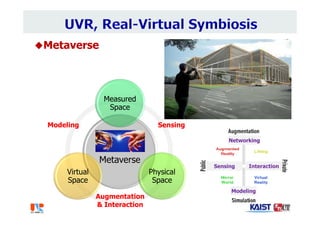
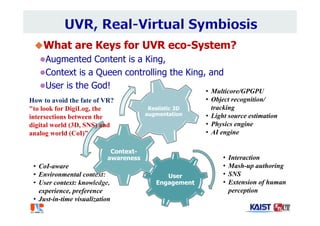
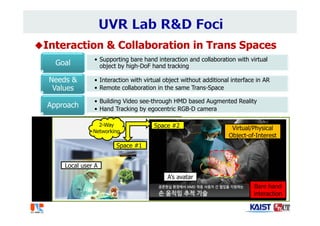
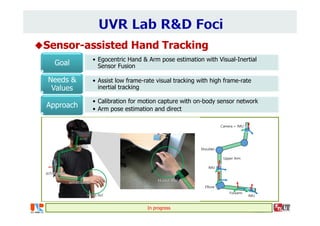
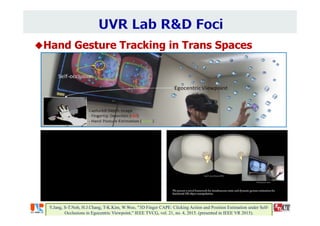
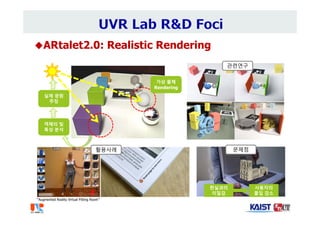
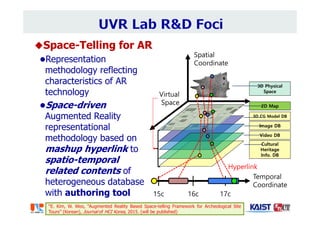
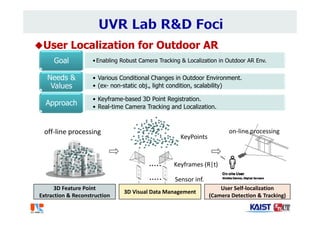
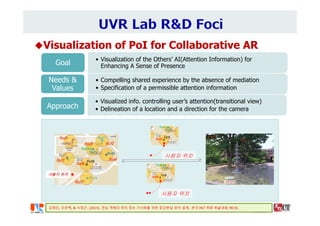
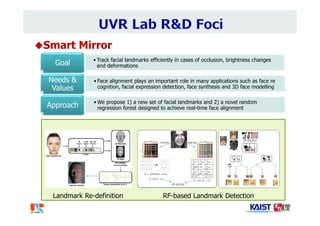
The document summarizes the work of Dr. Woontack Woo and the UVR Lab at KAIST. It discusses the lab's research into ubiquitous VR (UVR), which aims to develop new computing paradigms for augmented experiences in smart spaces. The UVR lab works on 3D tracking, hand interaction, collaboration between real and virtual spaces, and applications like AR authoring and sculpting. It also discusses trends in wearable AR/VR and the future of augmented humans. The document outlines several of the lab's current projects, including work on hand tracking, remote collaboration using HMDs, and realistic rendering in augmented reality.
![Woontack Woo (禹雲澤), Ph.D.
KAIST UVR Lab.
Joint WS@ [July 30, 2015]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uvr2015v5-150730003121-lva1-app6892/85/Introduction-to-UVR-Lab-2-0-1-320.jpg)




![Milgram's Reality-Virtuality Continuum [94]
Azuma's definition on AR [97]
combines real and virtual
is interactive in real time
is registered in real 3D world
R. Azuma, A Survey of Augmented Reality, Presence, Vol.6, No.4, Aug. 1997, pp. 355‐385.
P. Milgram and A. F. Kishino, Taxonomy of Mixed Reality Visual Displays, IEICE Trans. on I&S, E77‐D(12), pp. 1321‐1329, 1994.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uvr2015v5-150730003121-lva1-app6892/85/Introduction-to-UVR-Lab-2-0-7-320.jpg)