Embed presentation
Download to read offline




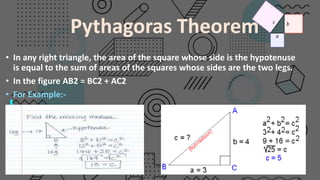
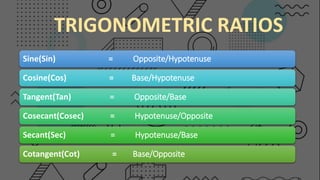
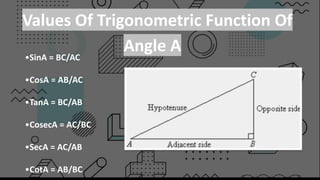


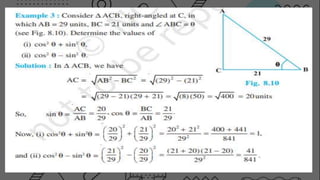


Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with triangles and uses ratios of sides to determine unknown angles or lengths. It defines trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent that relate the angles and sides of a right triangle. For example, the sine of an angle is equal to the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse. Trigonometry has applications in fields like surveying, navigation, and physics that require calculating distances and heights.











