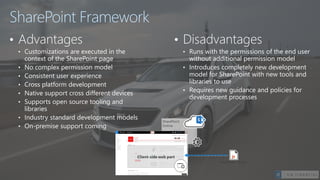
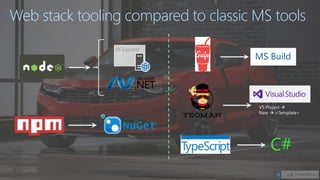
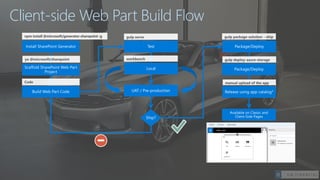
The document introduces the SharePoint Framework as a new approach for developing customizations for SharePoint. It summarizes the limitations of previous development models like farm solutions and add-ins. The SharePoint Framework allows customizations to run within the permissions of the current user and uses open source tools and libraries with an industry standard development model. It leverages common web development tools like Node.js, Yeoman, Gulp and TypeScript rather than traditional Microsoft tools. Customizations are developed as client-side web parts with a defined build flow to package and deploy solutions.