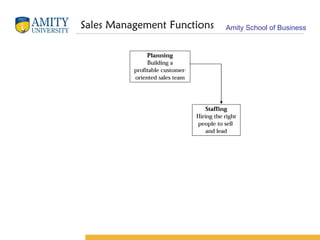
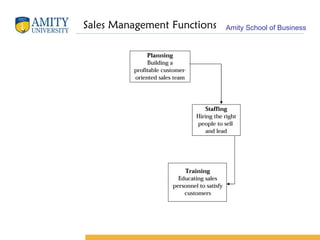
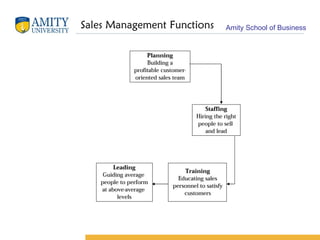
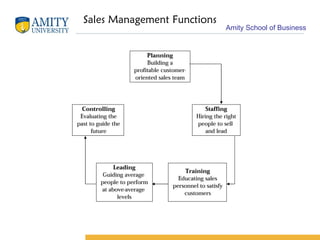
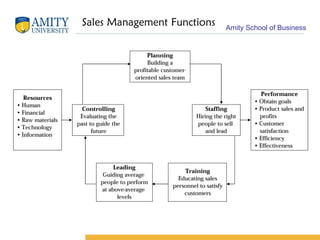
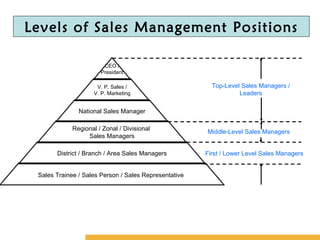
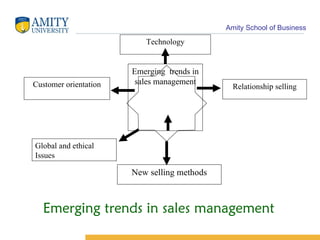
The document discusses key concepts in sales management including its evolution, objectives, functions, importance, and emerging trends. It describes the roles and skills of a modern sales manager and different levels of sales management positions. Emerging trends discussed include relationship selling, global and ethical issues, new selling methods, technology, enterprise resource planning (ERP), sales force automation (SFA), and vendor management systems.