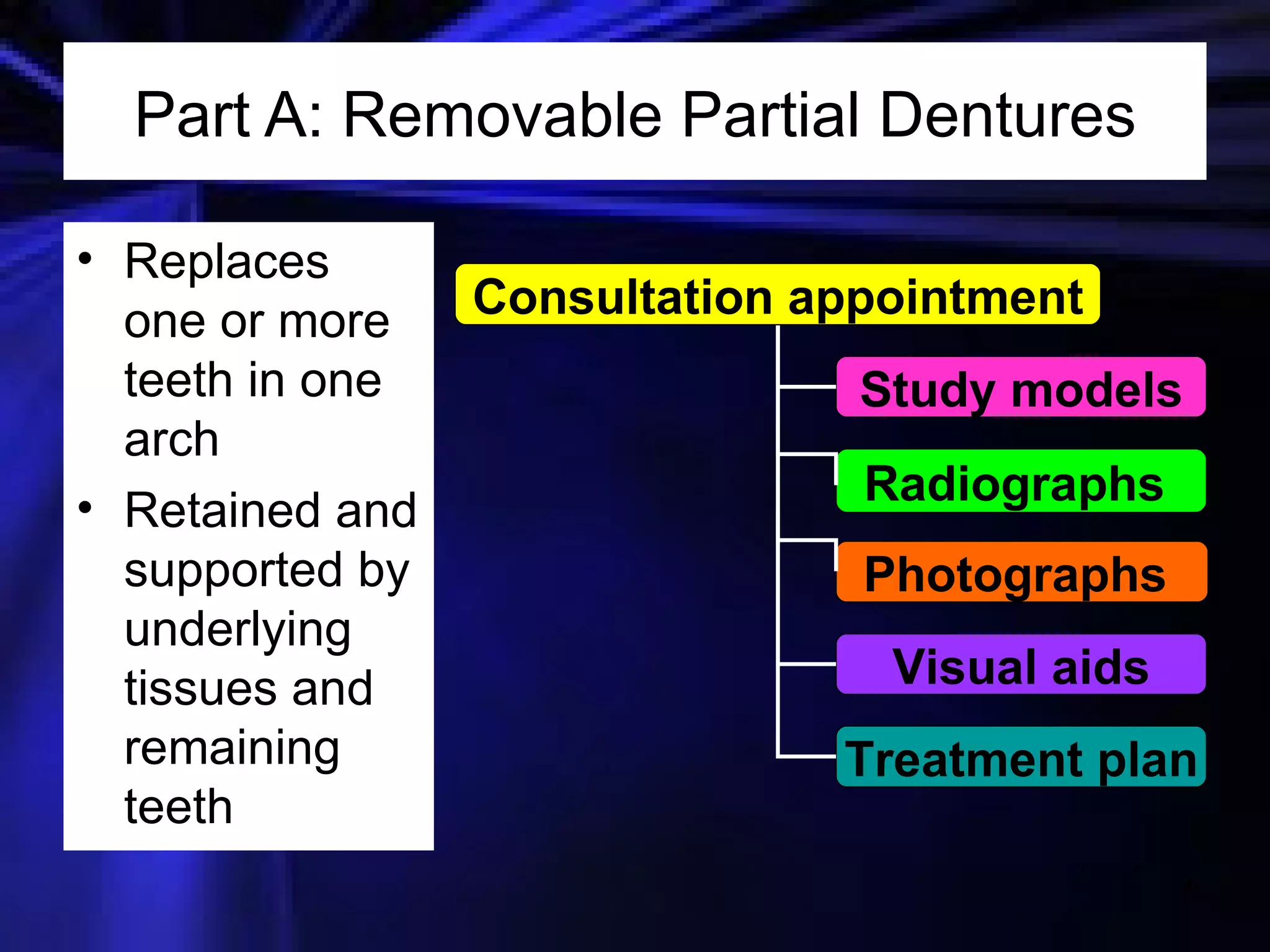
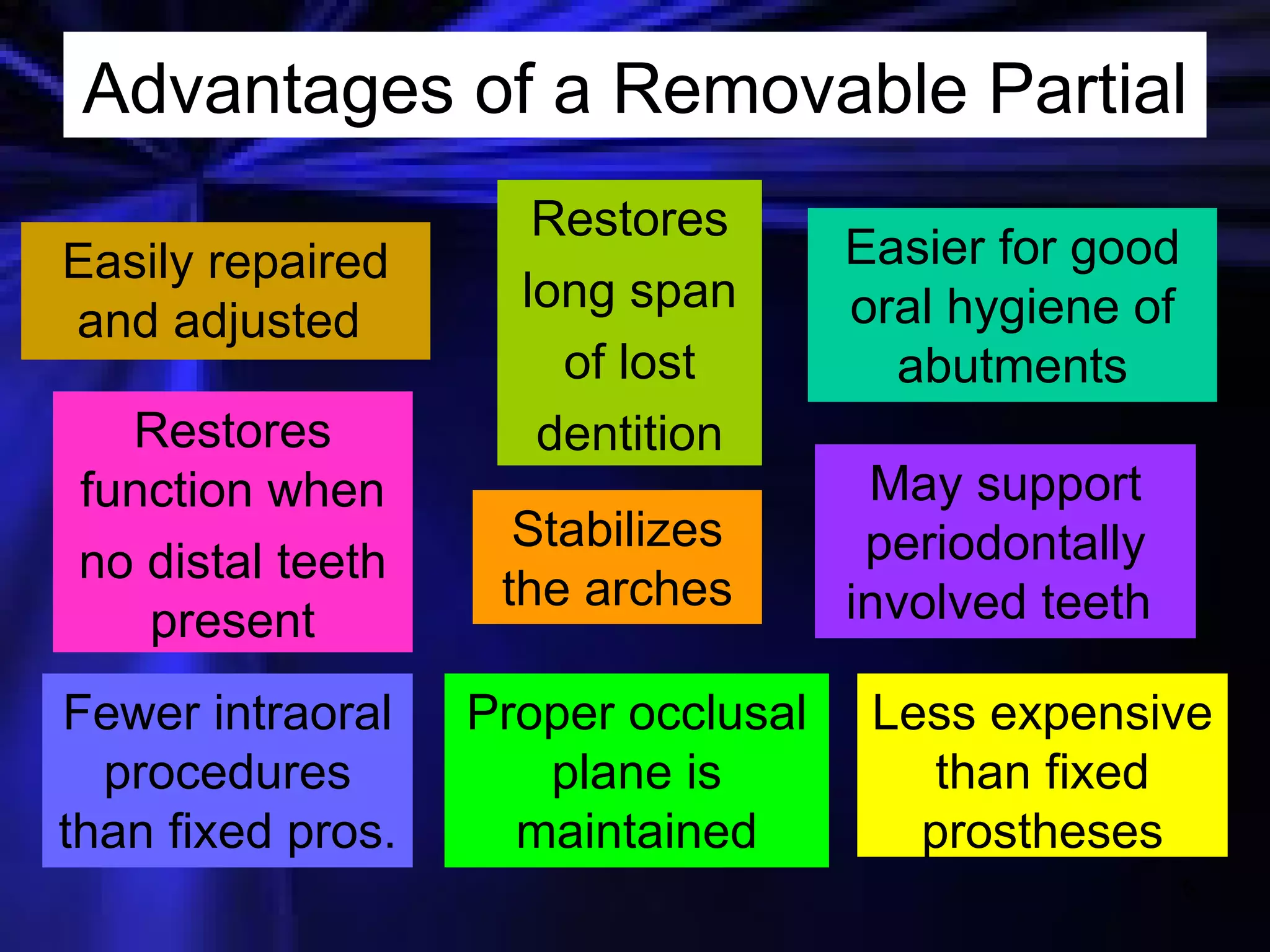
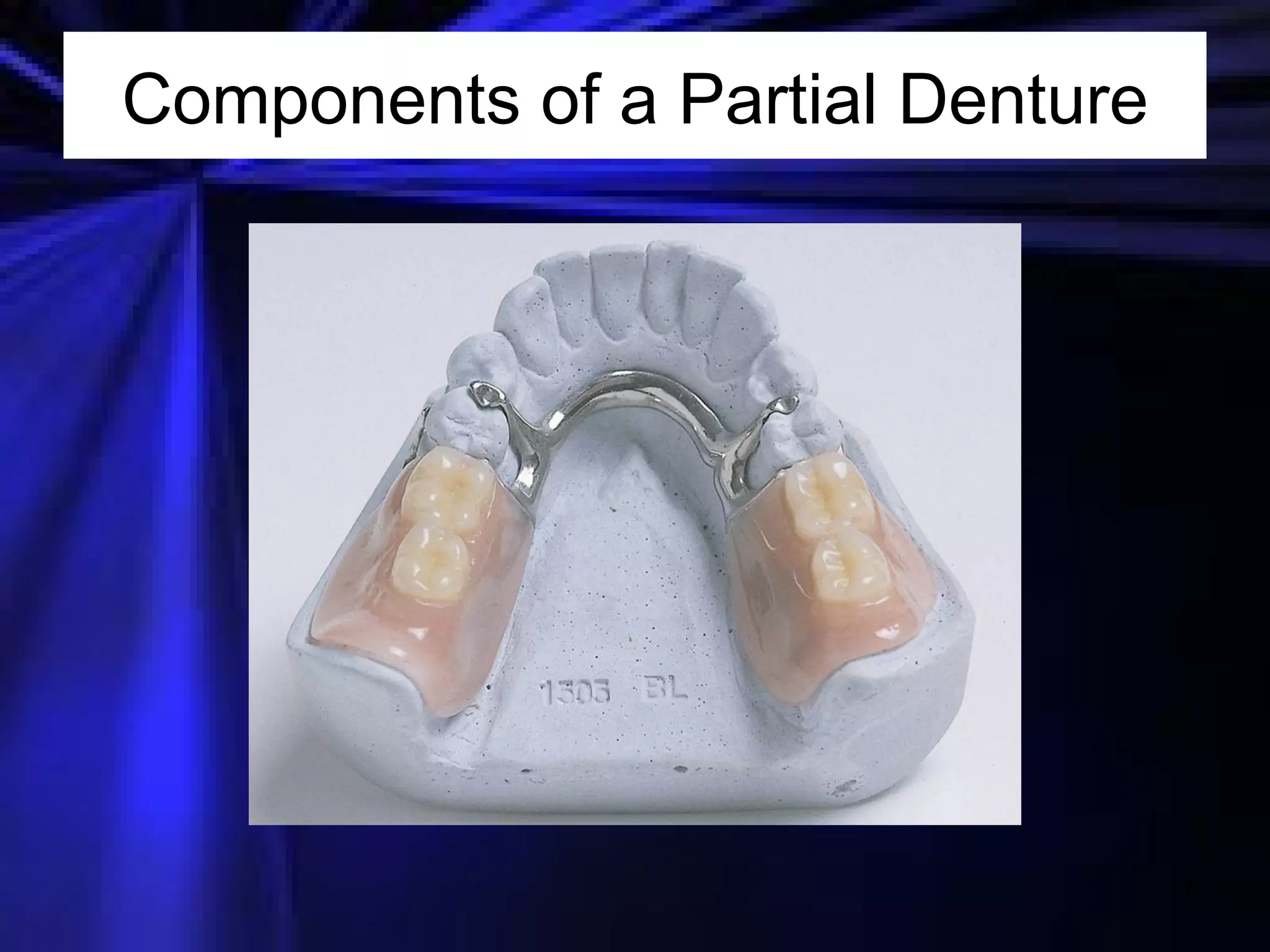
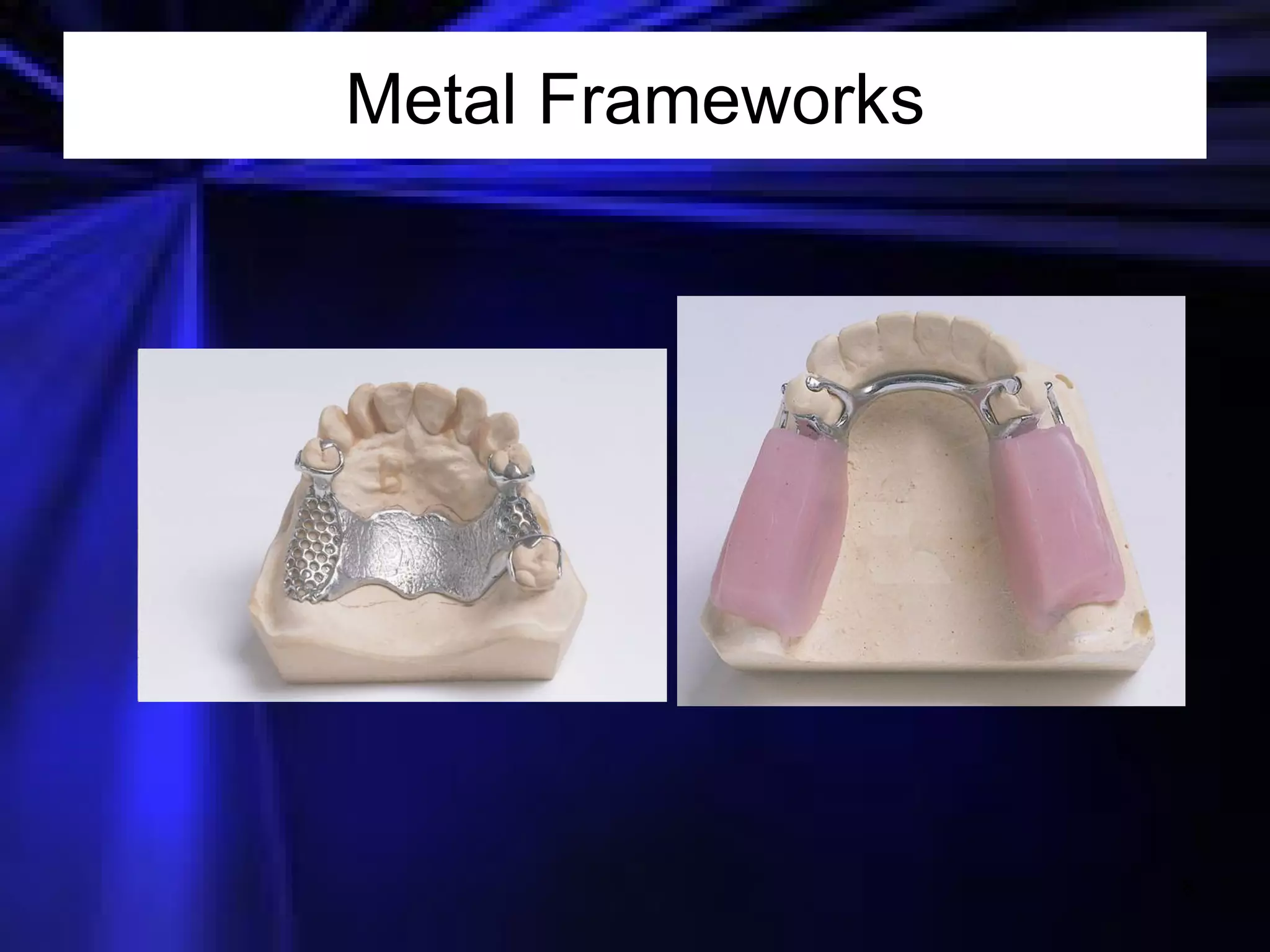
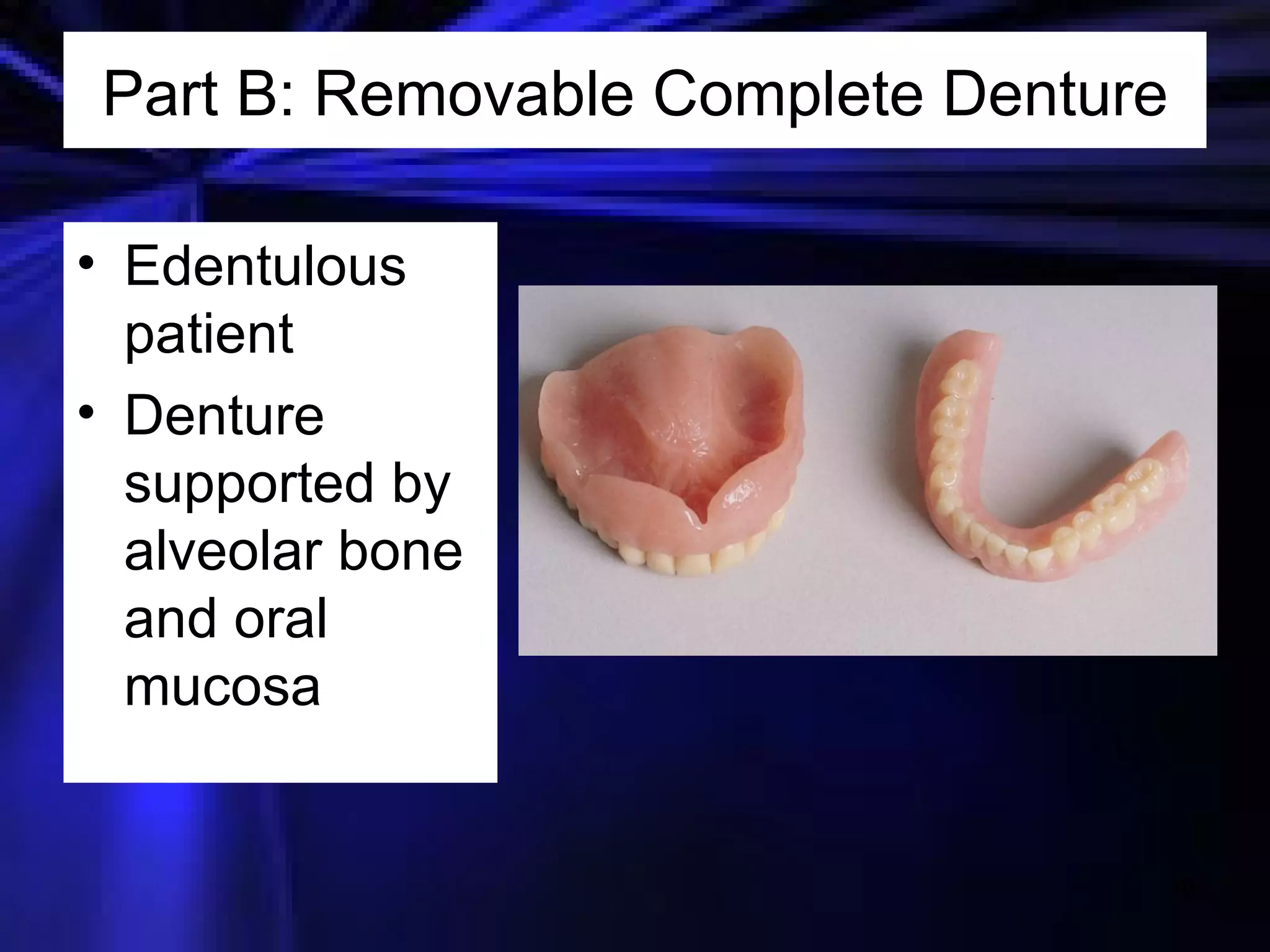
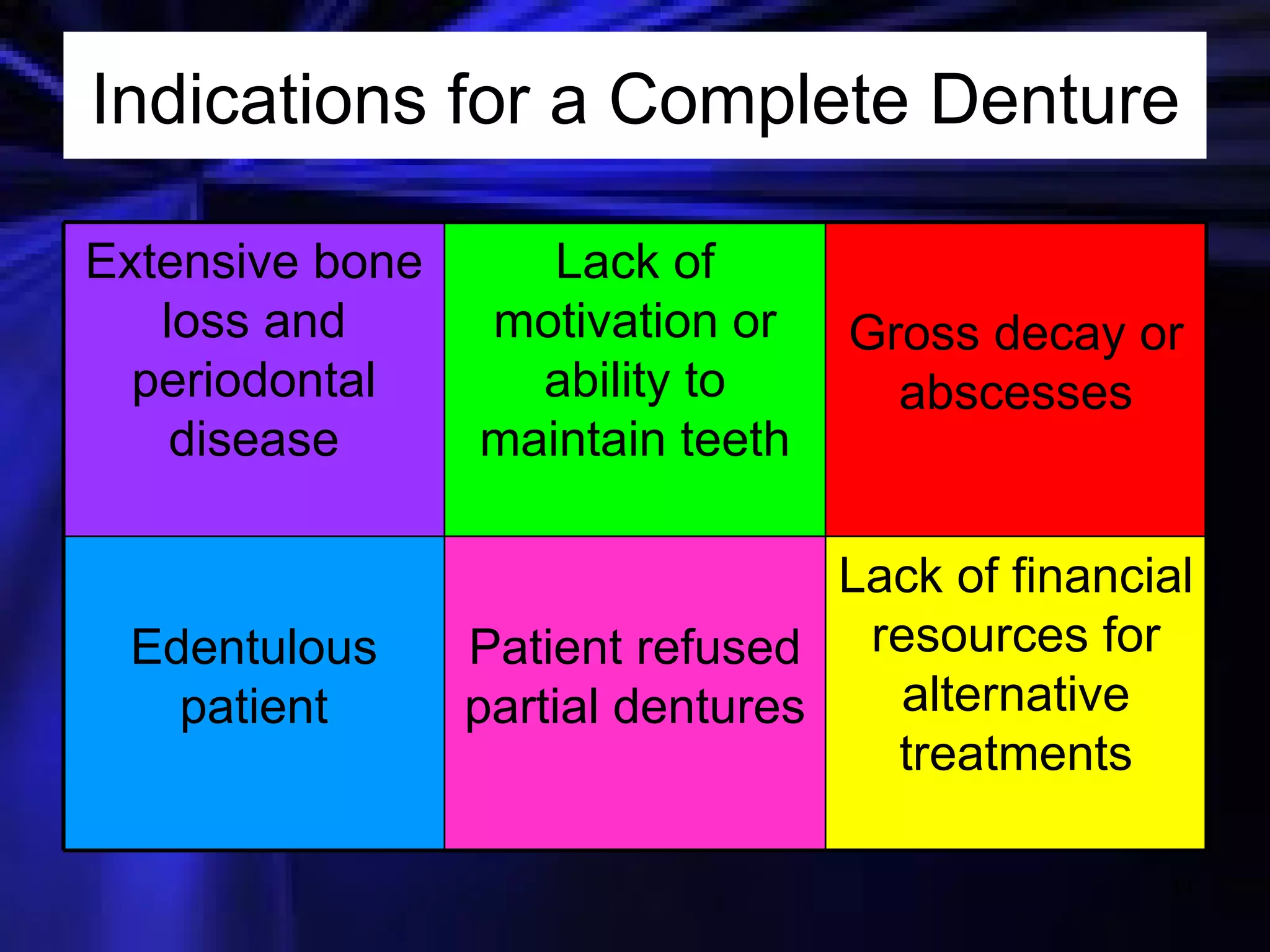
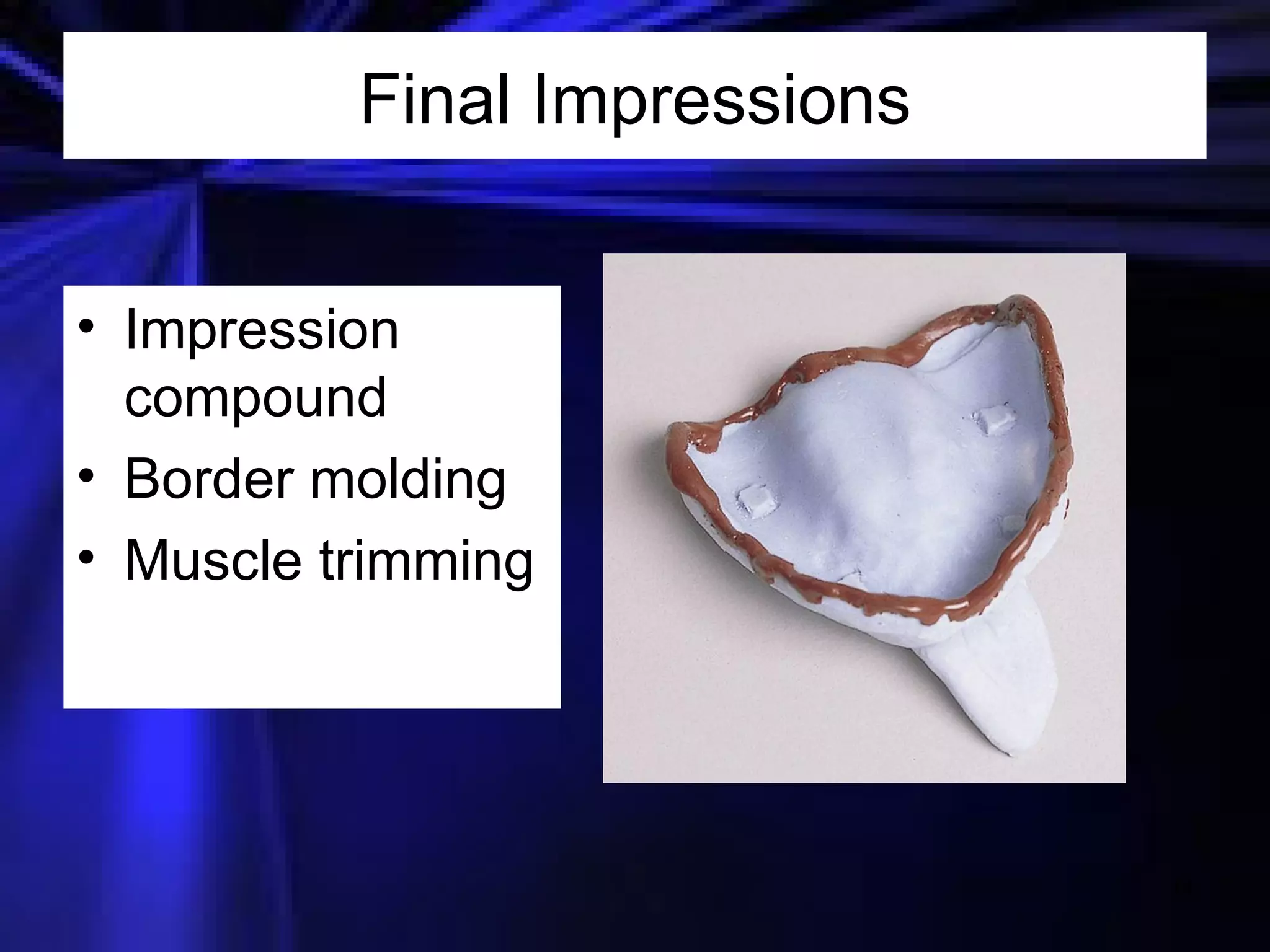
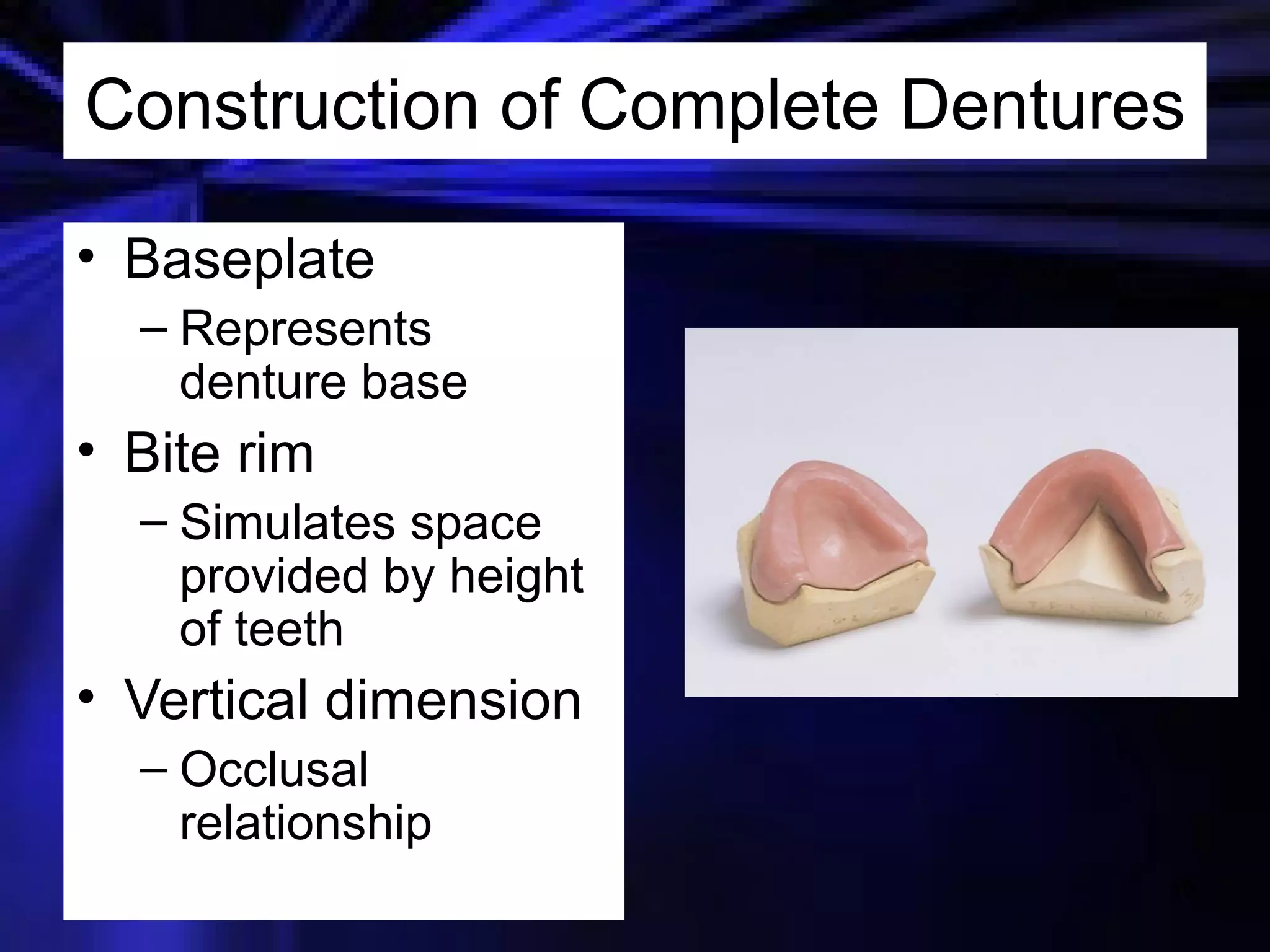
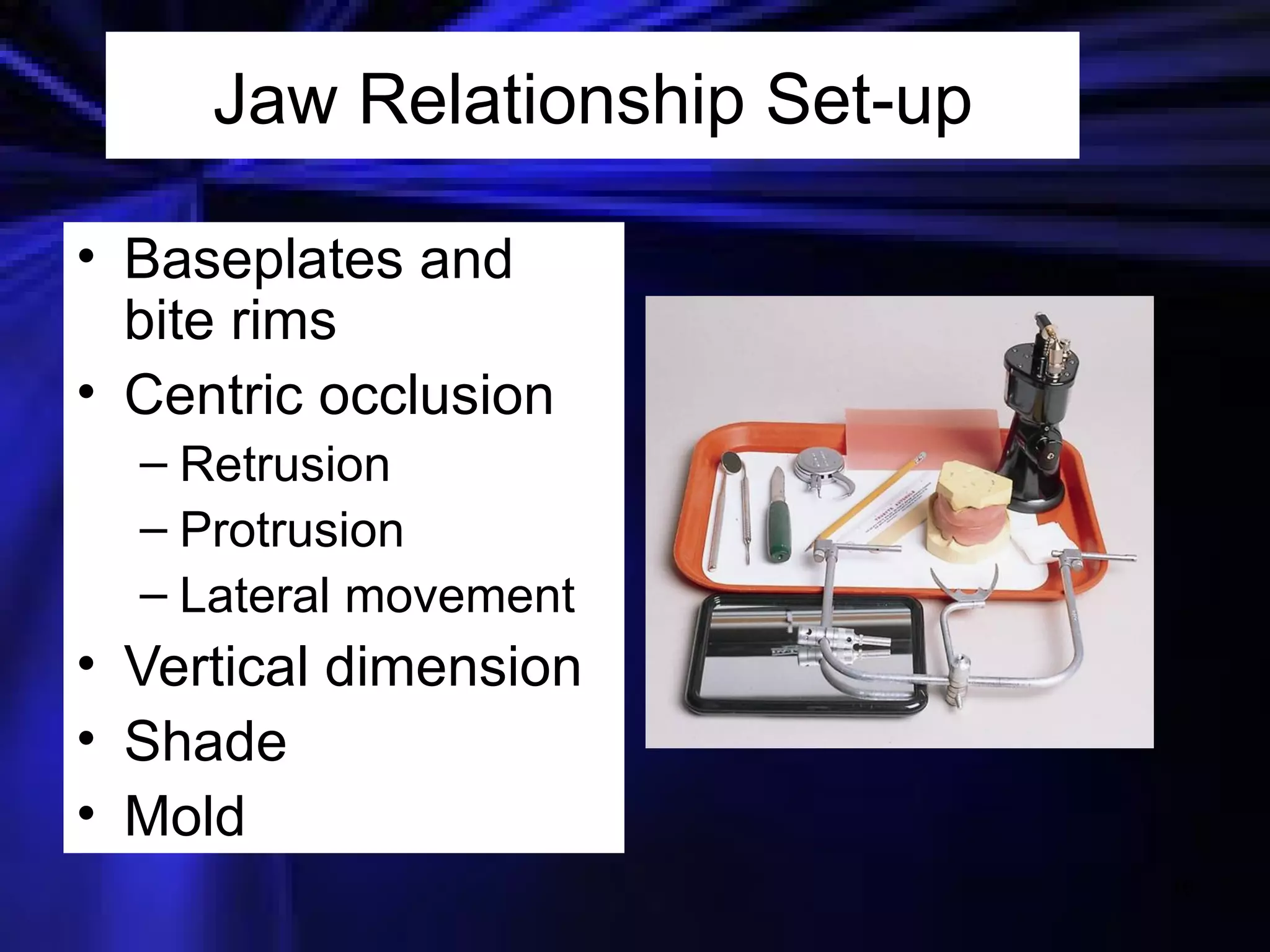
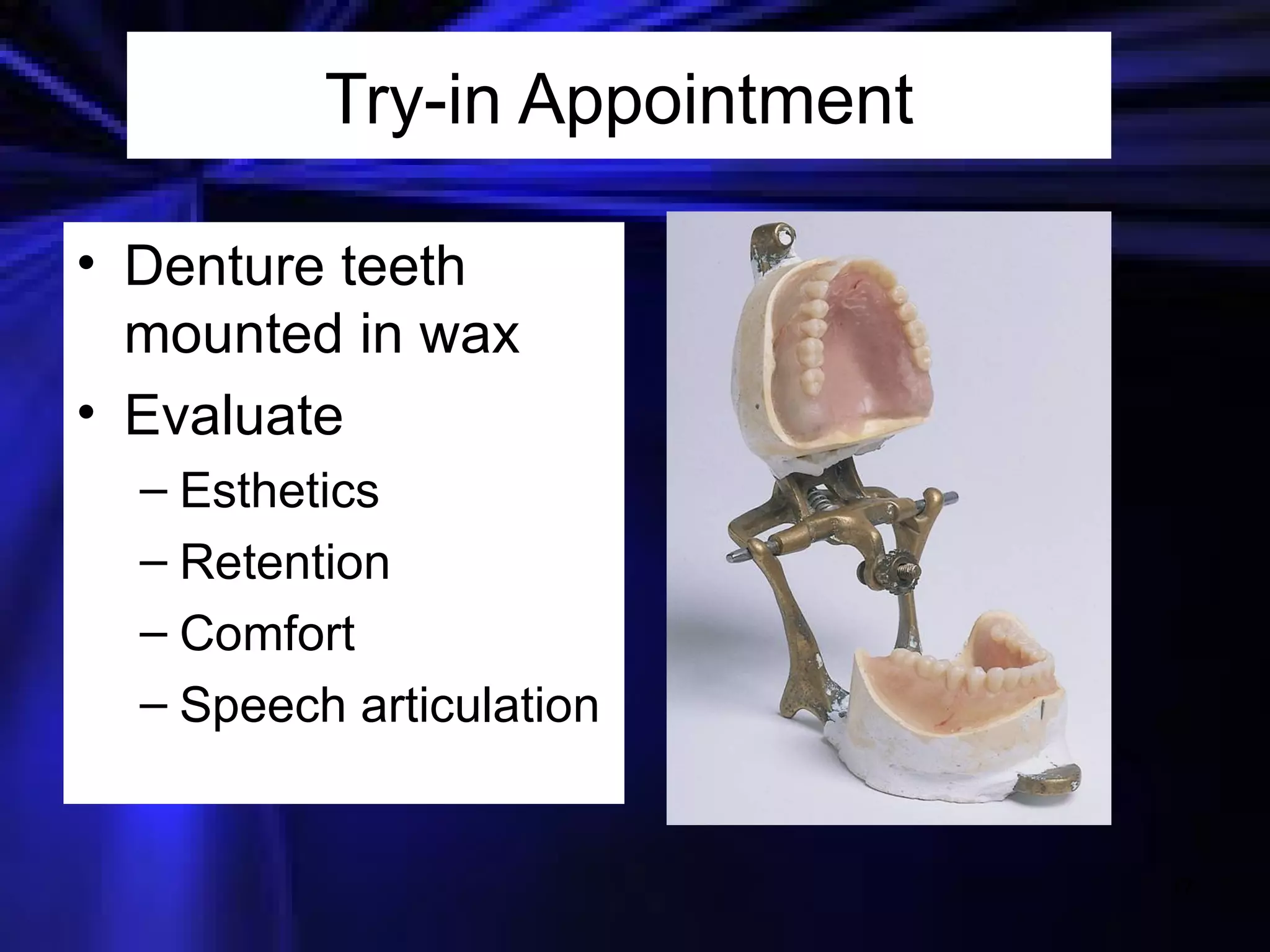
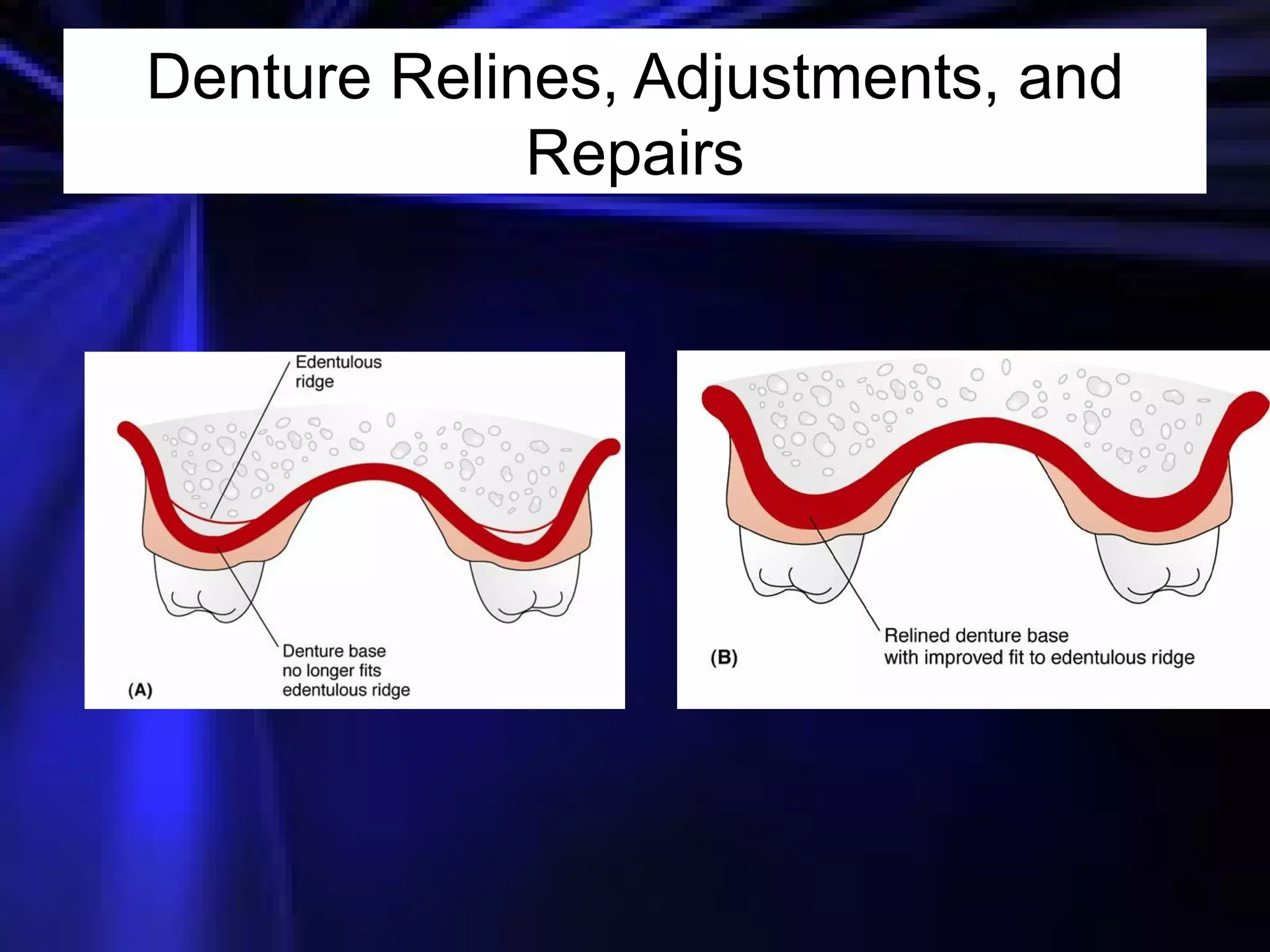
This document provides an introduction to removable prosthodontics, including removable partial dentures and complete dentures. It defines key terms and discusses the components, construction, and appointments for each type of removable prosthesis. Removable partial dentures are used when one or more teeth need to be replaced in one dental arch, while complete dentures are used when all teeth in both dental arches need to be replaced. The document also covers relining, adjusting, and repairing removable prostheses.