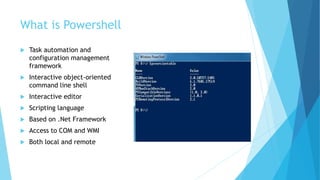
PowerShell is a task automation and configuration management framework built on the .NET framework, featuring an interactive command line shell and scripting language. It utilizes cmdlets for command execution and supports scripting with advanced features like pipelining, error handling, and object-oriented programming through classes. The document provides essential commands, execution policies, and resources for getting started with PowerShell.












![Class Syntax
Class <Class_Name>
{
#Properties
<Data_Type> $<Variable_Name>
}
#Methods
[Return Type] <Method_Name> {
# Script
}
#Creating an object
$<Object_Name> = New-Object –TypeName <Class_Name>
#Calling a method
<Object_Name>.<Method_Name>()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powershellpresentation-170328192826/85/Introduction-to-Powershell-Version-5-14-320.jpg)
![Class Example
class Person {
#Properties
[string]$lastName
[string]$firstName
#Methods
[void] SetLast ( [string]$ln )
{
$this.lastName = $ln
}
[string] ToString ( [String]$firstName,
[String]$lastName )
{
return $firstName + " " + $lastName
}
}# end class Person](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powershellpresentation-170328192826/85/Introduction-to-Powershell-Version-5-15-320.jpg)


