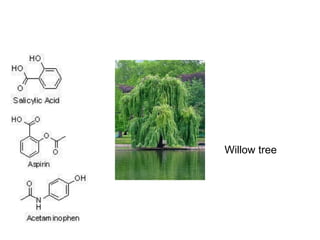
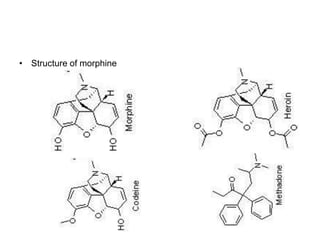
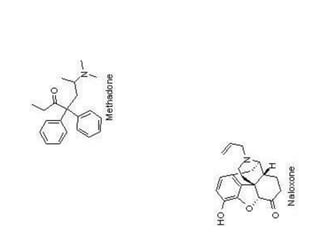
The document provides an overview of the field of pharmacy. It defines pharmacy as the science of preparing and dispensing drugs and medicines. The key areas covered include the differences between pharmacy and pharmacists, core pharmacy subjects such as pharmaceutics, medicinal chemistry, and pharmacology. It also discusses complementary subjects like anatomy and pathology. The document outlines career opportunities in pharmacy such as working in community pharmacies, hospitals, industry, and academia. It concludes by mentioning opportunities for further education in pharmacy including masters and PhD programs.










![Pharmaceutical jobs
• Community pharmacy
• Hospital pharmacy
• Clinical pharmacy
• Industrial pharmacy
• Government services
(Policy (MoHSW),
Regulatory (TFDA),
Pharm. Council,
Army, police, prisons,
Refugee camps]
• Forensic / legal,
• Administrative
• Academic
• Media / journal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopharmacy-230506122016-ae84768d/85/INTRODUCTION-TO-PHARMACY-ppt-14-320.jpg)
