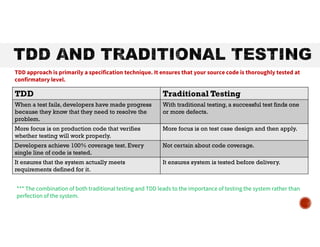
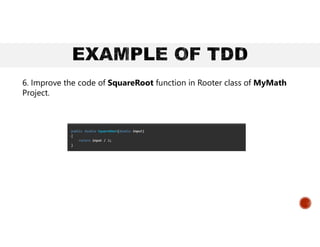
The document outlines test-driven development (TDD), a software development approach where test cases are written before the actual code to ensure functionality and quality. It explains the TDD process, including the 'red-green-refactor' cycle, and highlights the benefits of TDD such as cost reduction, easier refactoring, and improved team collaboration. Additionally, it distinguishes between acceptance TDD and developer TDD, providing examples of implementing TDD in a C# project.