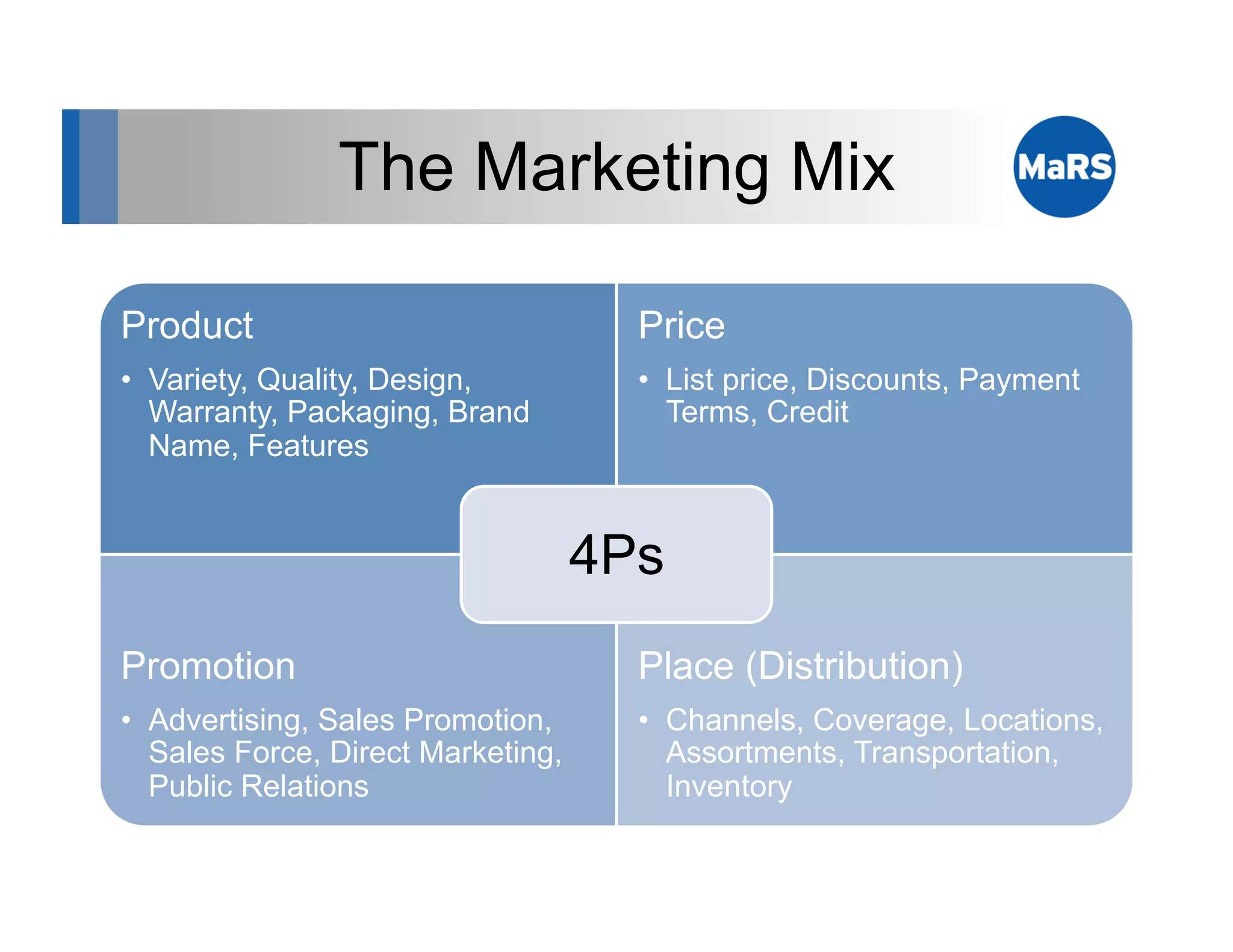
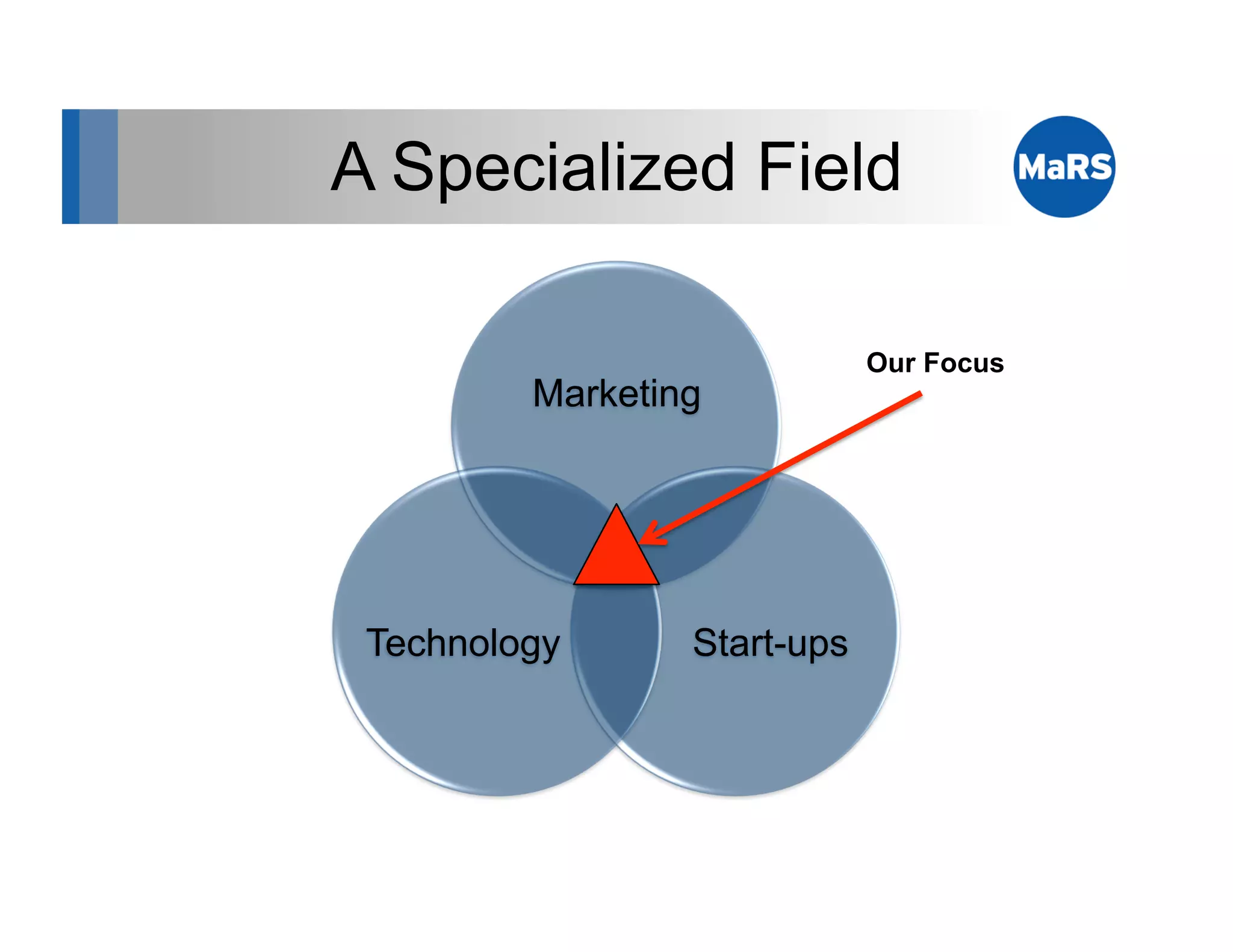
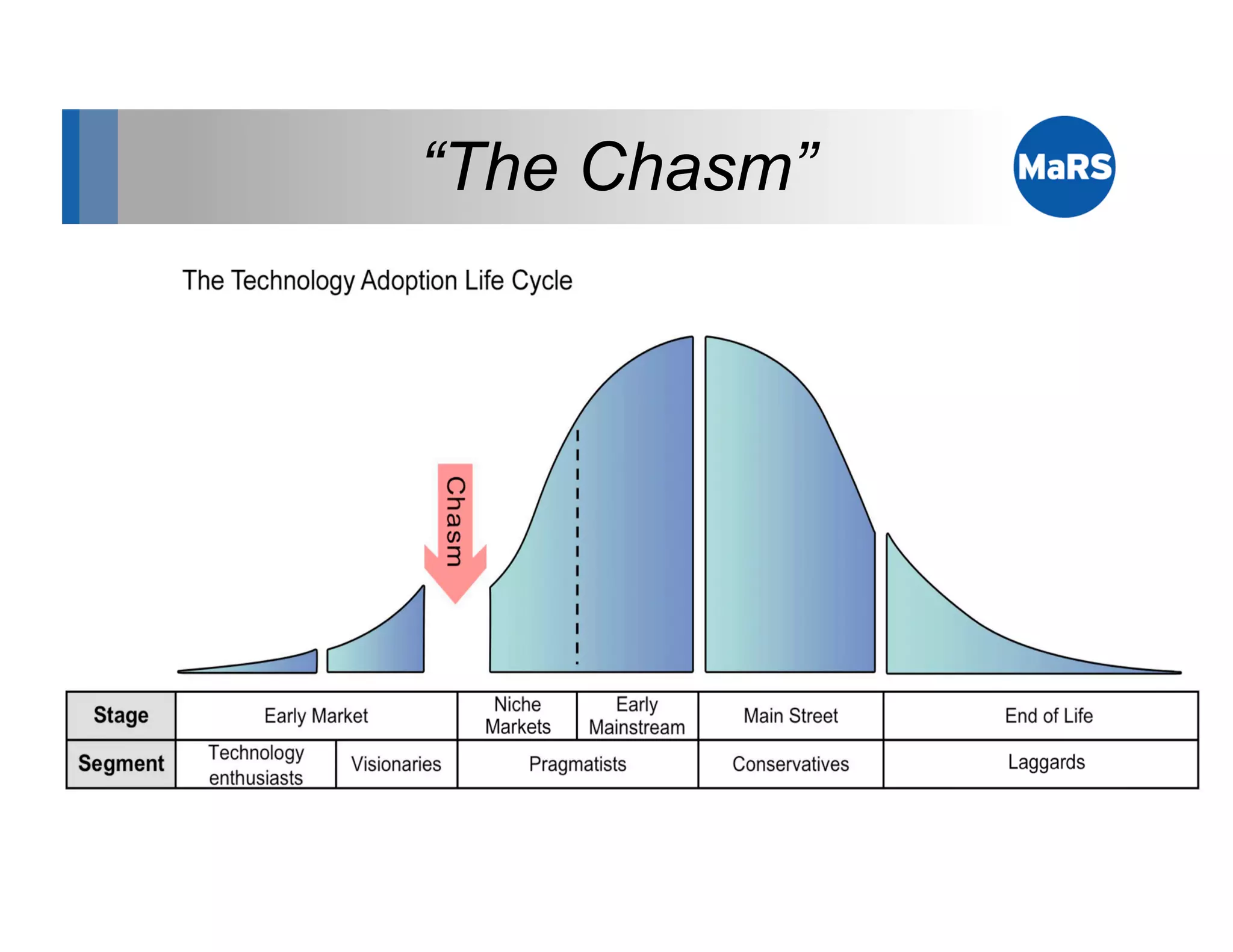
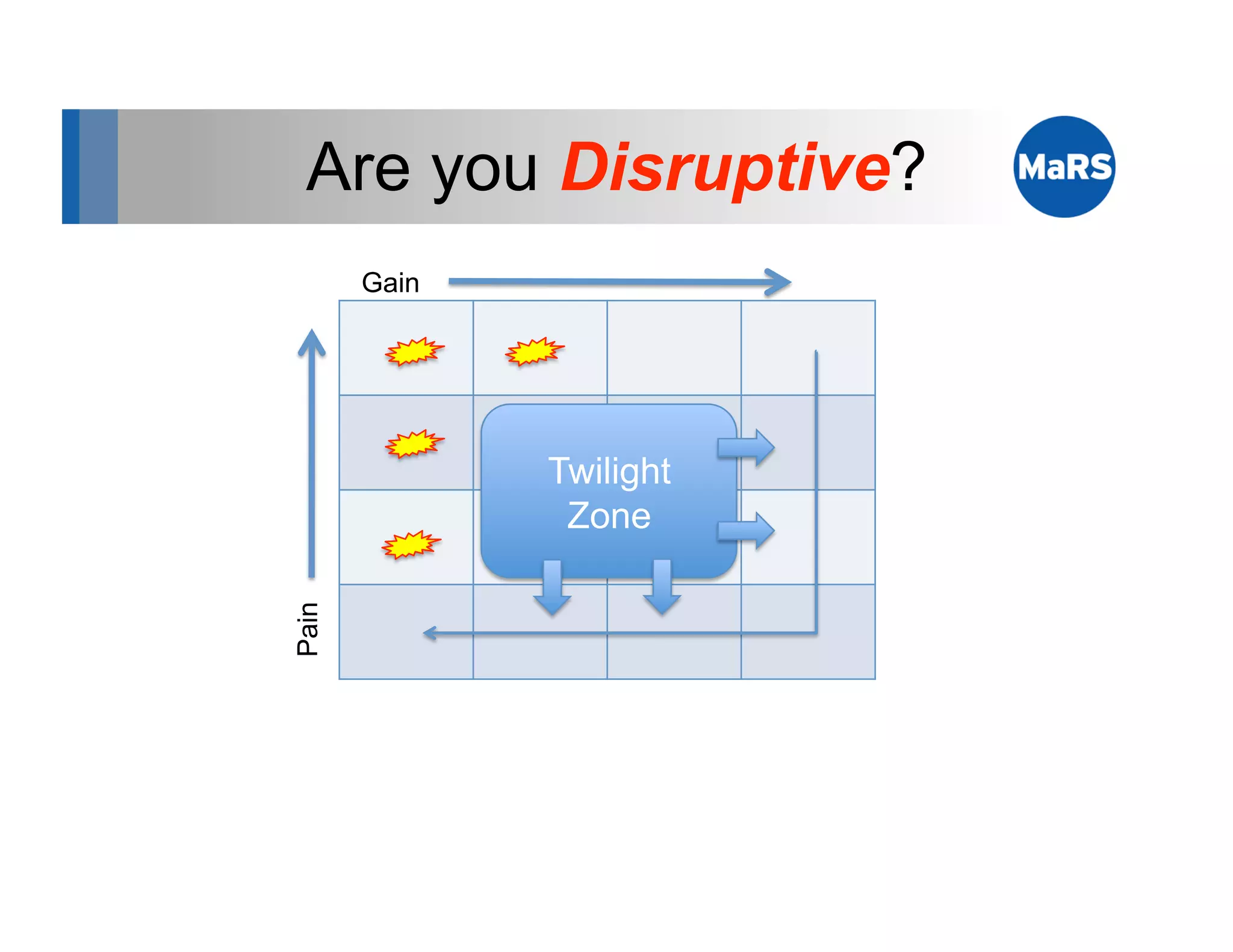
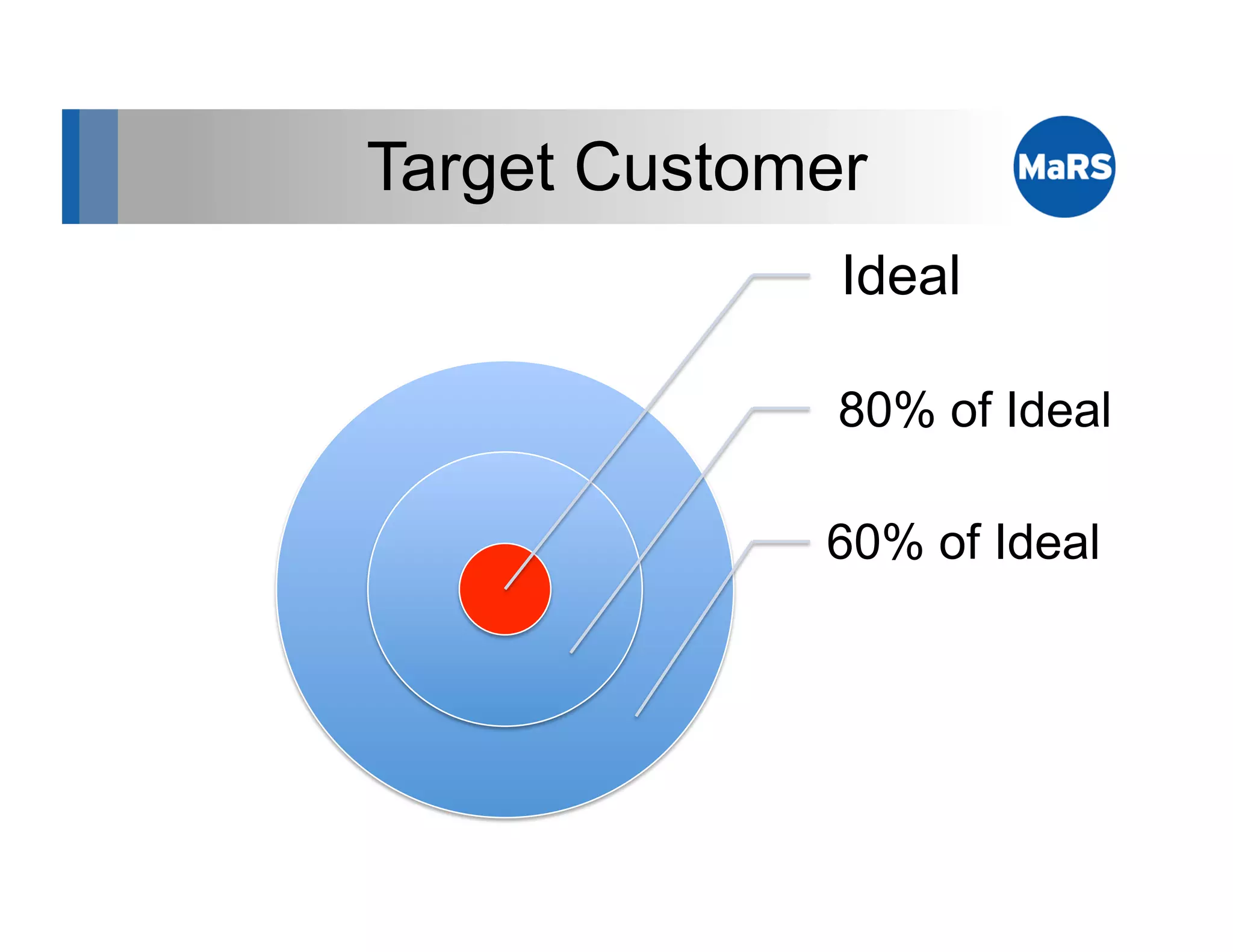
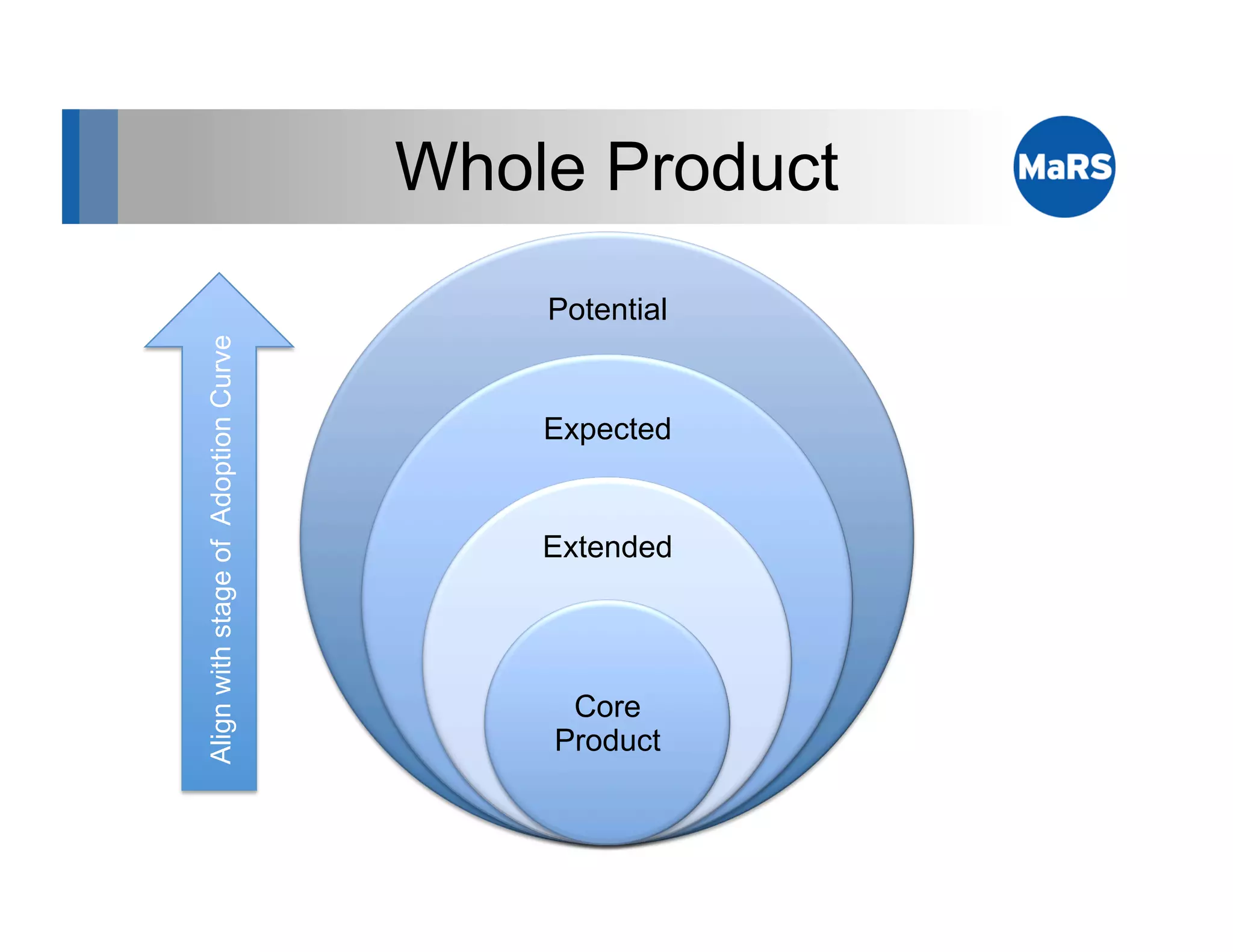
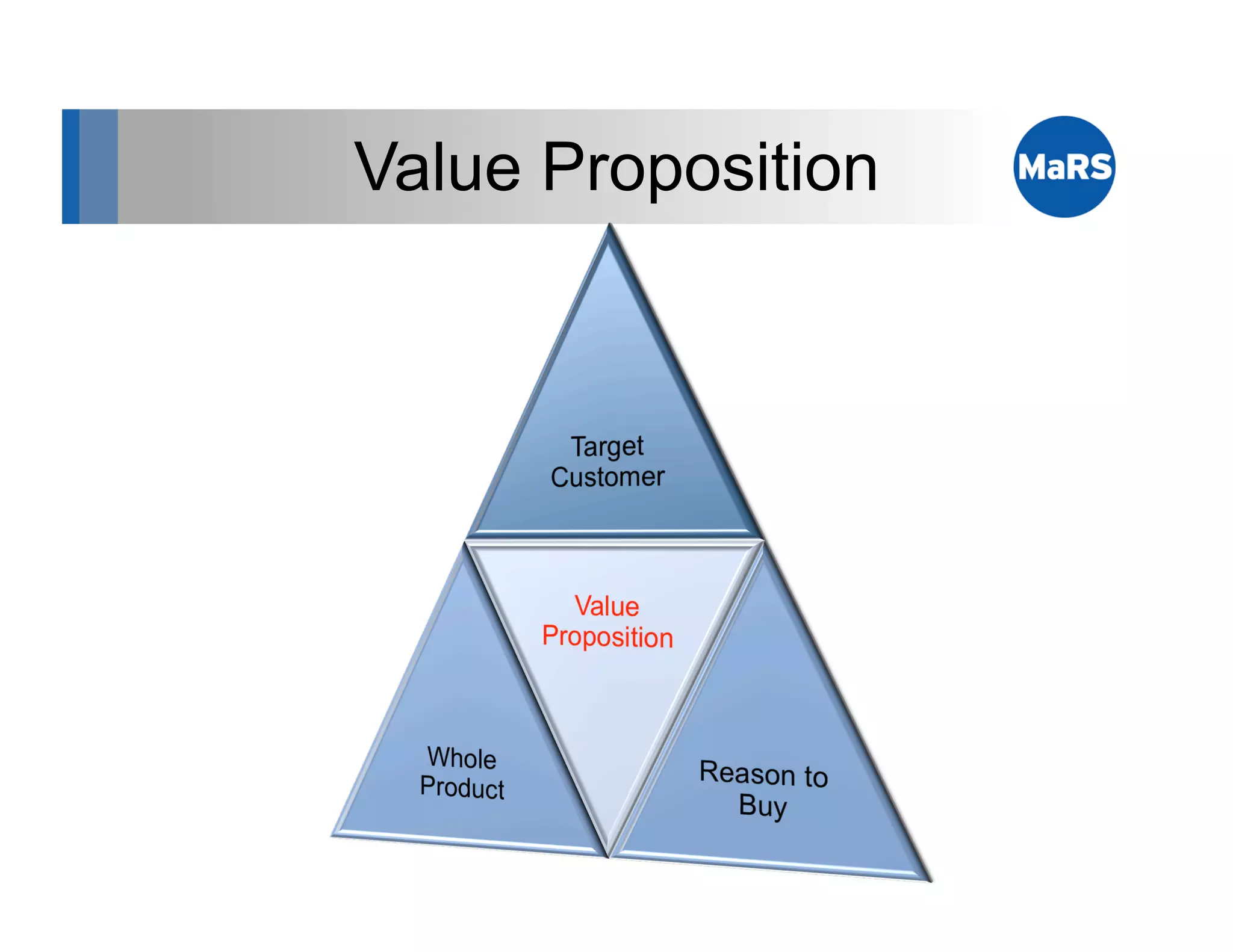
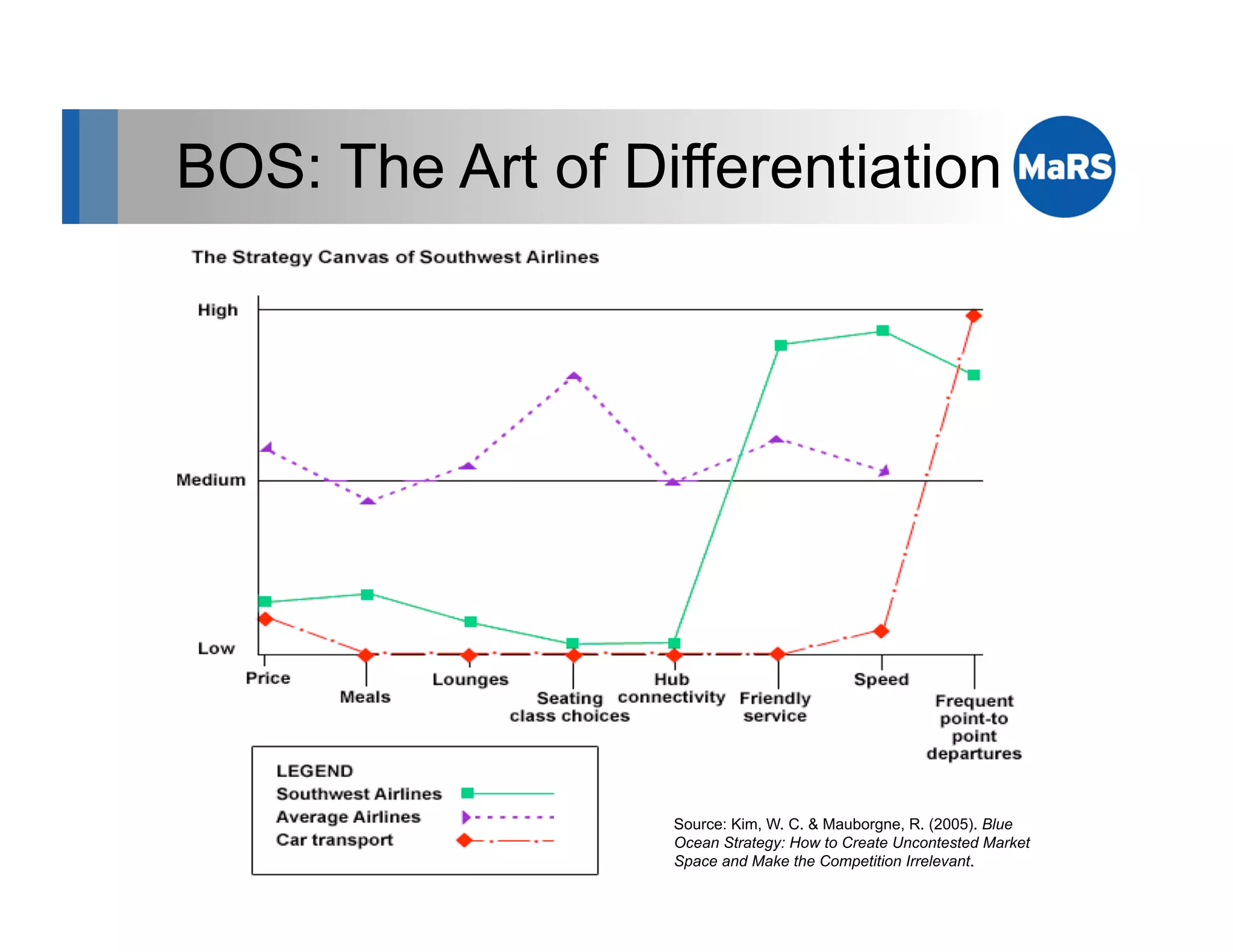
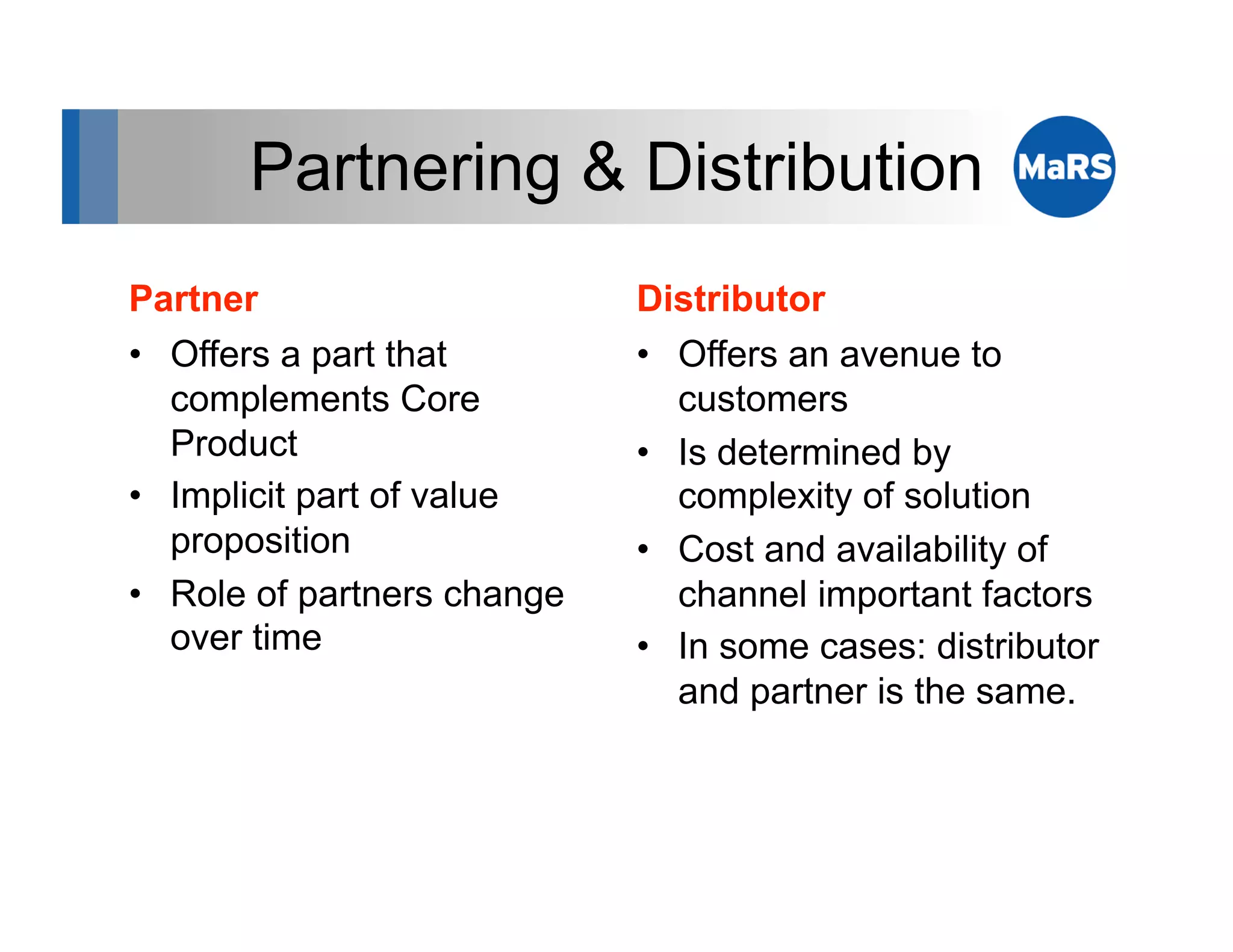
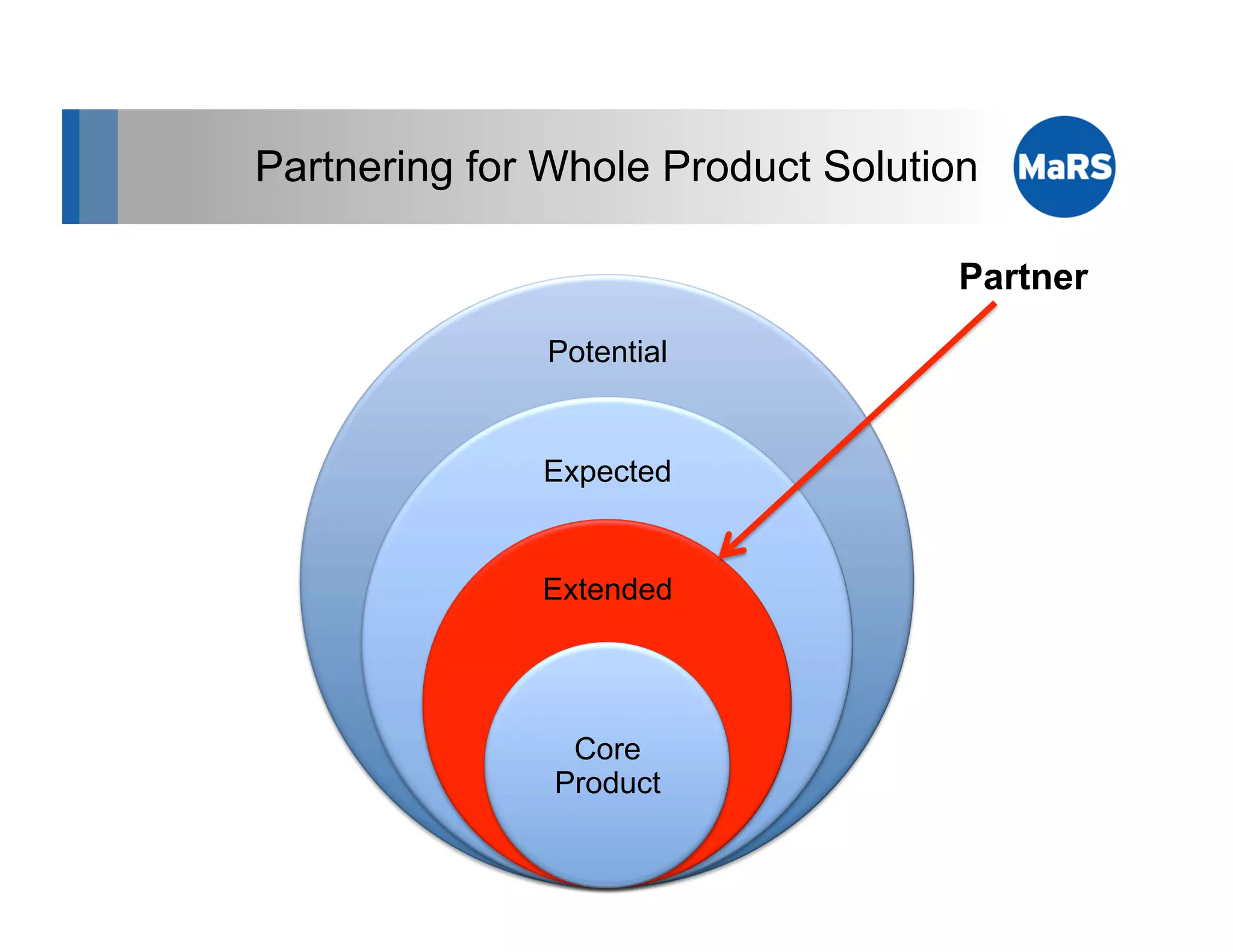
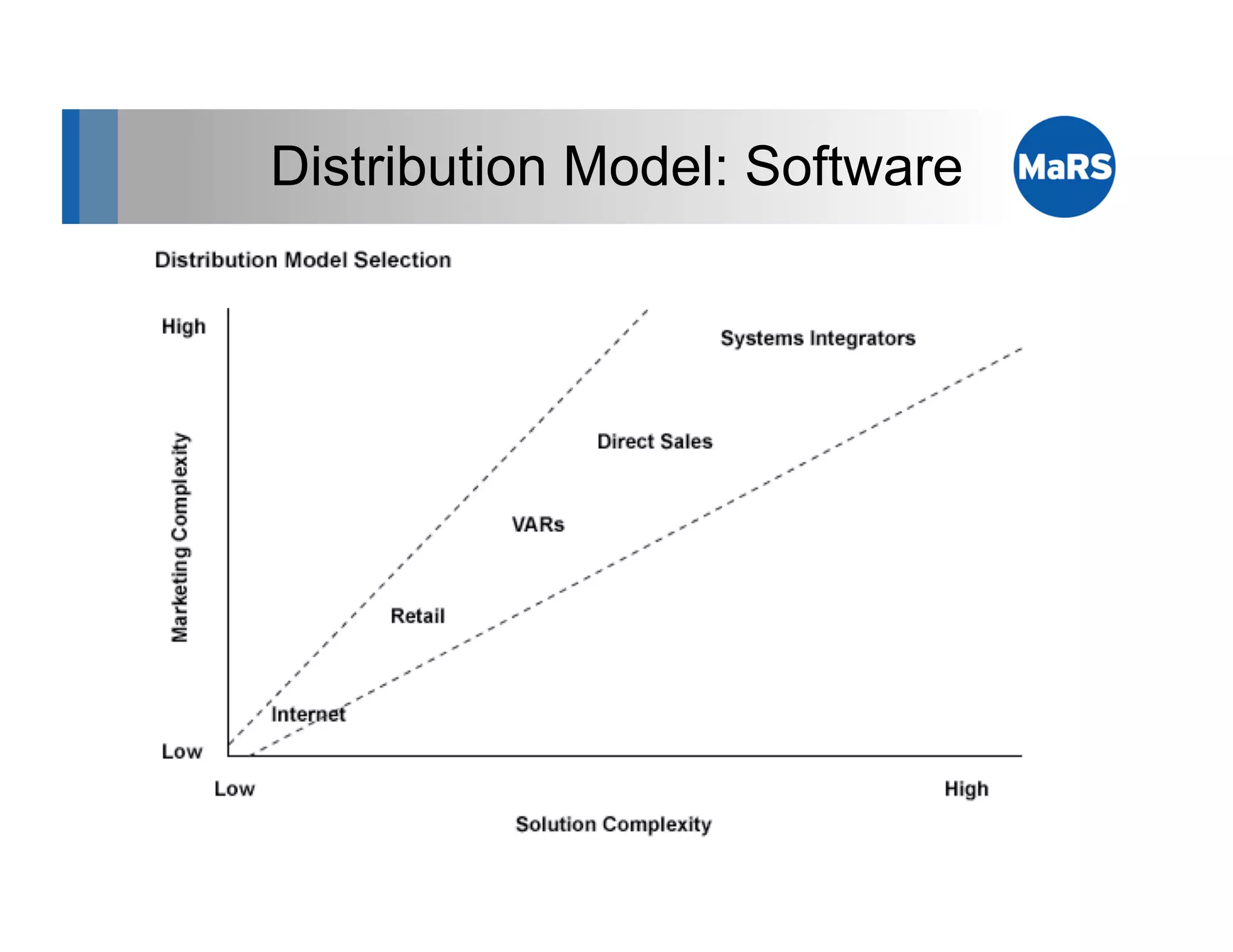
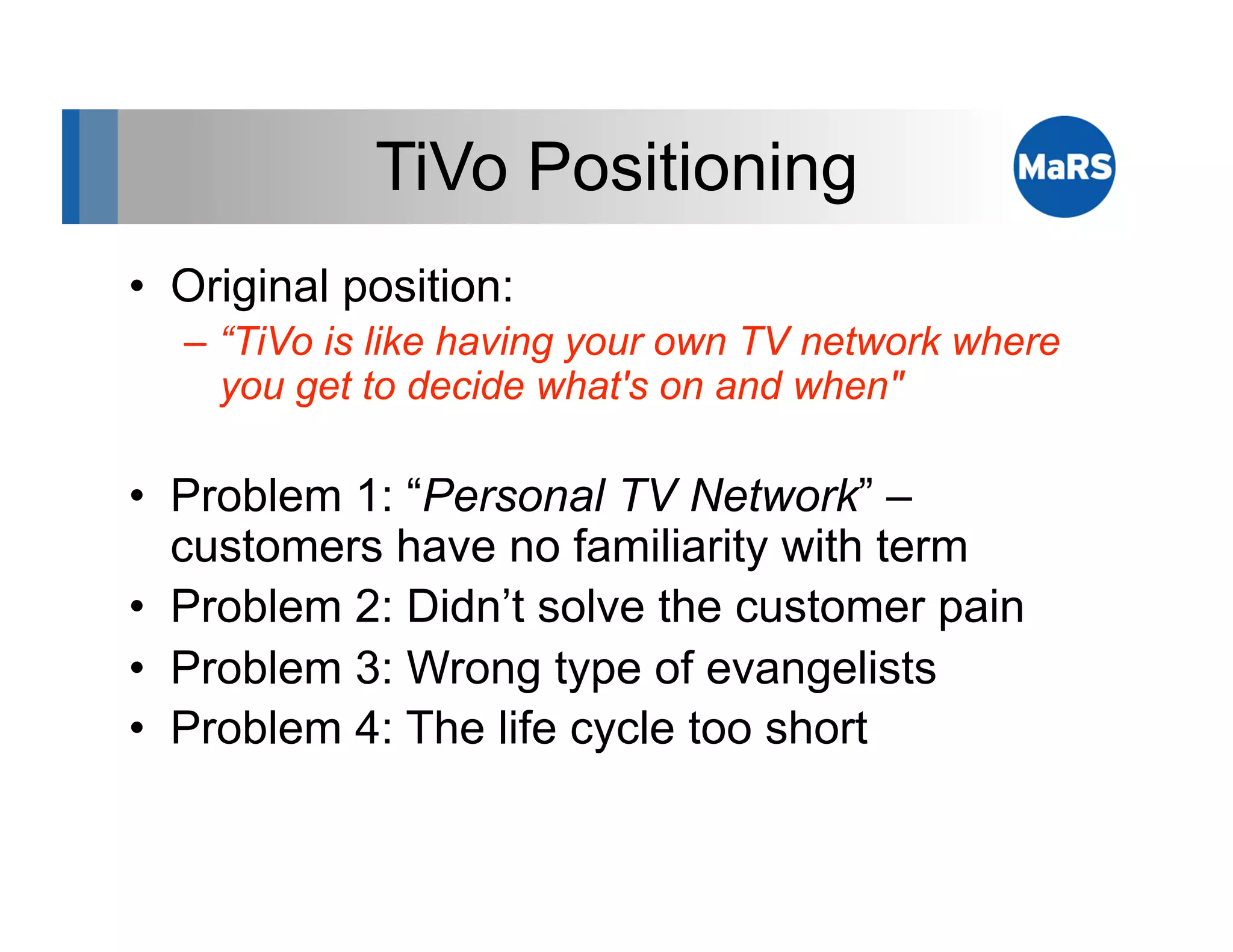
The document outlines key marketing concepts, focusing on the definition and processes involved in marketing, including an introduction to the marketing mix and strategic approaches for technology start-ups. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer pain, market analysis, and competition, providing frameworks such as SWOT and PEST analyses to evaluate business ideas. Additionally, it discusses the significance of effective positioning and pricing strategies in appealing to target customers.