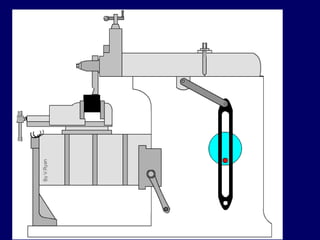
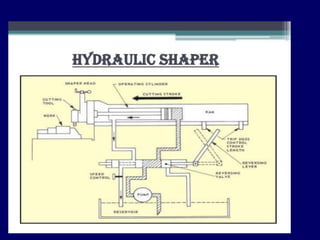
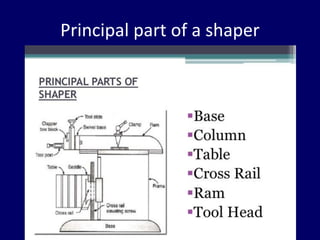
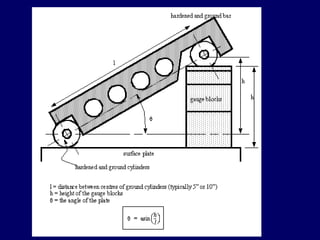
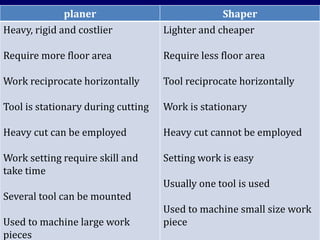
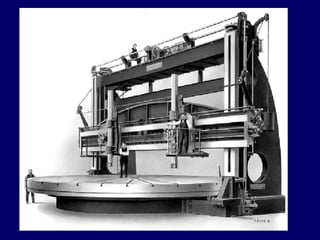
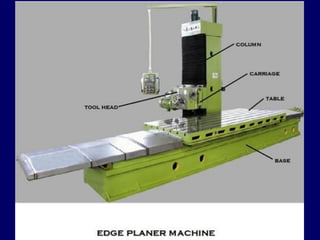
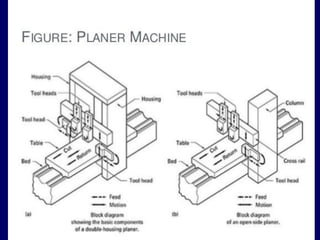
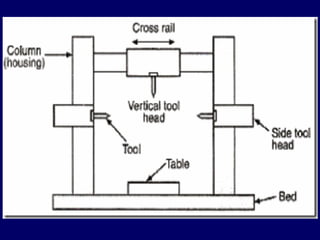
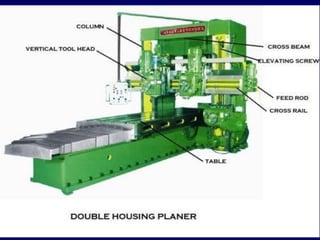
This document discusses shaper and planer machines used in manufacturing. It describes the main components and functions of shapers, including that they cut horizontally and only during the forward stroke. It also classifies shapers by mechanism, position/travel, and cutting stroke. The document then covers planers, noting they are used for larger workpieces and the tool is stationary during cutting. It lists types of planers and provides specifications and safety precautions for operating shaper and planer machines.