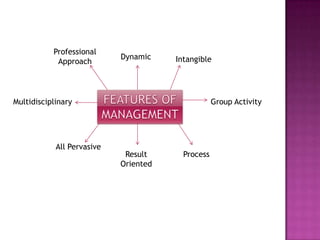
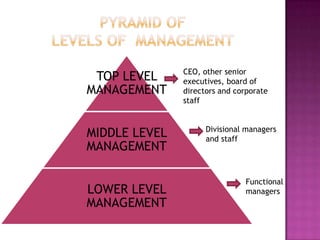
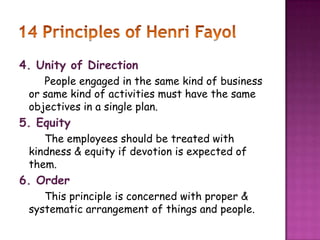
This document discusses the key concepts and principles of management. It defines management as the process of coordinating organizational activities and planning for the future. Management involves forecasting, planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating, and controlling organizational activities. The document also discusses management as both an art and a science, involving creative problem-solving skills as well as systematic processes. It outlines Henri Fayol's six primary management functions and fourteen principles of management, such as division of labor, unity of command, and centralization of decision-making. Overall, the document provides an overview of classic management theories and principles.