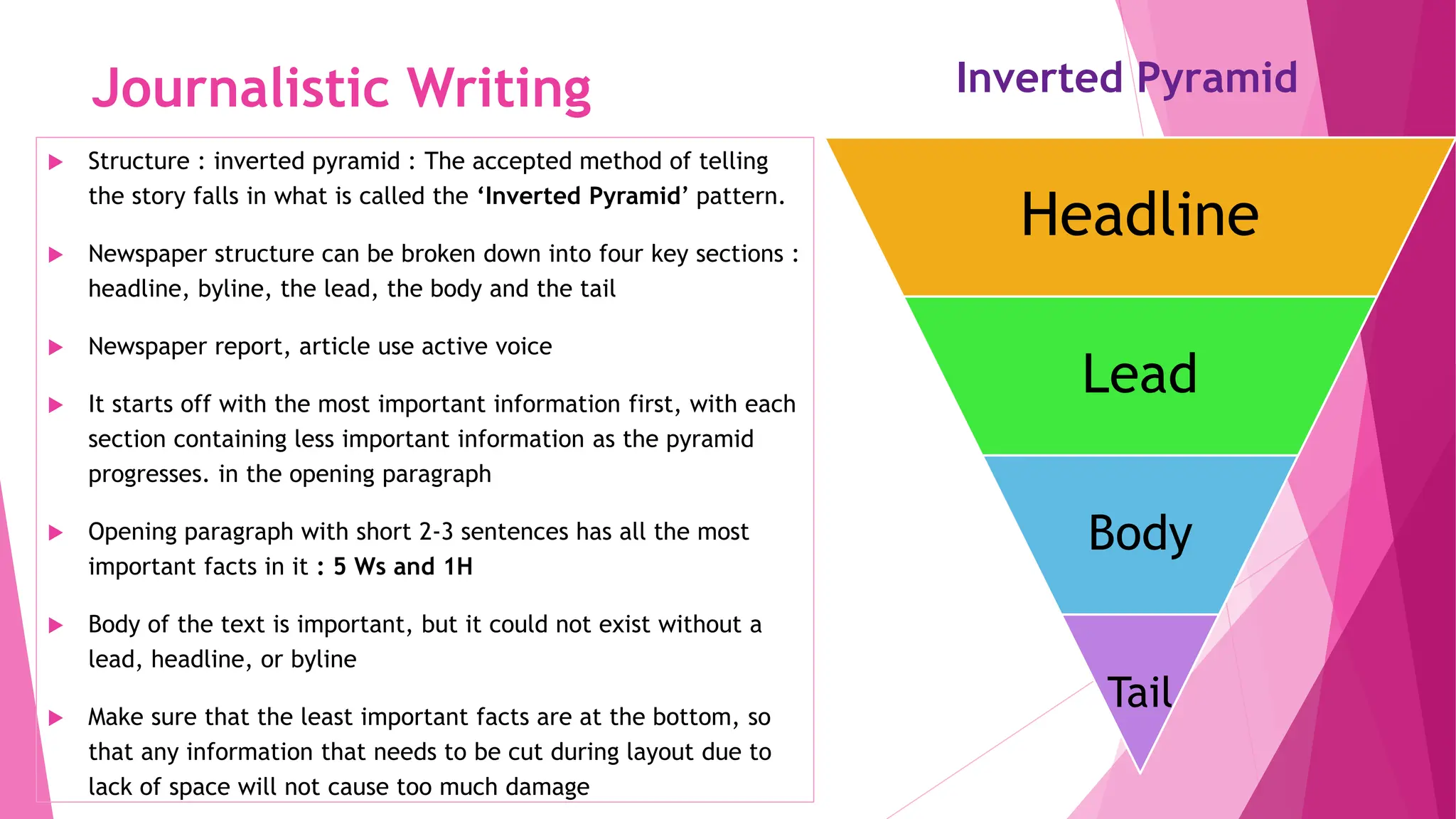
The document provides a comprehensive overview of journalism, emphasizing the importance of various forms, including political journalism, and the role of media in society. It outlines key concepts, types of journalism, and the skills and qualities required to be a successful journalist. Additionally, it discusses the evolution of journalism and the impact of technology on news dissemination.