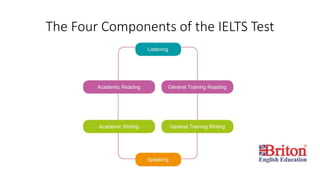
IELTS is an English language test that assesses reading, writing, listening and speaking skills. It is recognized by over 9,000 organizations for study or work where English is used. The test consists of four parts - Listening (30 minutes), Reading (60 minutes), Writing (60 minutes with two tasks), and Speaking (11-14 minutes with three parts). Scores are reported on a band scale from 1 to 9 to indicate proficiency level. Test takers should prepare by practicing each component and considering an official practice test to familiarize themselves with the format.