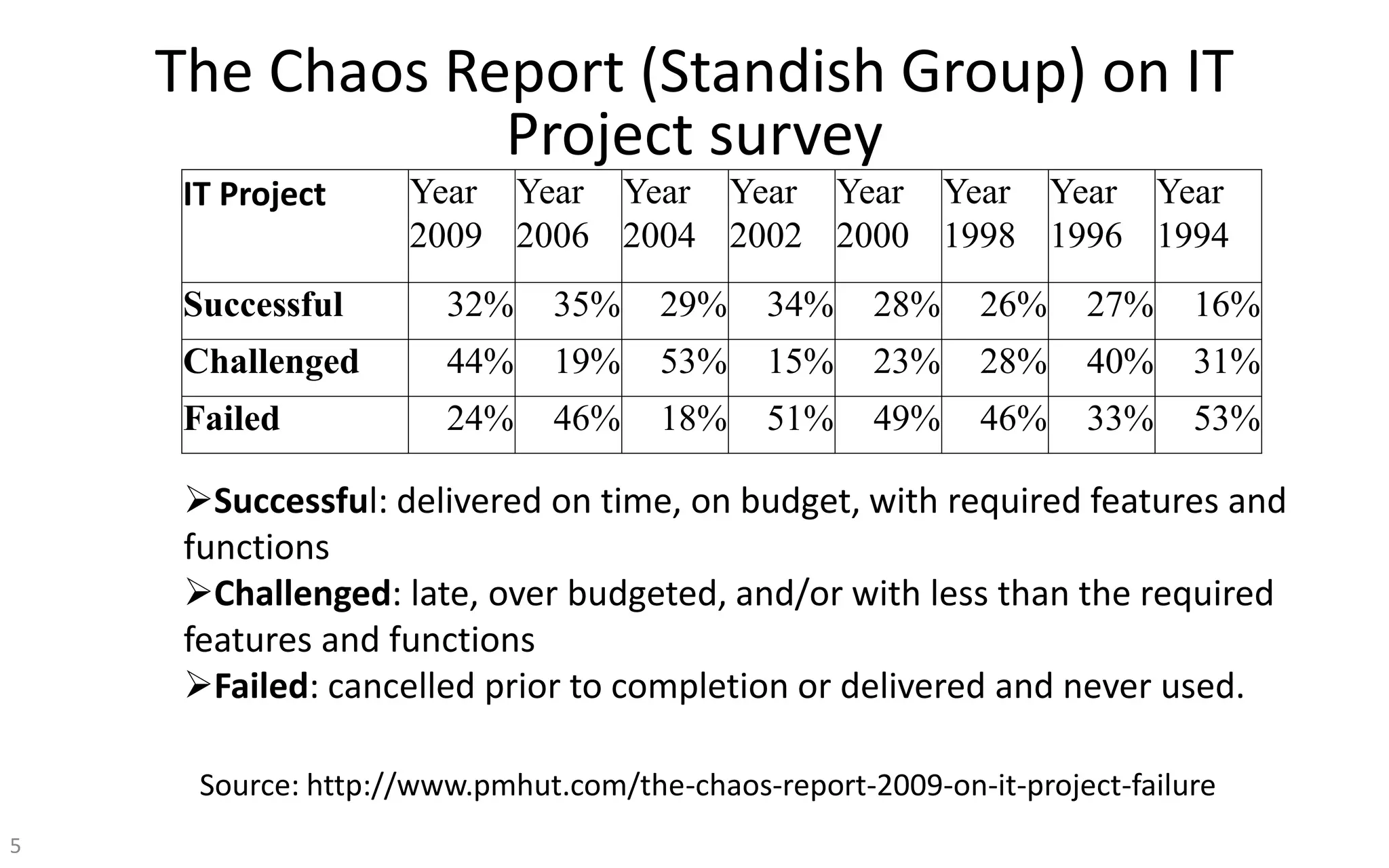
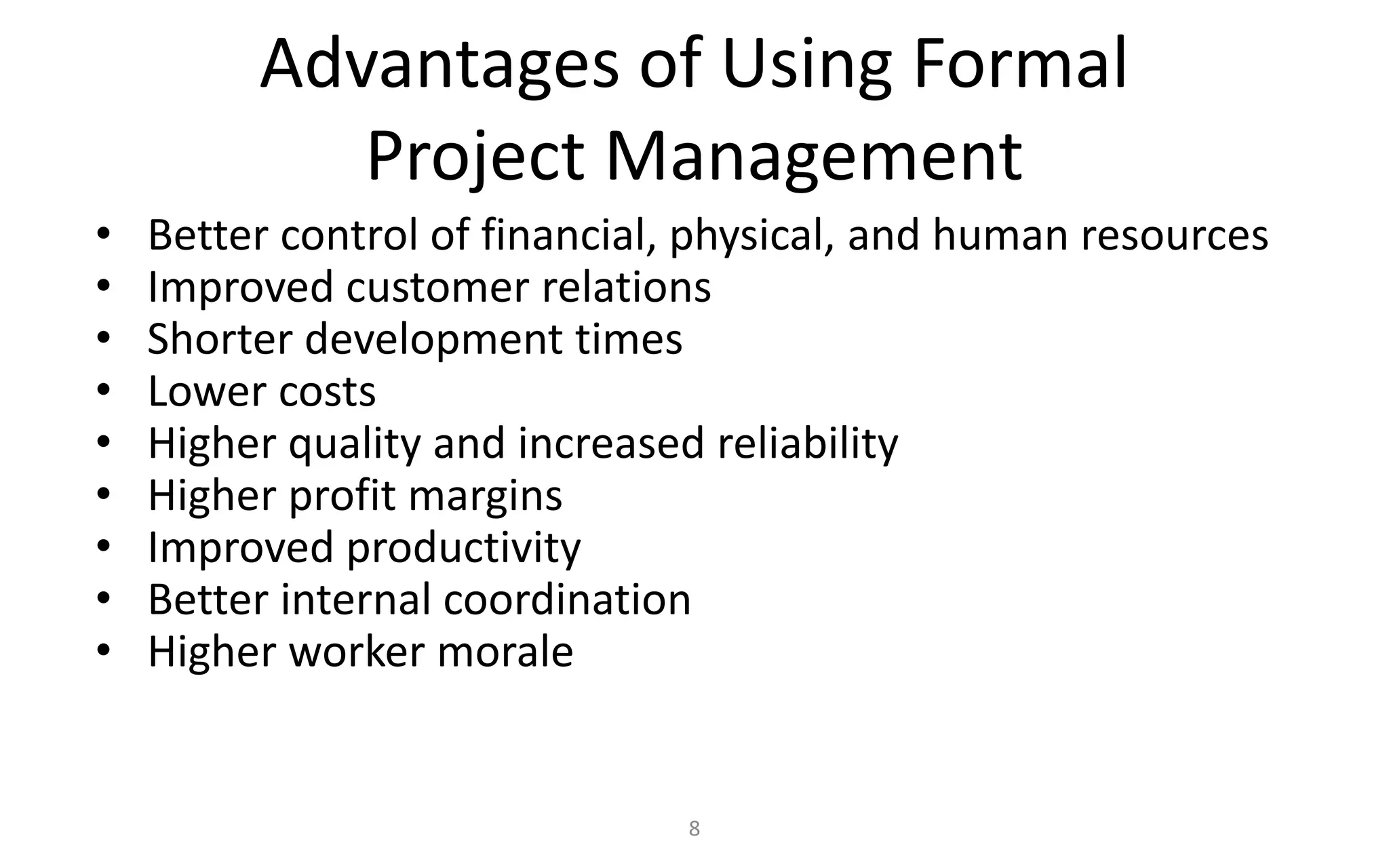
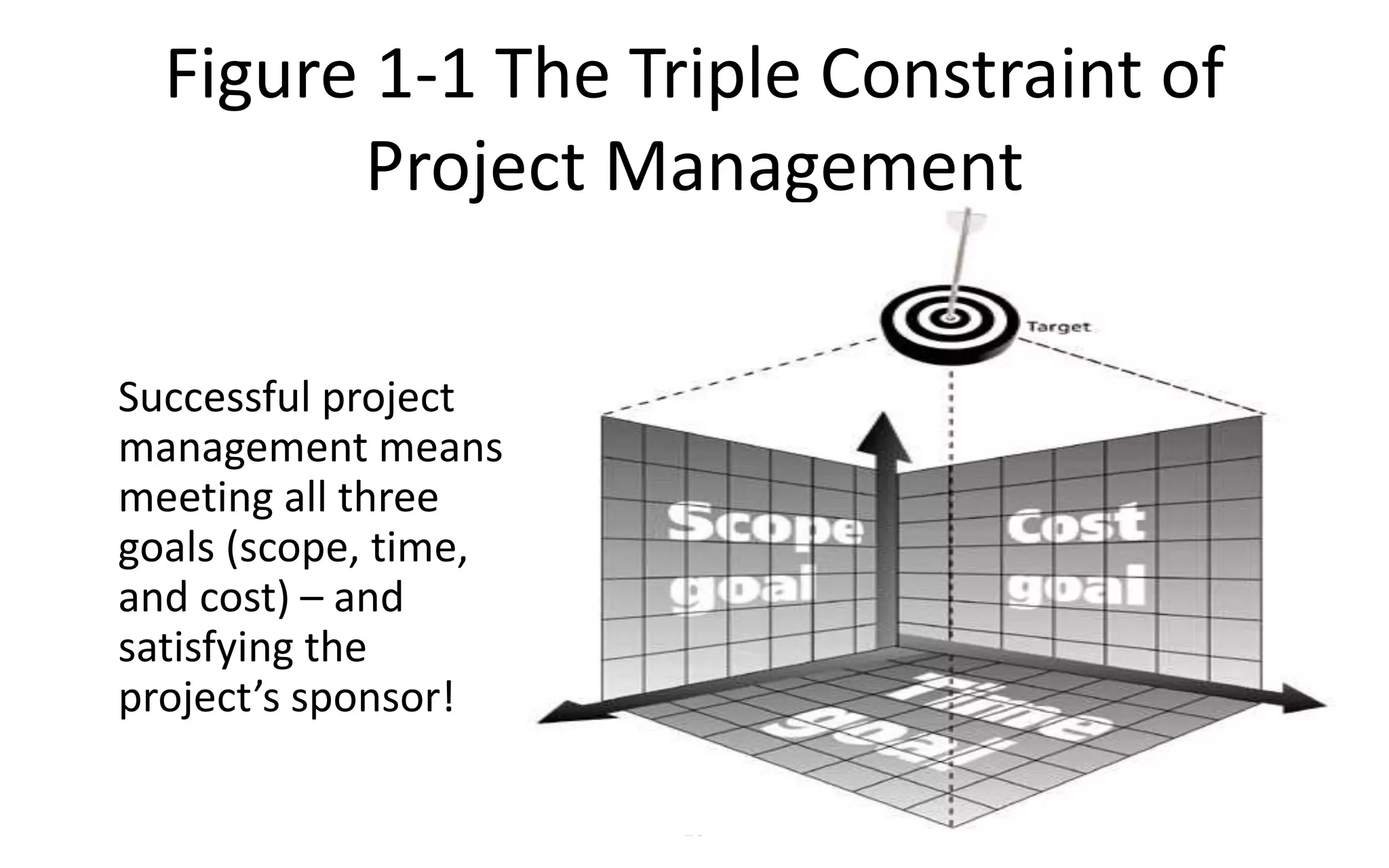
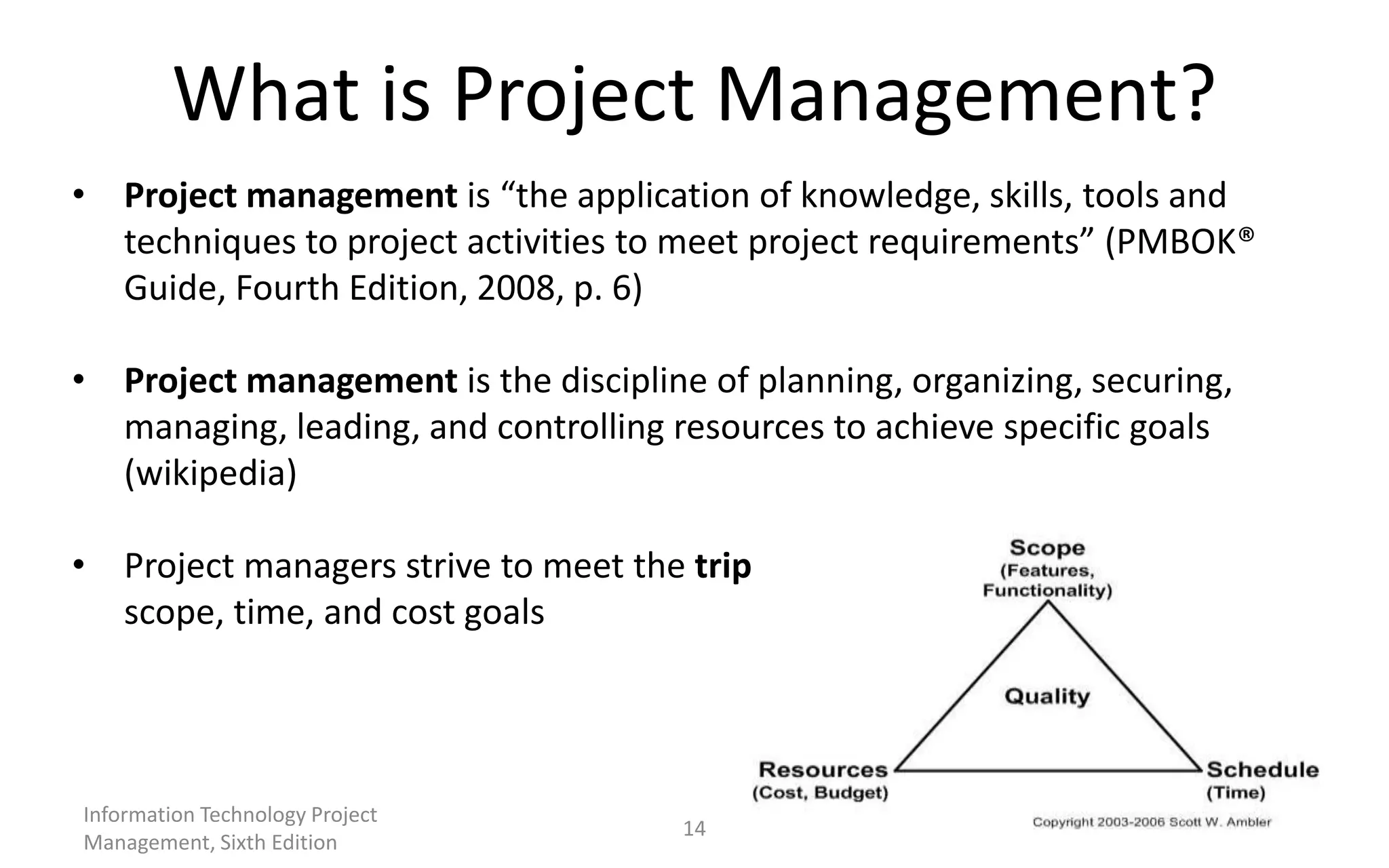
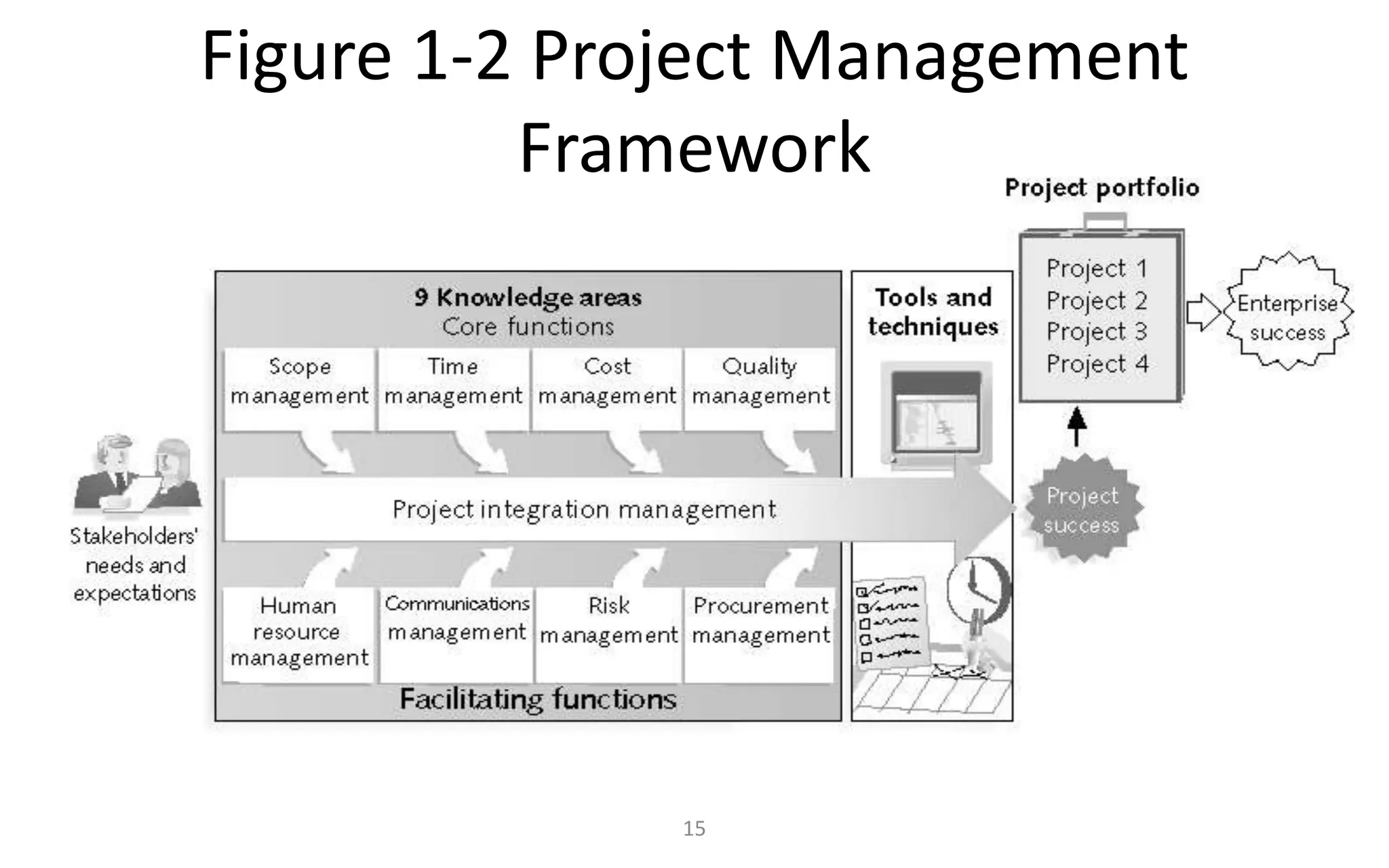
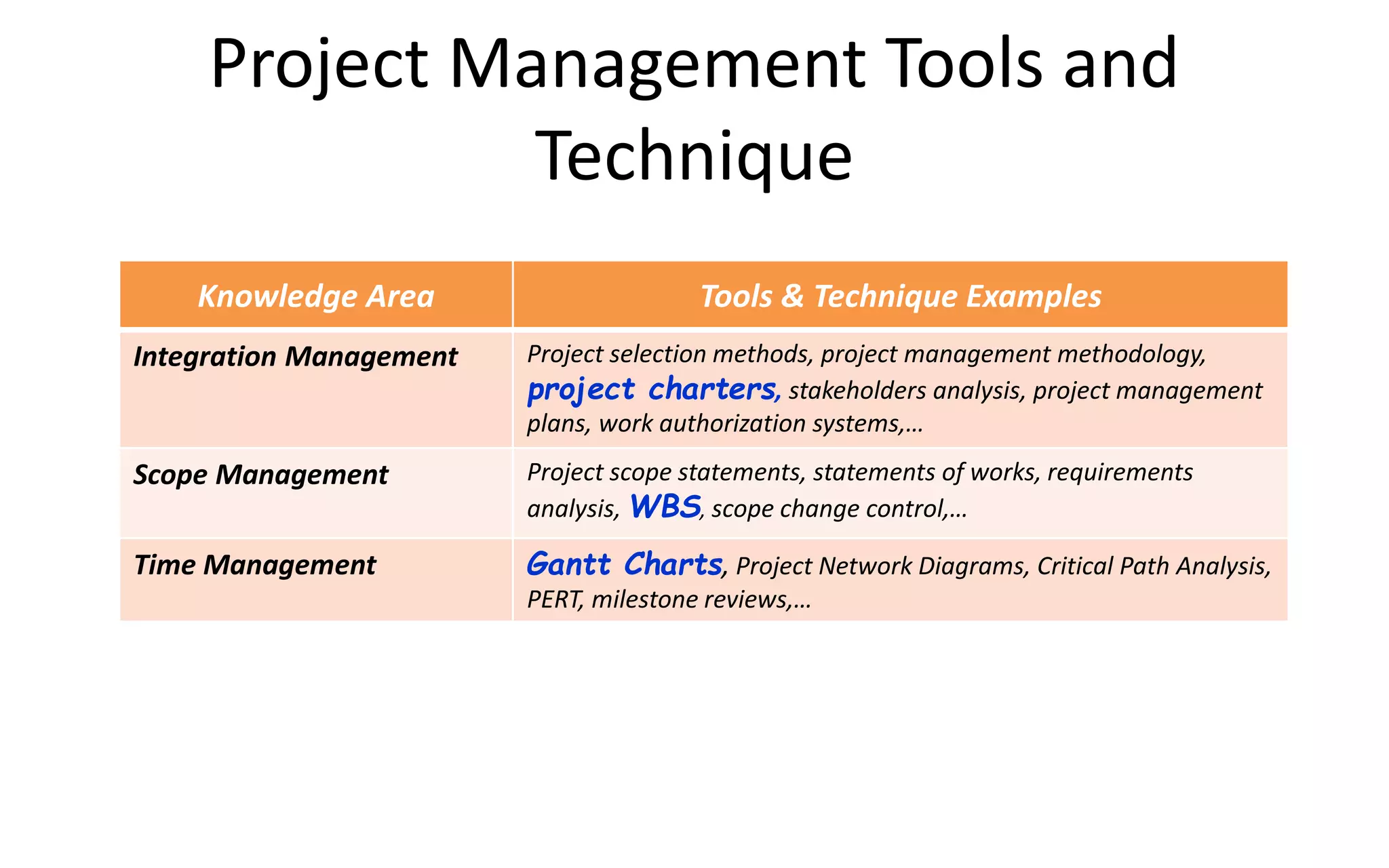
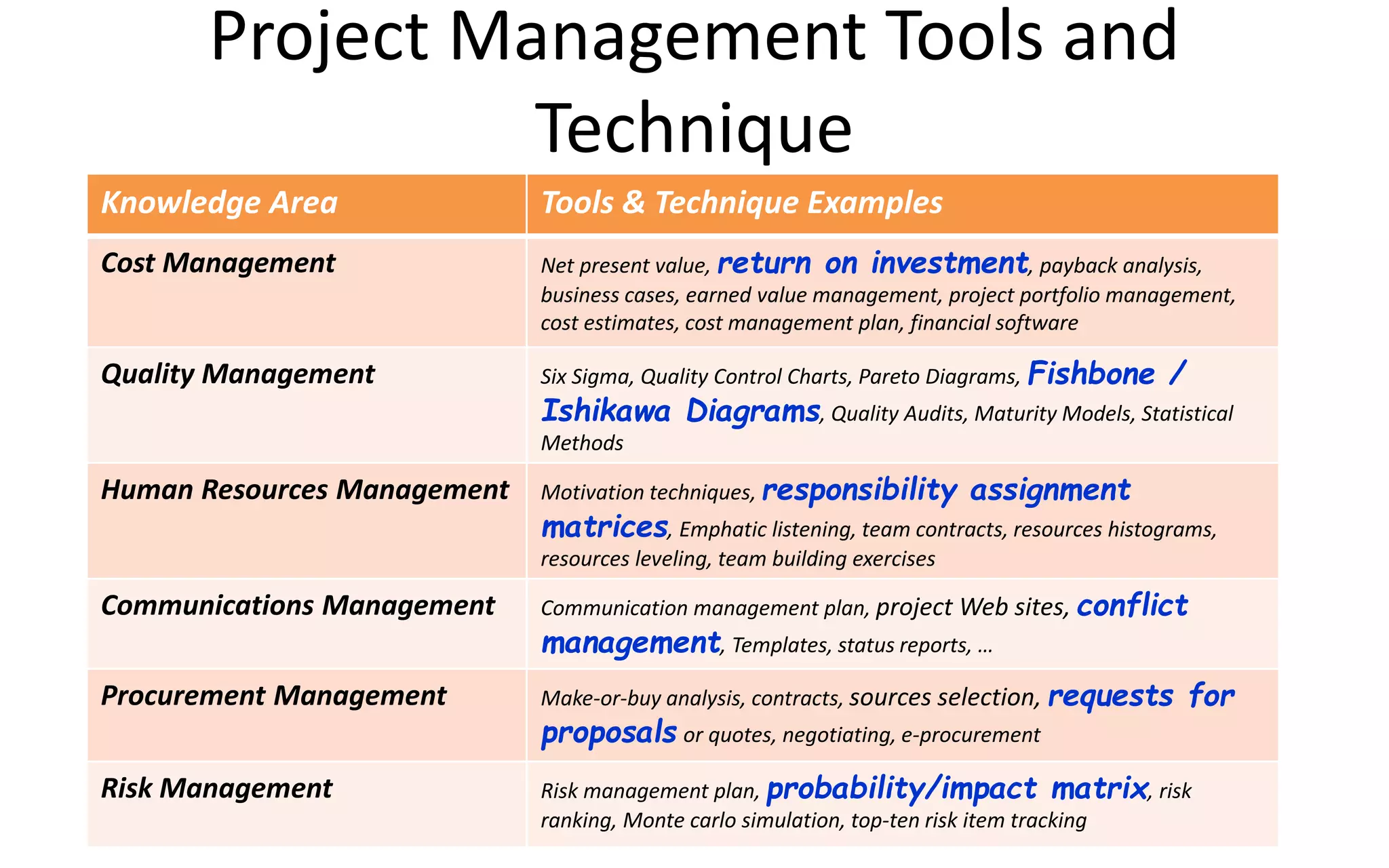
The document introduces IT project management, explaining that it is needed to better manage the large amounts of money spent on IT projects globally each year. It describes what a project is, provides examples of IT projects, and discusses key elements of project management including stakeholders, knowledge areas, tools/techniques, and defining success. Additionally, it notes that many IT projects historically failed or were over budget/late, demonstrating the importance of using formal project management practices.