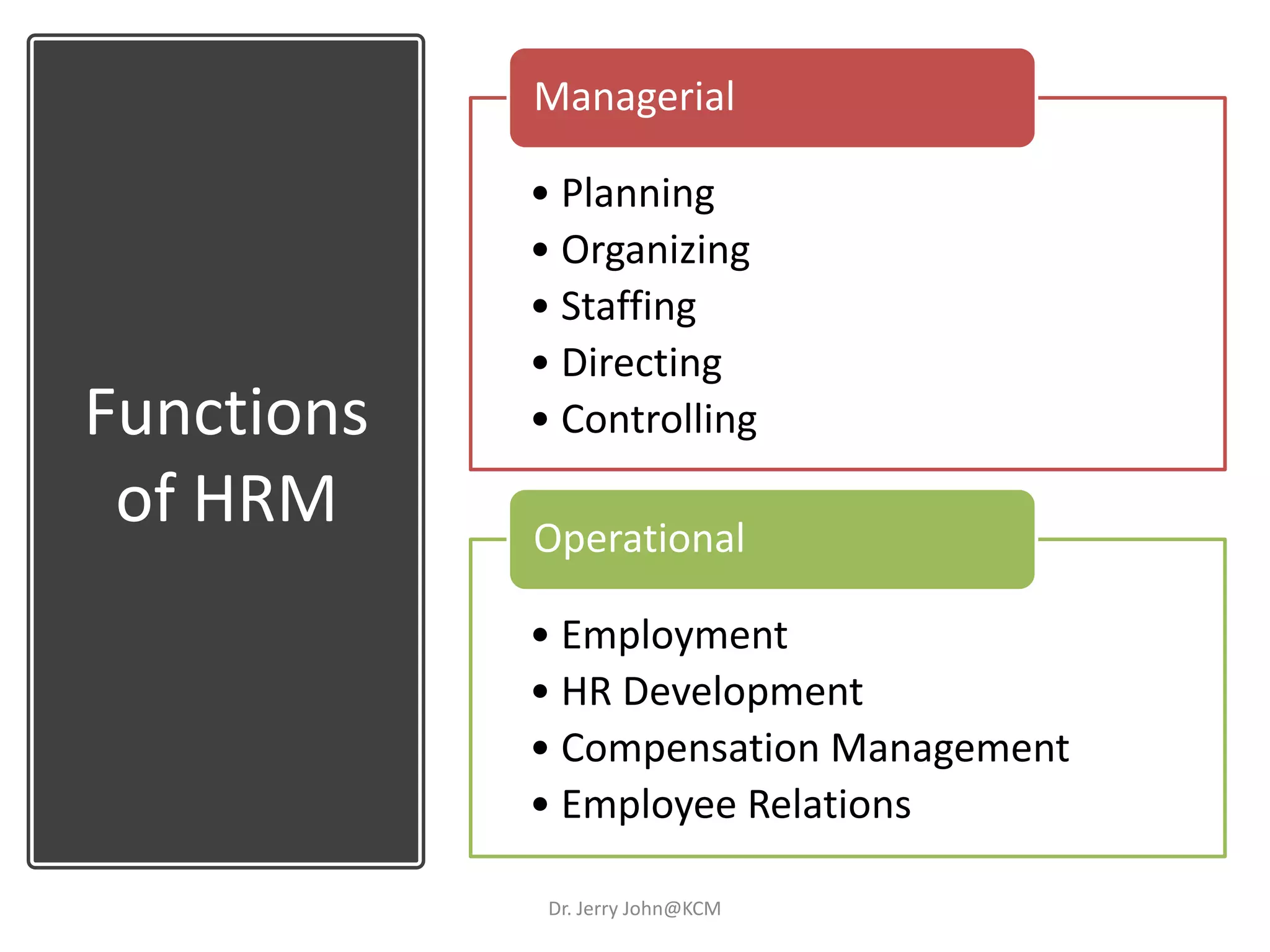
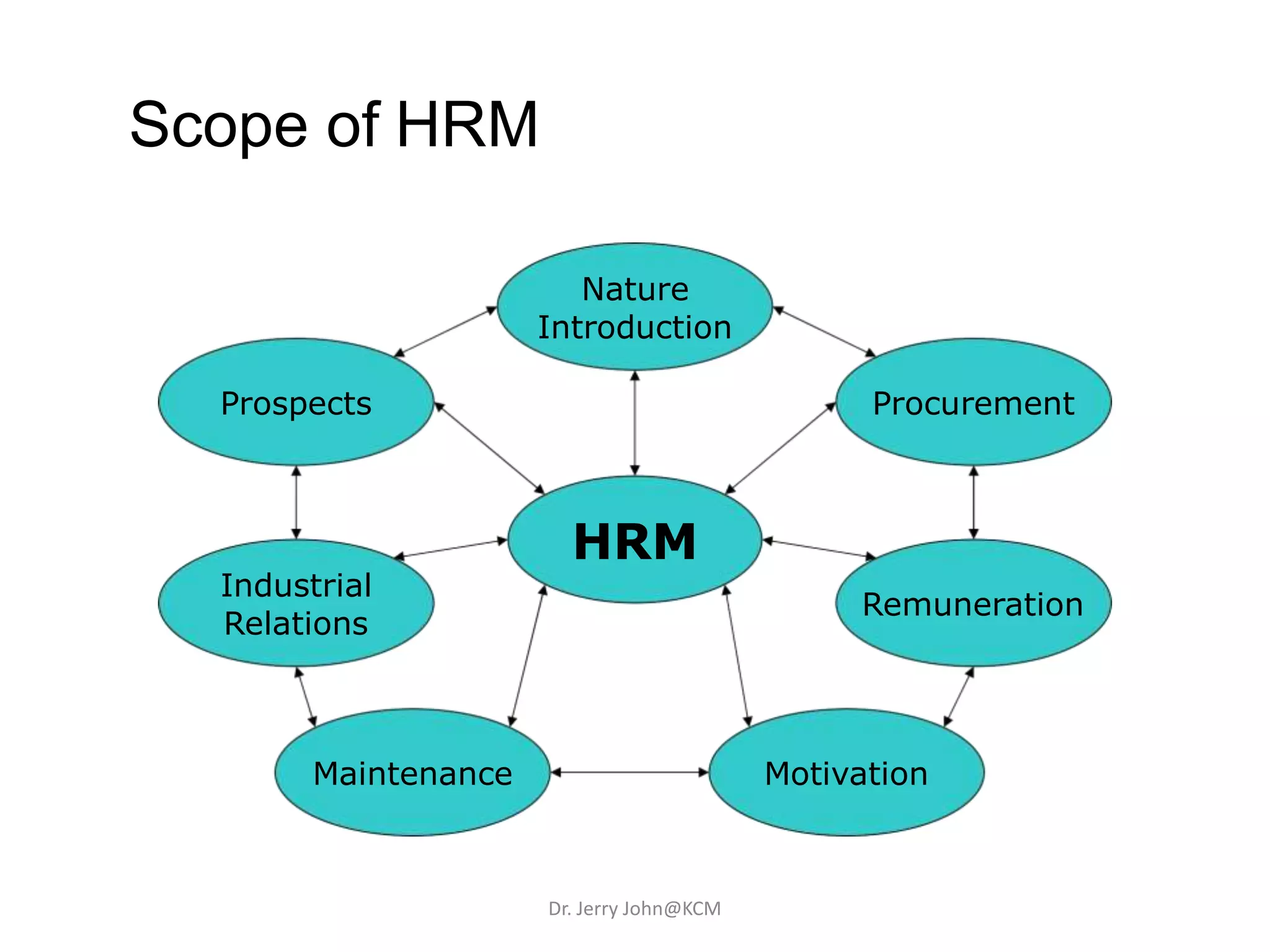
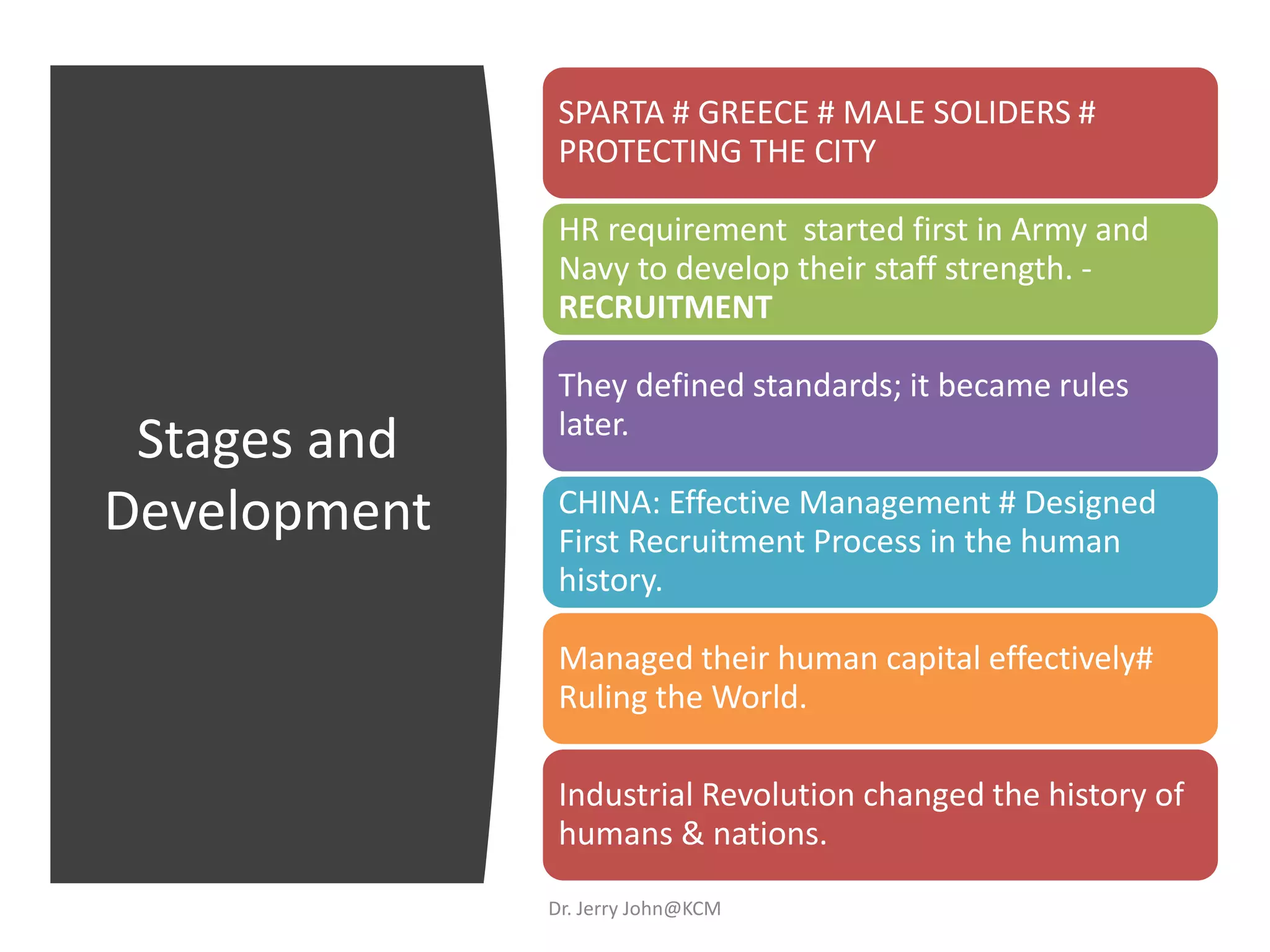
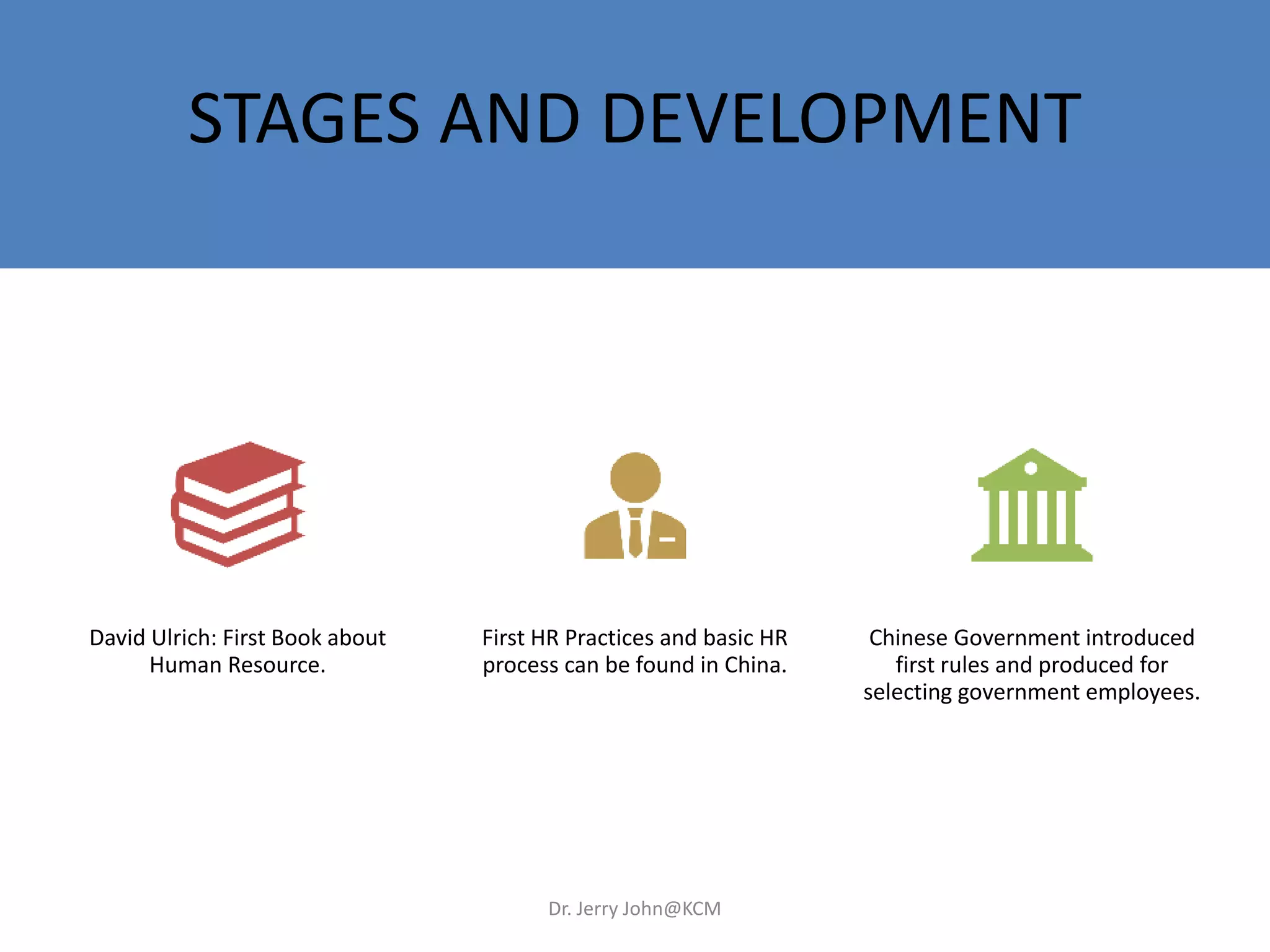
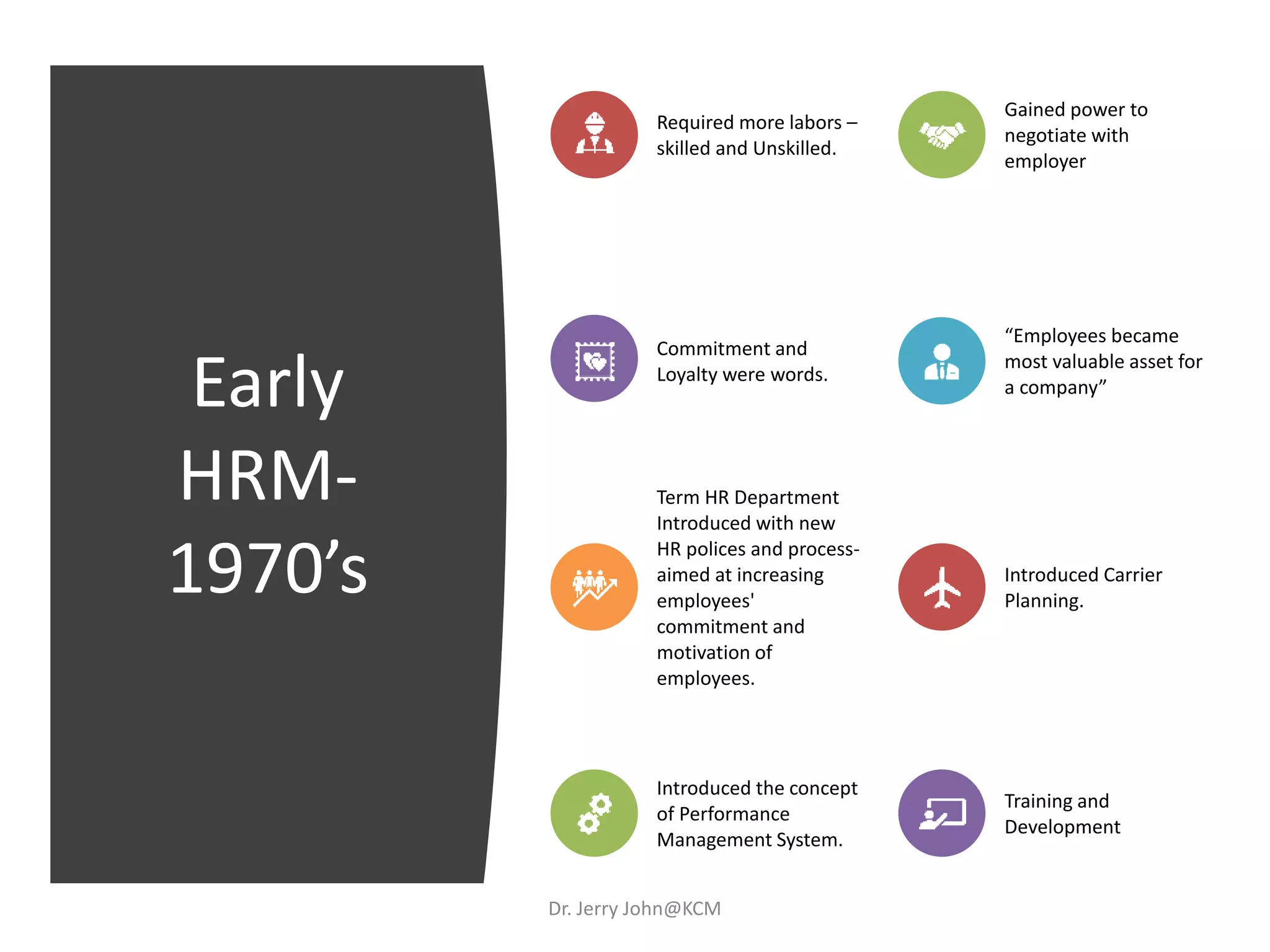
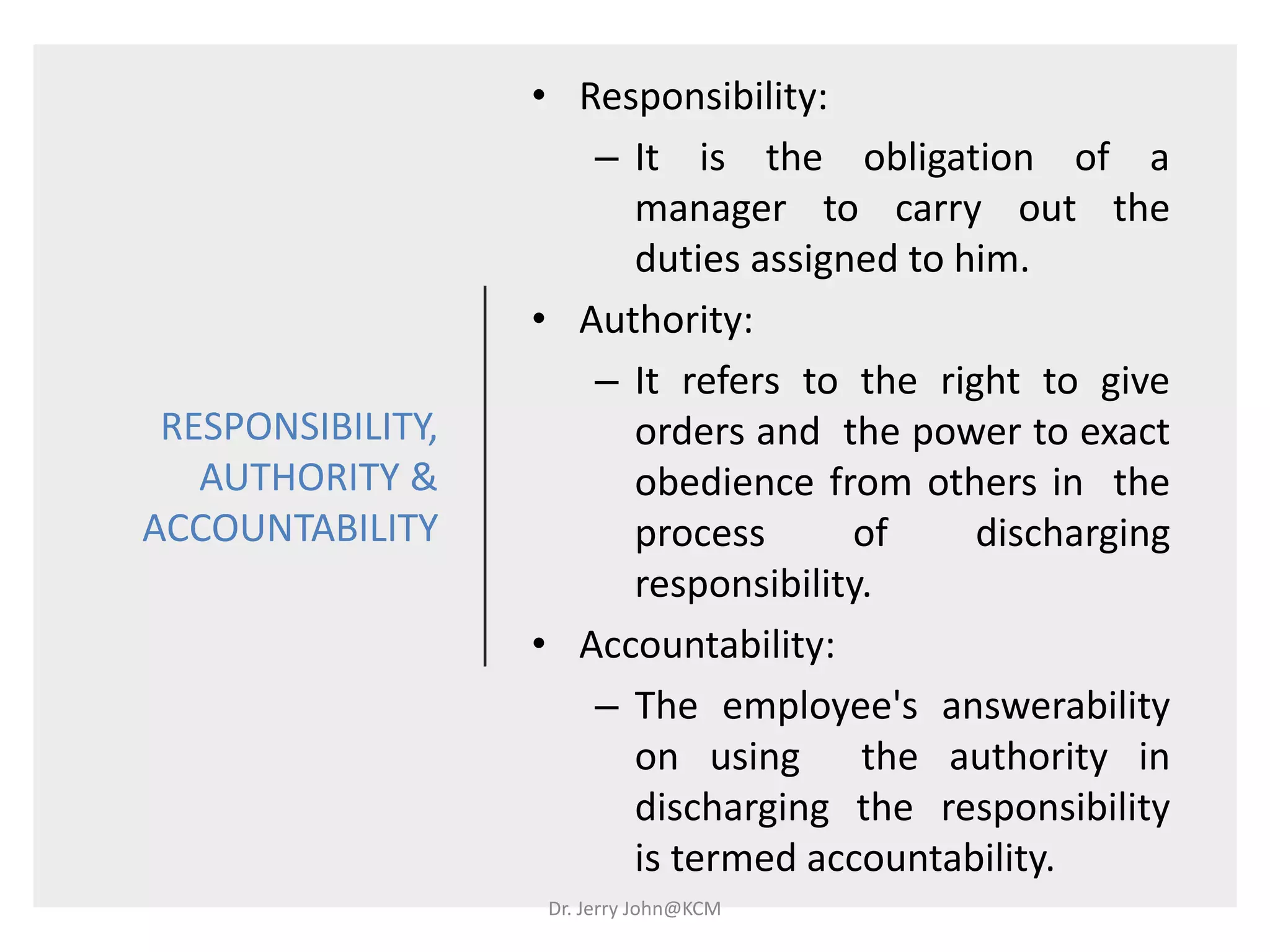
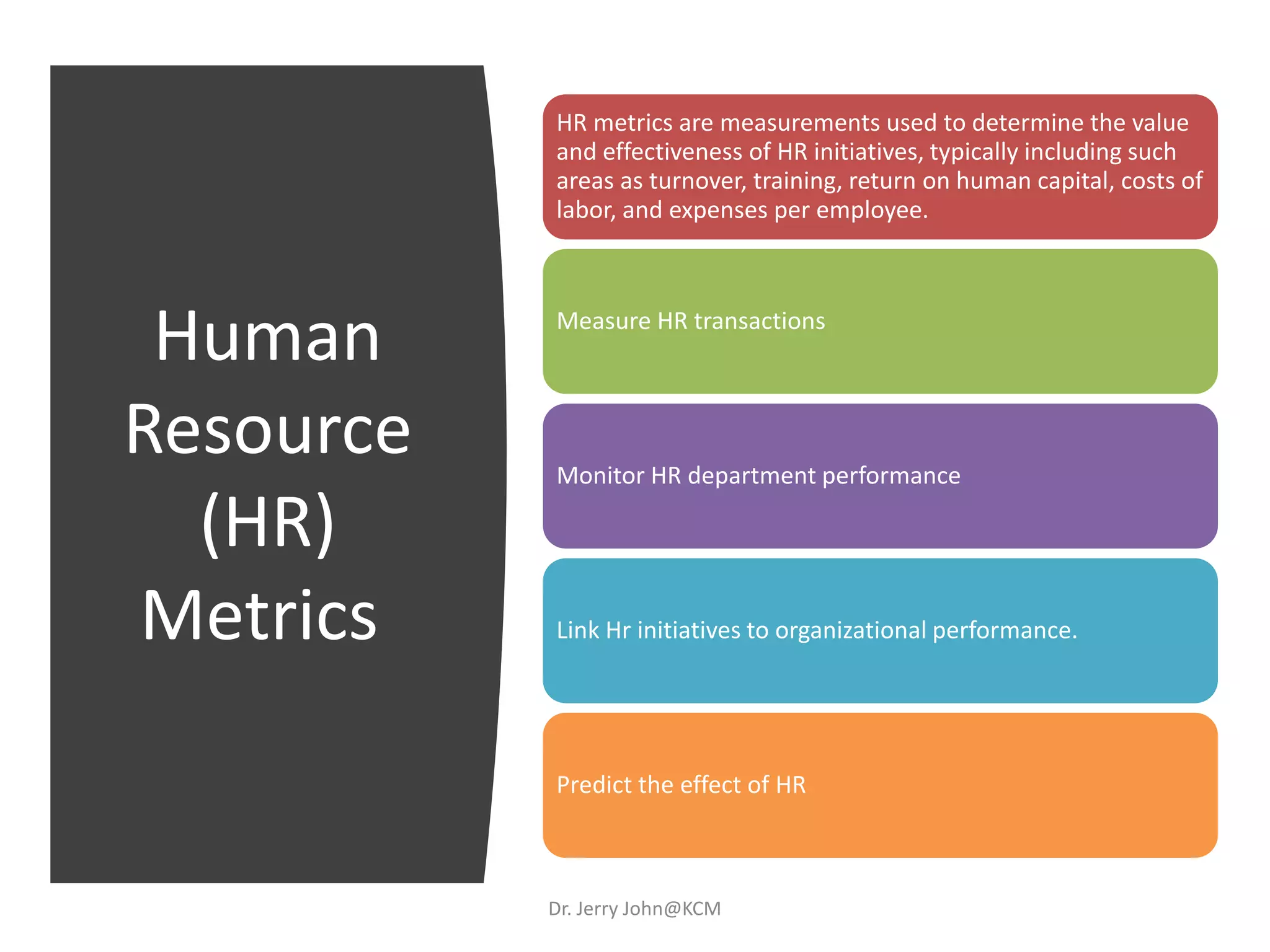
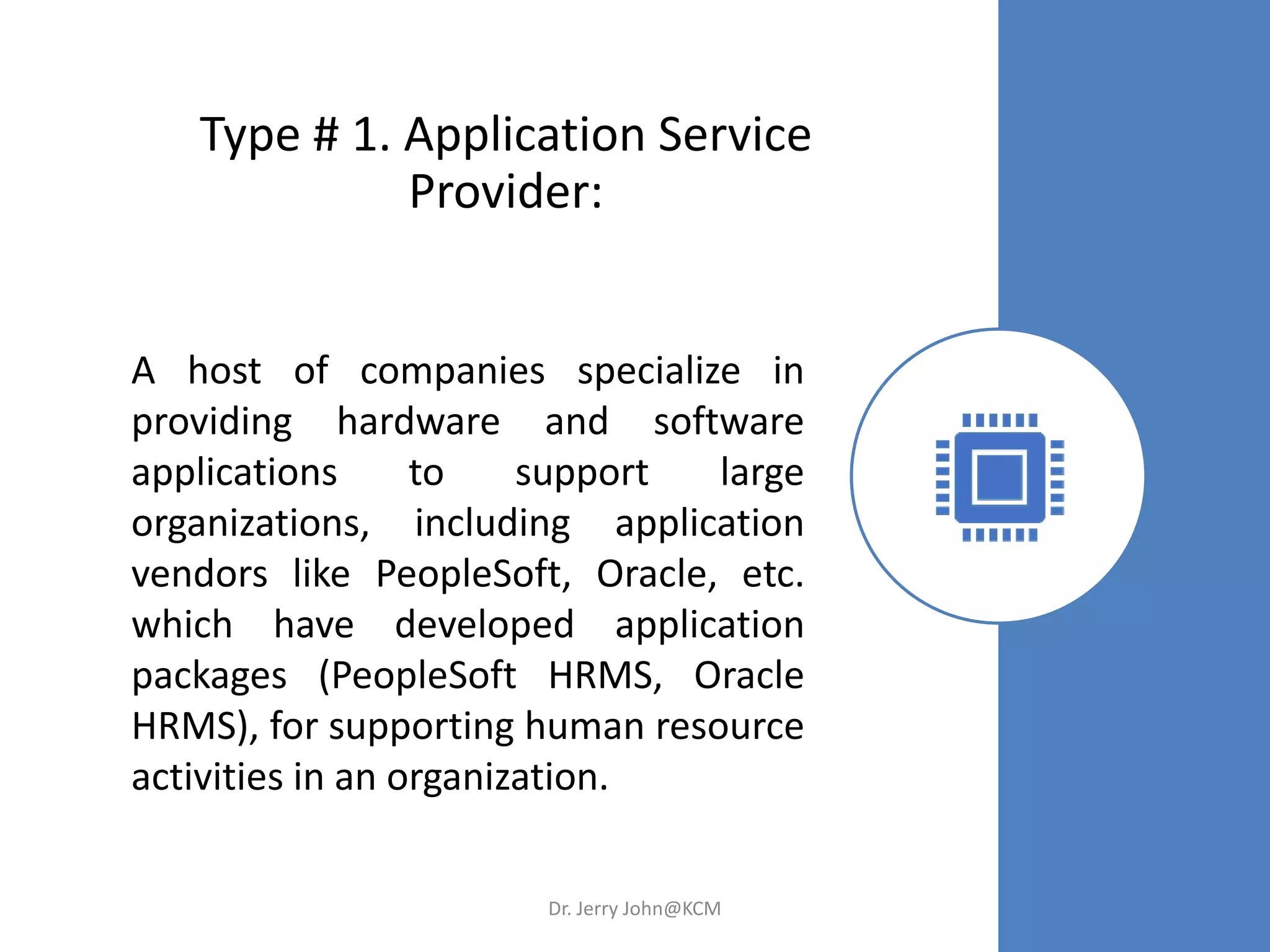
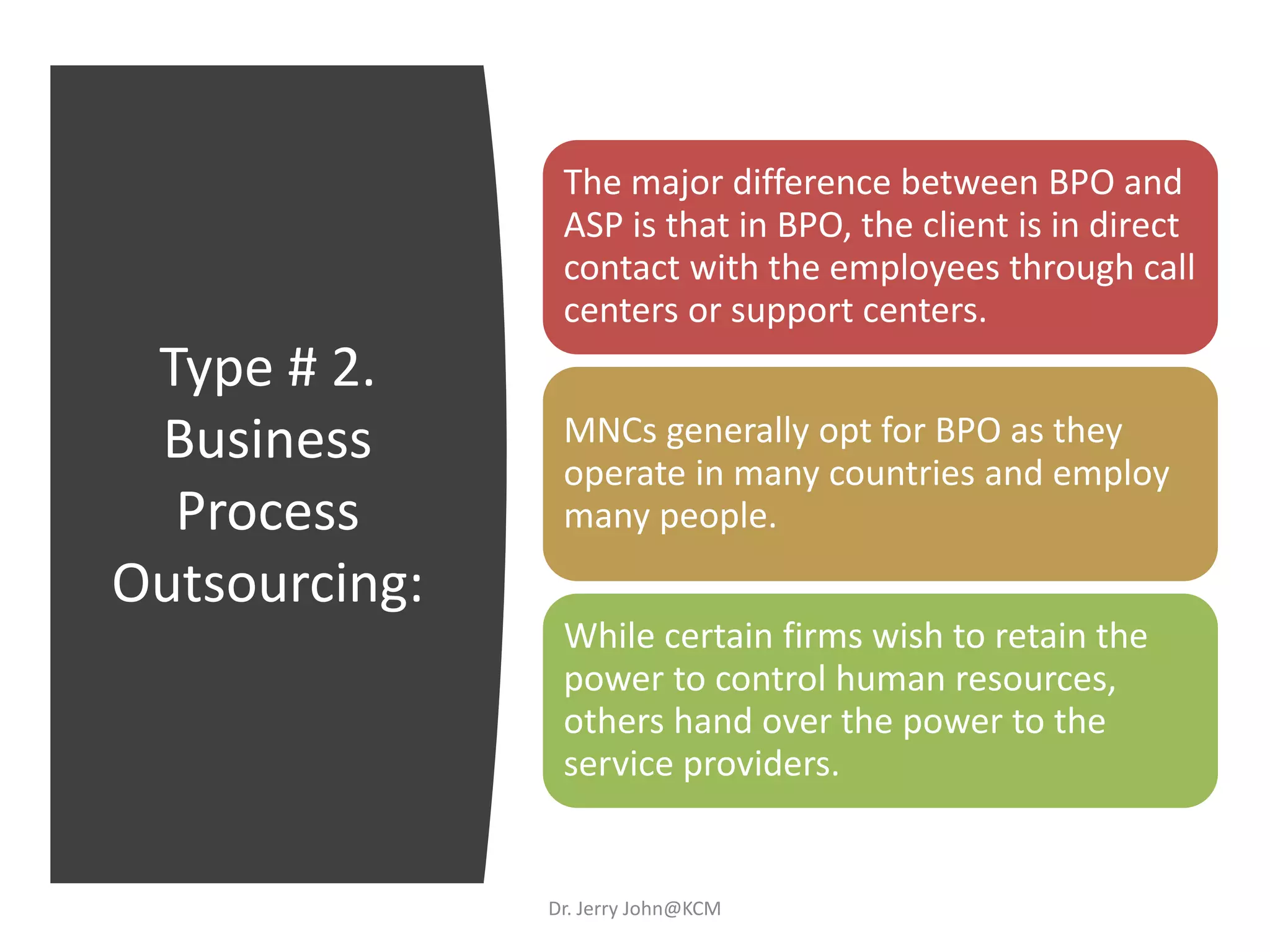
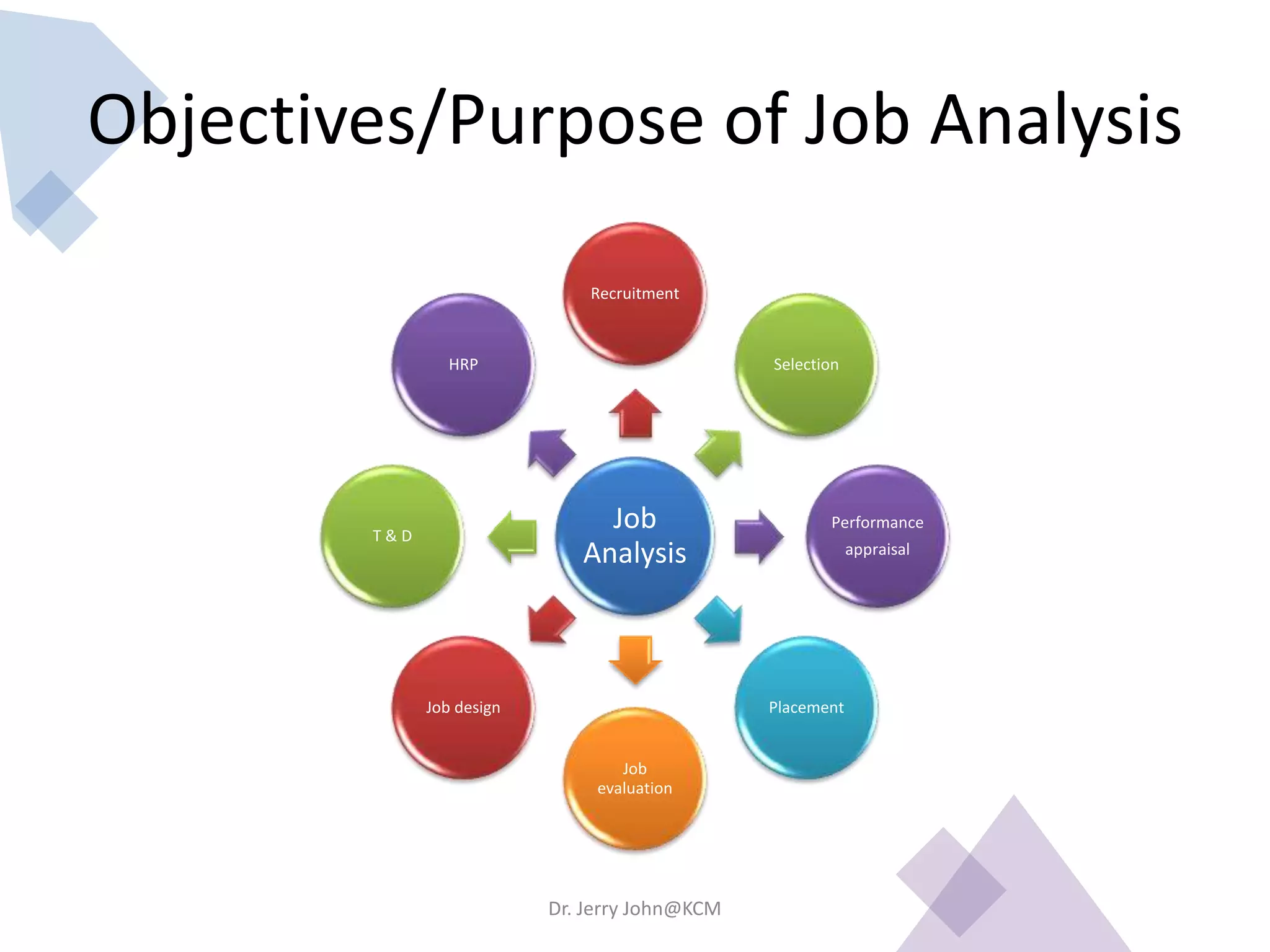
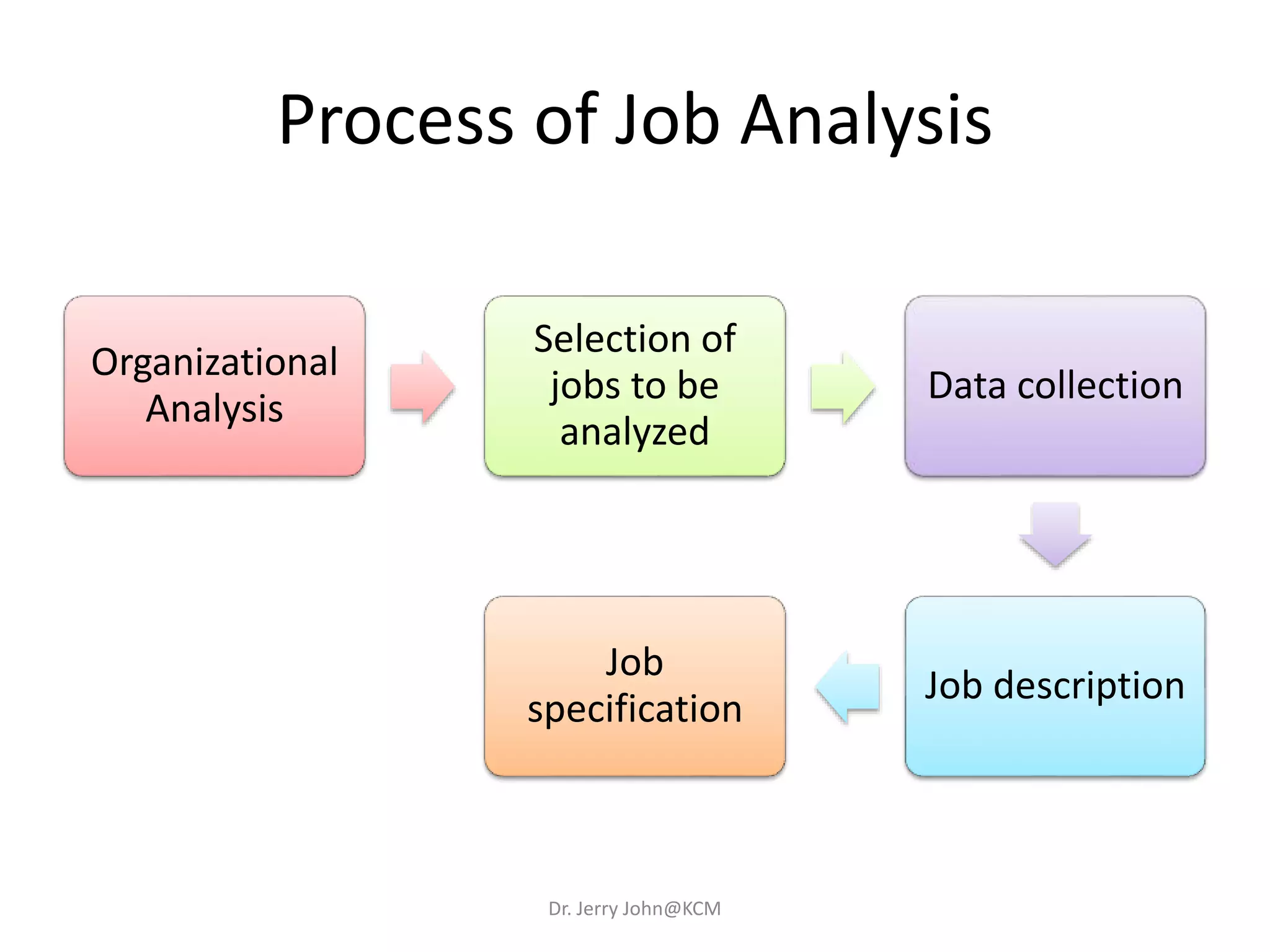
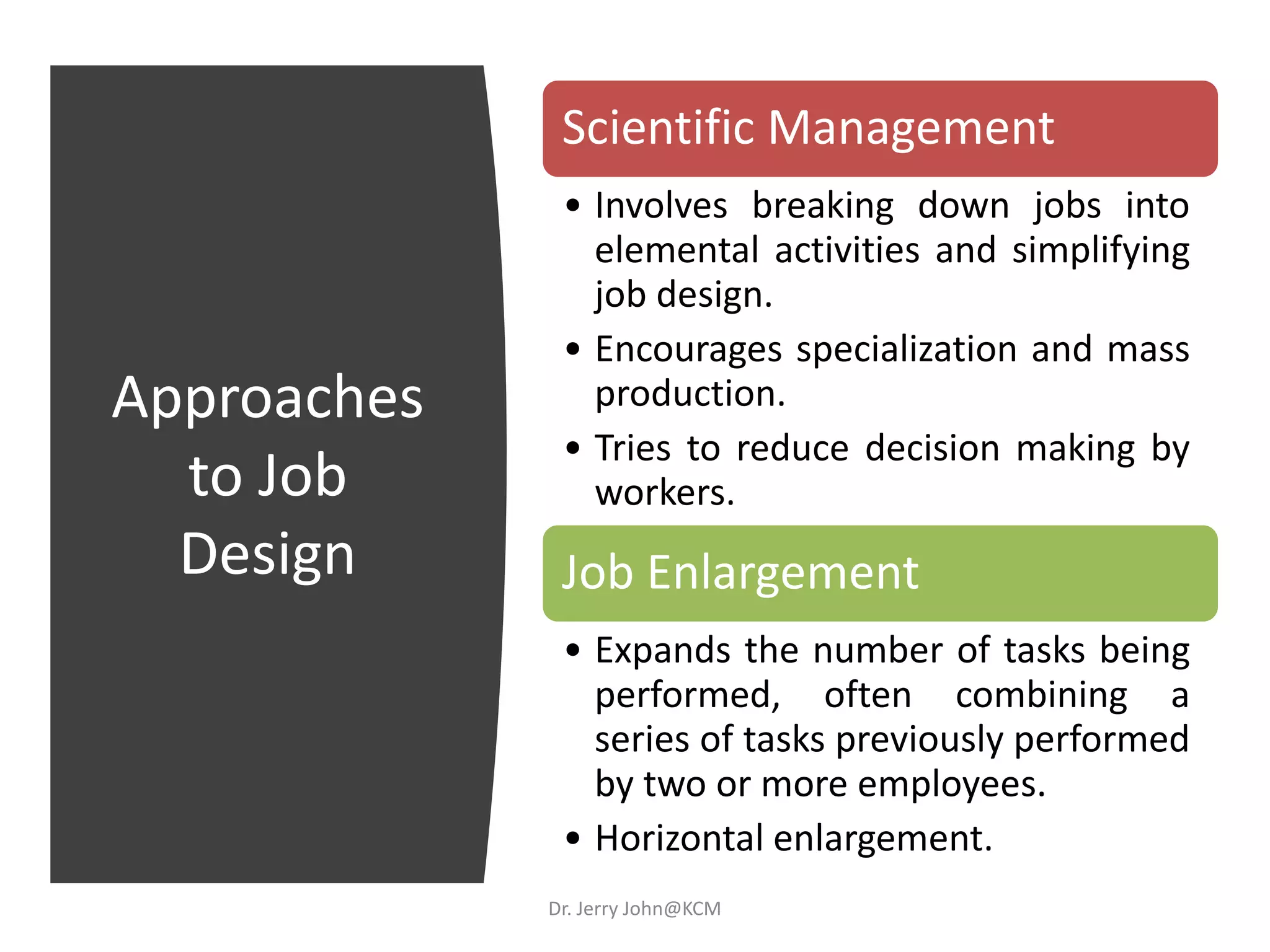
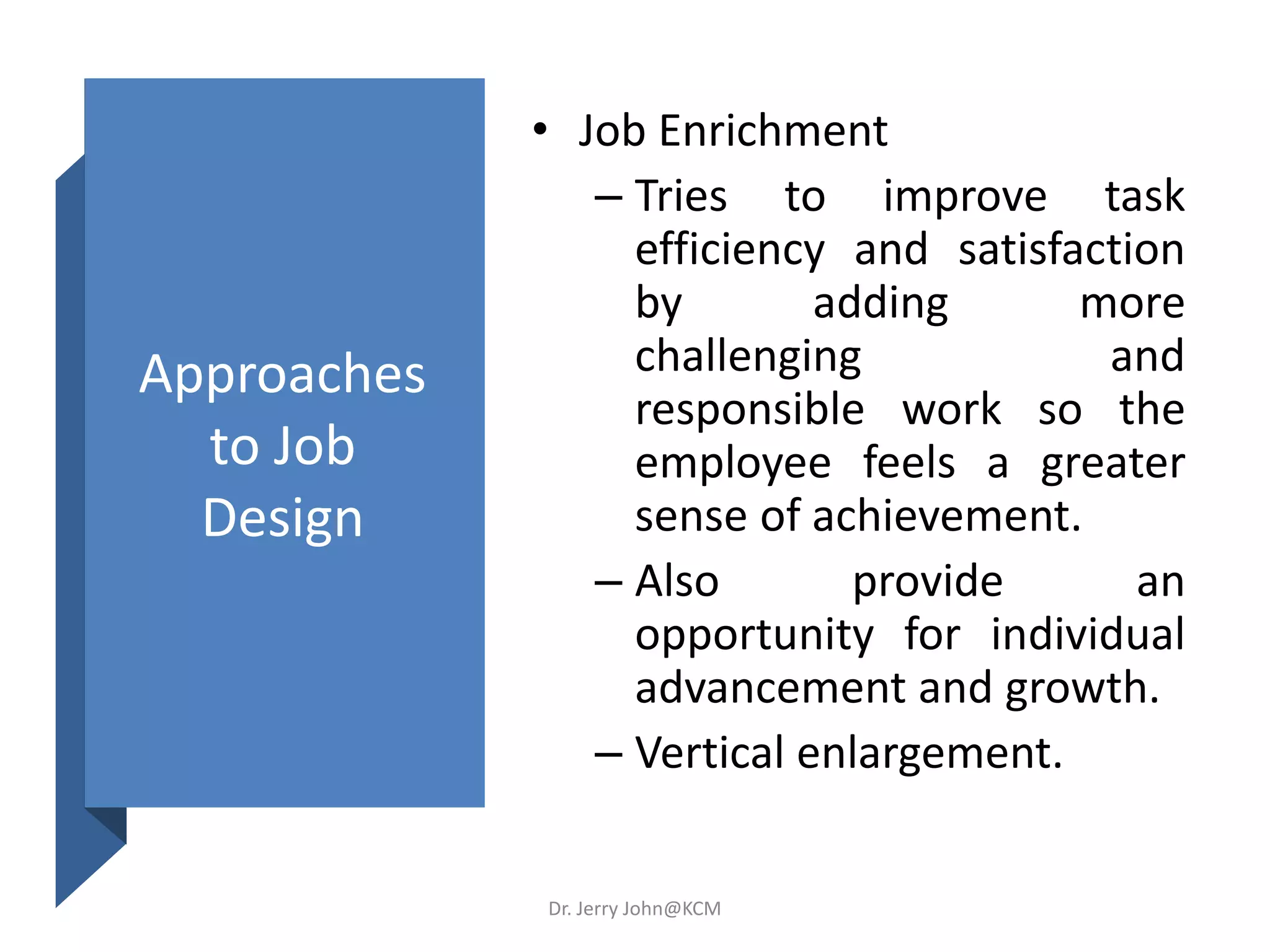
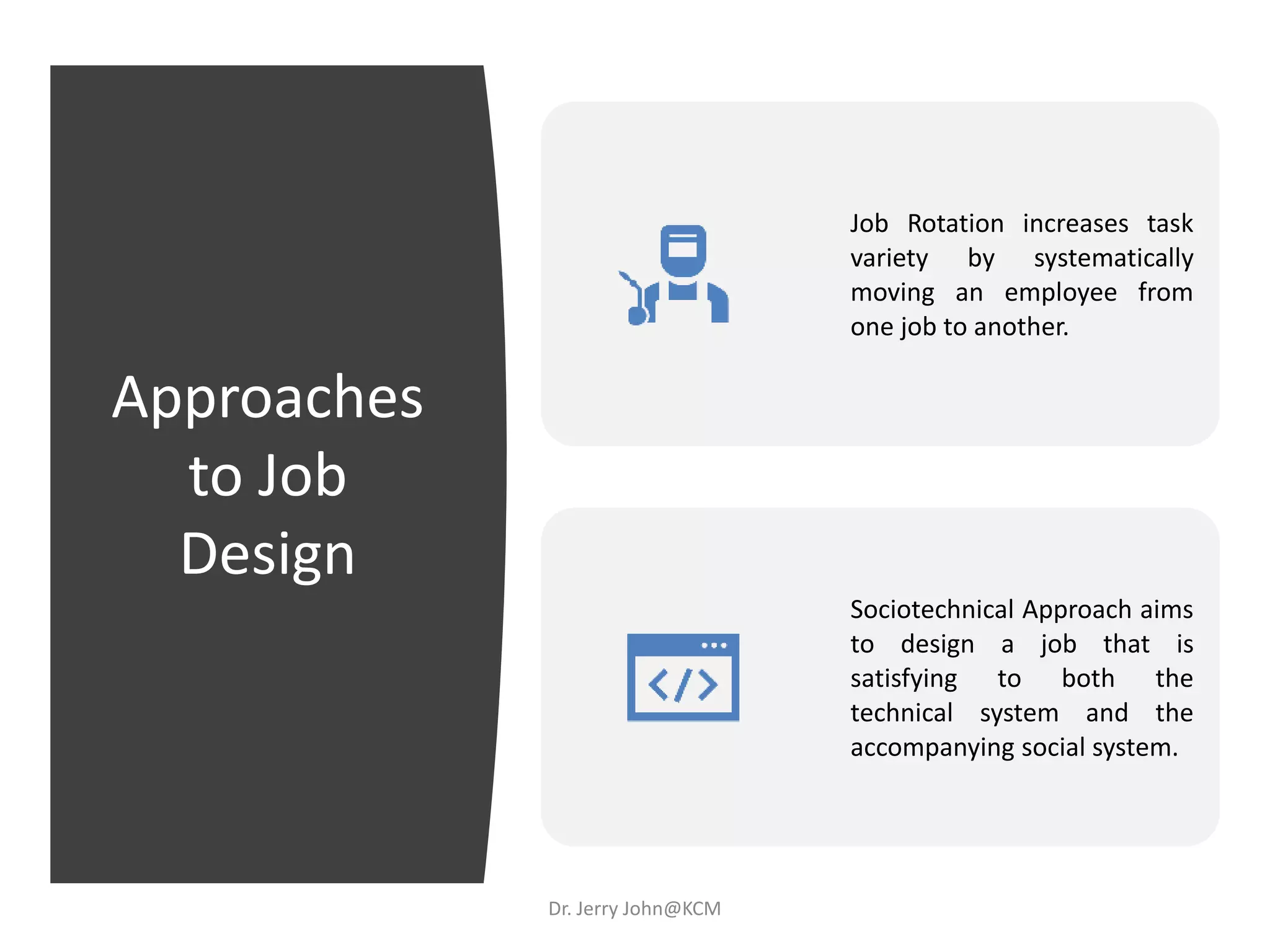
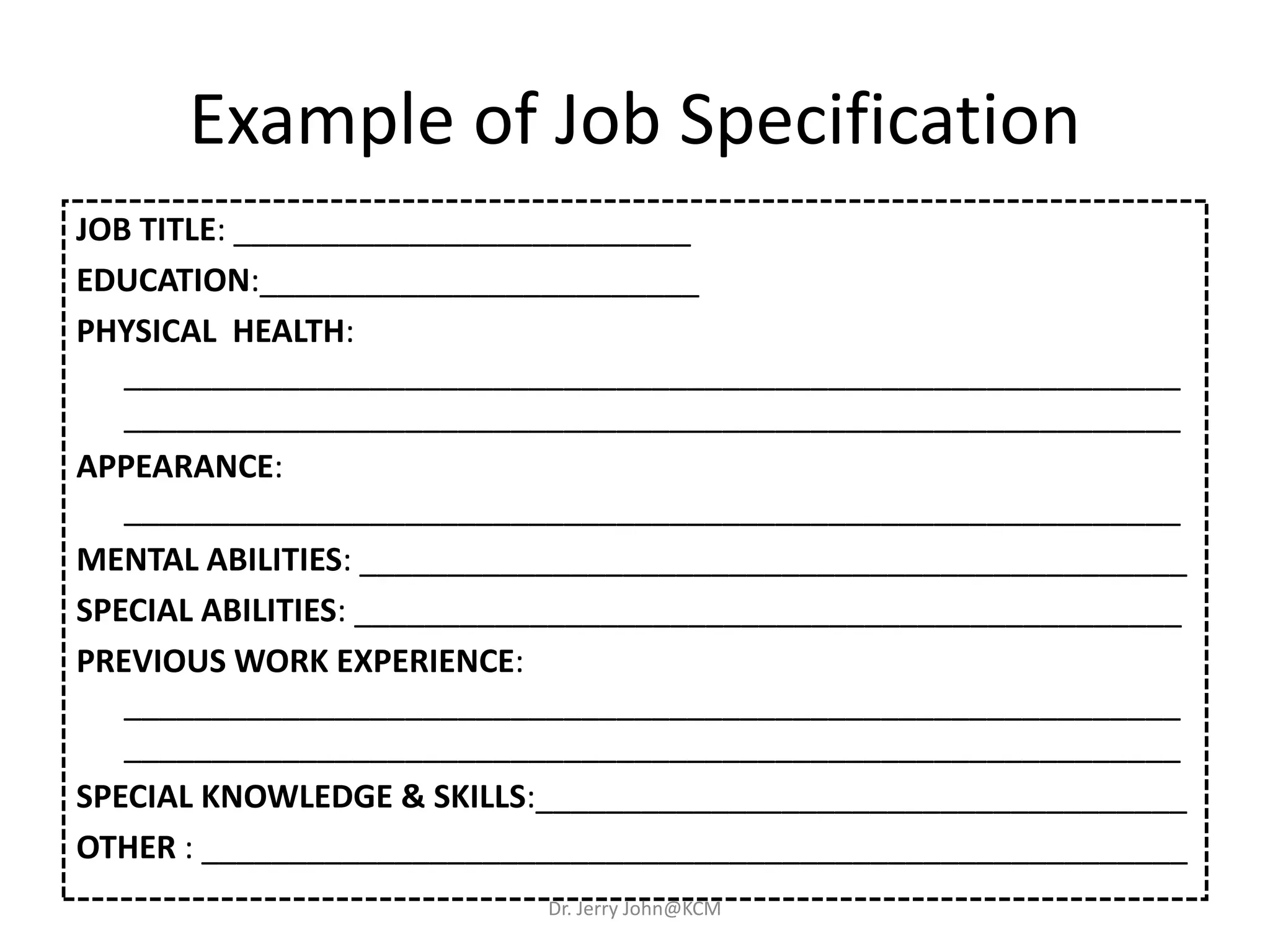
The document provides an extensive overview of Human Resource Management (HRM), detailing its definition, functions, history, and importance within organizations. It outlines the key responsibilities of HR professionals, the evolution of HR practices from the industrial revolution to modern outsourcing trends, and emphasizes the significance of effective human resource planning and job design. Additionally, it discusses the metrics used to measure HR effectiveness and the necessity of HR audits for compliance and performance management.