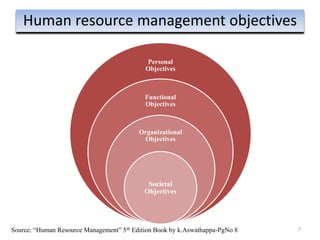
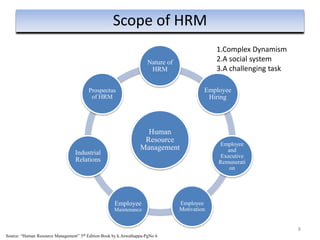
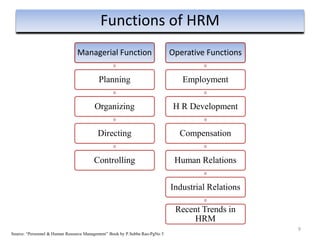
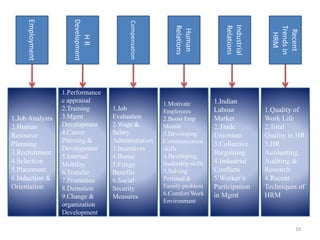
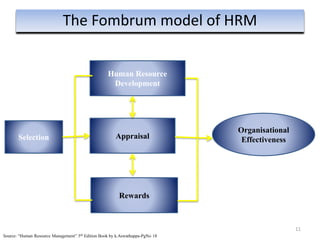
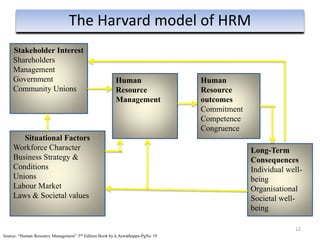
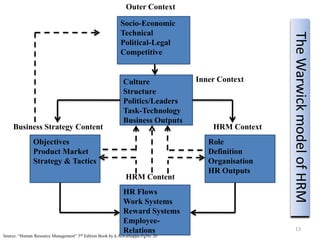
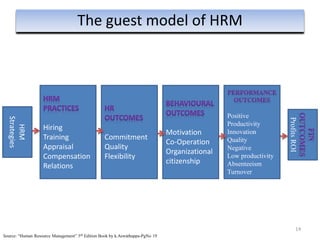
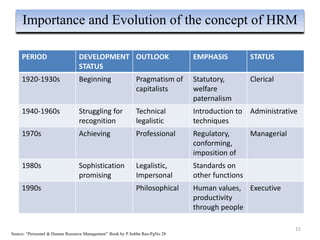
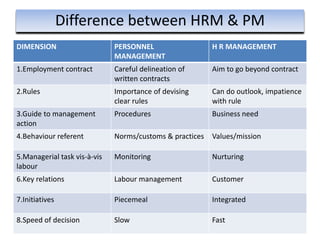
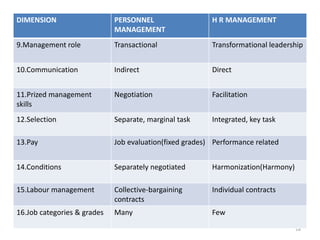
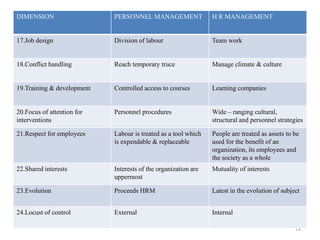
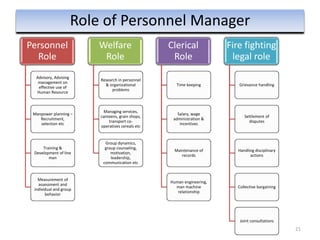
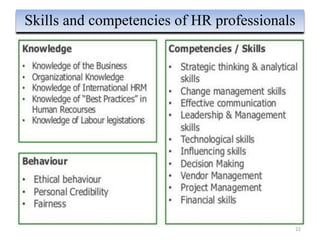
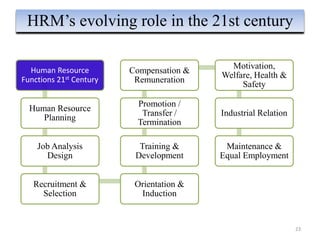
The document provides an overview of Human Resource Management (HRM), detailing its significance, functions, and the evolution of the HR field. It outlines key HRM activities such as hiring, training, and employee relations, contrasting HRM with traditional personnel management approaches. Additionally, it discusses various models of HRM and emphasizes the need for strategic management of human resources in modern organizations.