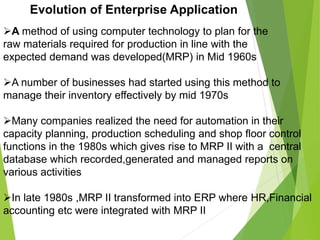
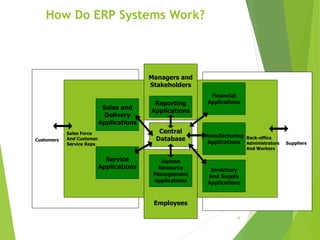
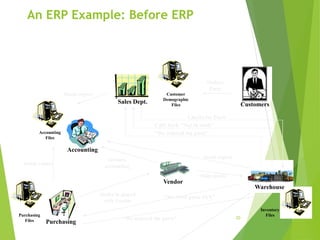
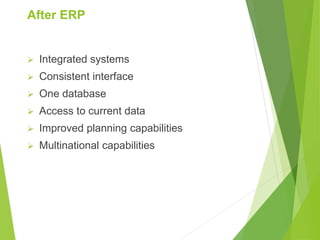
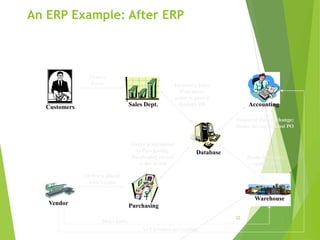
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems evolved from earlier systems like material requirements planning (MRP) and manufacturing resource planning (MRP II) by integrating additional business functions. ERP combines databases across departments into a central database accessible to all employees. It automates business processes and provides consistent, integrated data across modules. Implementing ERP requires changes to business processes, organizational structure, and technology. Success requires strong leadership, communication, and balanced project teams. Selecting an ERP vendor involves evaluating features, implementation plans, and client feedback before selecting a solution.