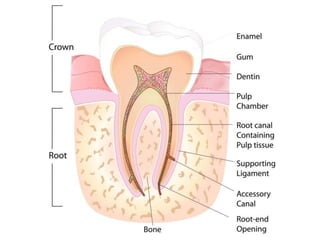
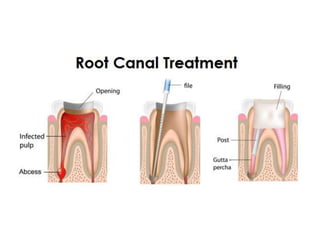
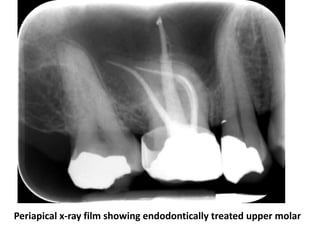
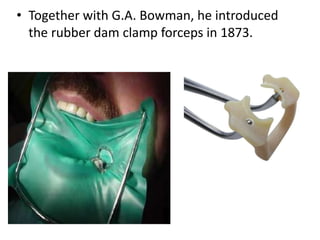
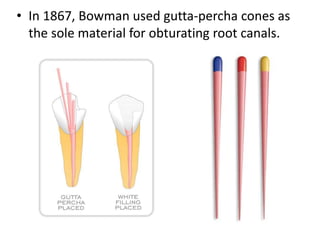
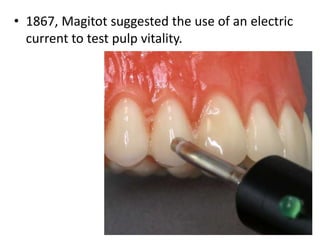
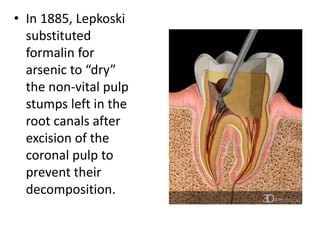
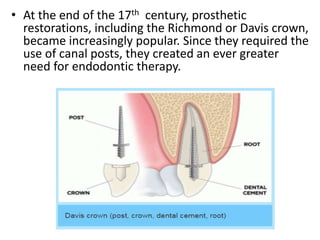
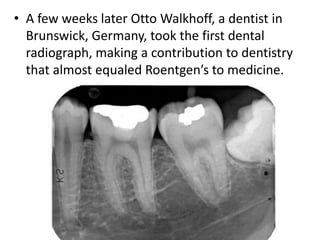
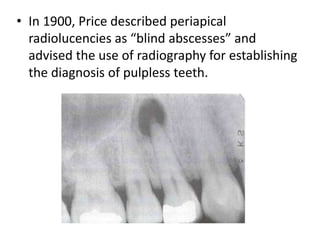
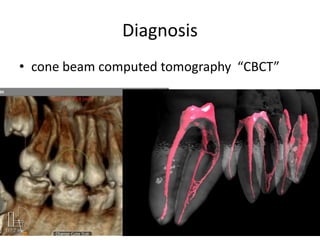
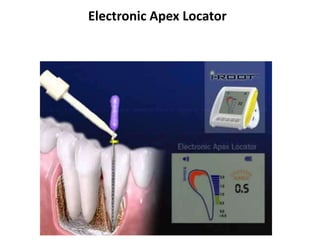
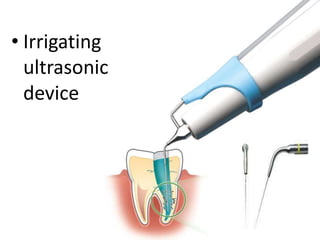
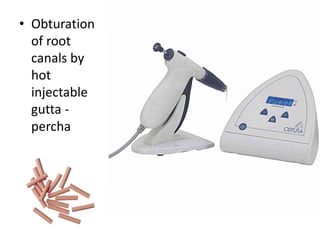
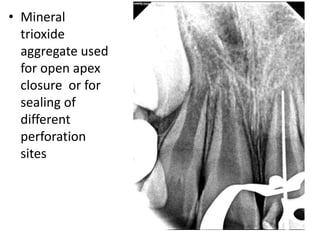
This document provides a history of endodontics from the 17th century to present day. It describes how endodontic procedures have evolved from early attempts to relieve pain by removing pulp tissue, to modern advancements like digital radiography, rotary instruments, ultrasonic irrigation and new filling materials like mineral trioxide aggregate. The document also discusses important figures who advanced the field through the introduction of gutta-percha, rubber dams, x-rays and the concept of aseptic technique. Overall it traces the progression of endodontic treatment and technology.