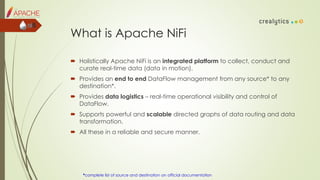
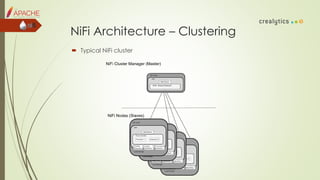
The document is an introduction to dataflow management using Apache NiFi, covering its history, features, architecture, and core components. It discusses how NiFi serves as an integrated platform for real-time data management and automation, highlighting common dataflow challenges and providing live demos and testing methodologies. The presentation aims to familiarize users with building dataflow processors, deploying dataflows, and future plans for NiFi enhancements.
















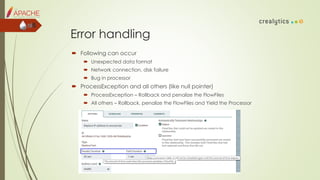
![ Add Maven dependency
Call static newTestRunner method of the TestRunners class
Call addControllerService method to add controller
Set properties by setProperty(ControllerService, PropertyDescriptor, String)
Enable services by enableControllerService(ControllerService)
Set processor property setProperty(PropertyDescriptor, String)
Override enqueue method for byte[], InputStream, or Path.
run(int); This will call methods with @OnScheduled annotation, Processor’s
onTrigger method, and then run the @OnUnscheduled and finally @OnStopped
methods.
Validate result by assertAllFlowFilesTransferred and assertTransferCount methods.
Access FlowFiles by calling getFlowFilesForRelationship() method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodataflowmanagementusingapachenifi-170302103009/85/Introduction-to-data-flow-management-using-apache-nifi-26-320.jpg)