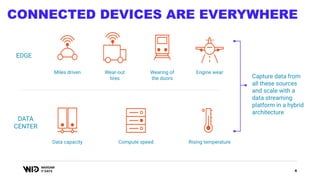
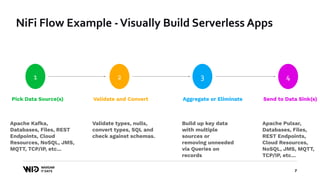
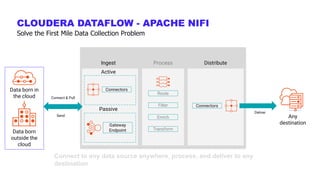
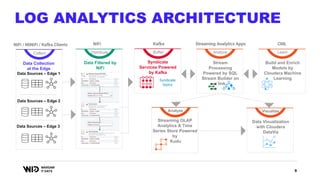
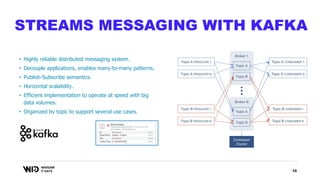
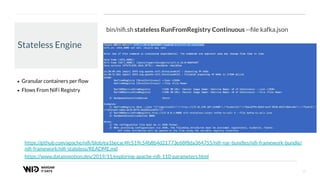
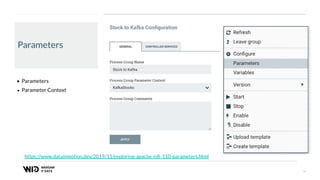
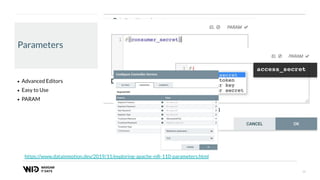
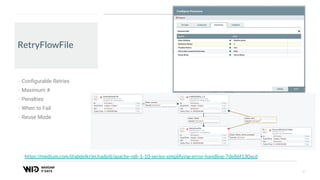
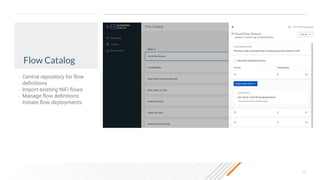
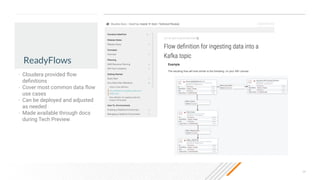
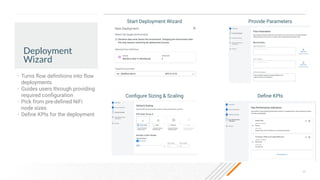
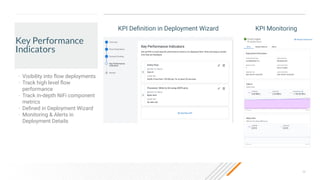
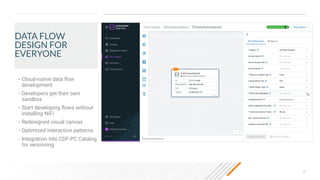
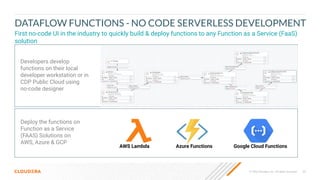
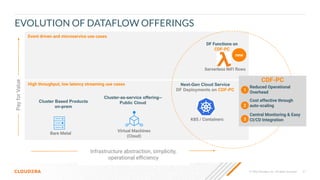
The document outlines a presentation on real-time data streaming technologies focusing on Apache NiFi, Kafka, and Flink, emphasizing their applications in data collection and processing across various sectors. It highlights key features such as clustering, concurrent processing, and cloud-native development while showcasing the competitive advantages of real-time analytics. Additionally, it discusses deployment strategies, data flow design, and the evolution of data flow offerings in modern environments.