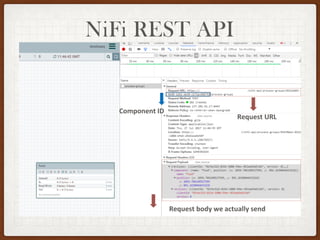
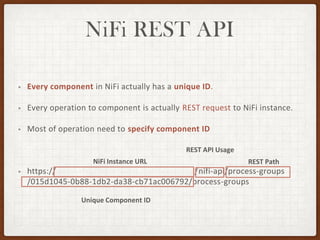
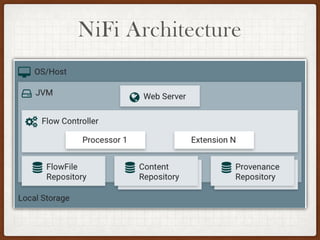
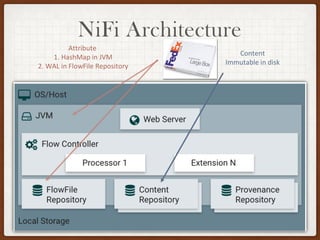
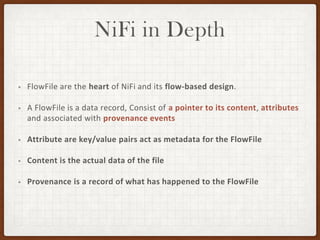
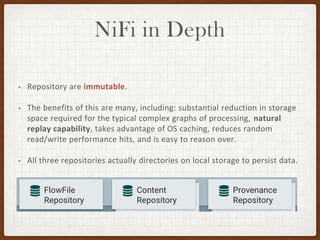
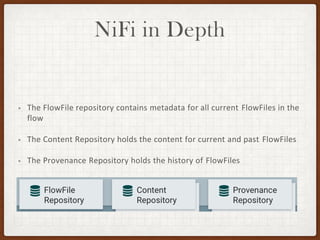
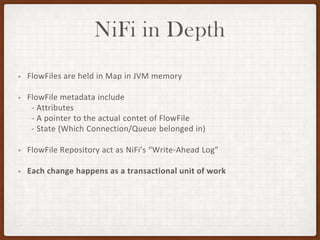
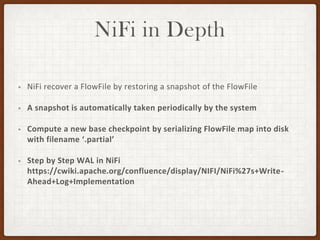
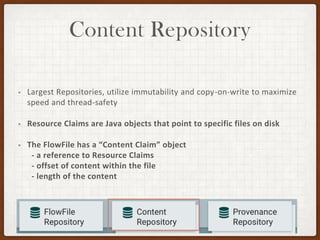
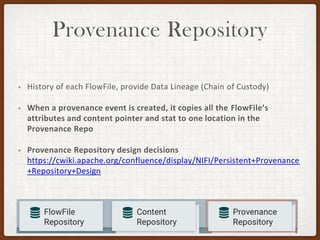
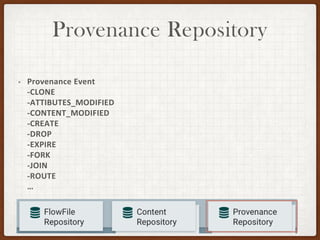
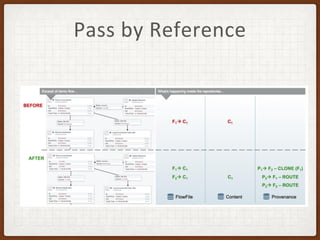
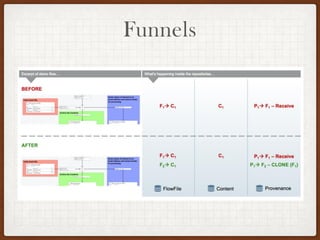
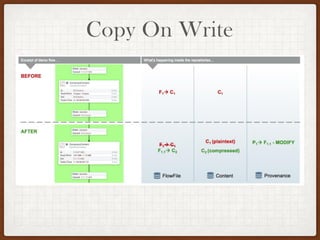
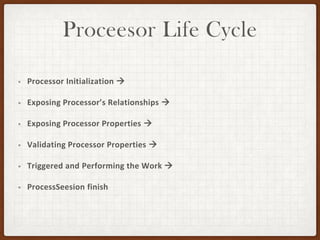
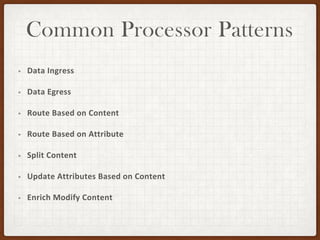
This document summarizes a presentation on developing with Apache NiFi. It discusses NiFi's REST API for programmatic access, the NiFi developer guide for building custom processors, and tips for contributing to the NiFi project through the GitHub pull request process. Key aspects of the NiFi architecture like its repositories and FlowFile lifecycle are also overviewed.