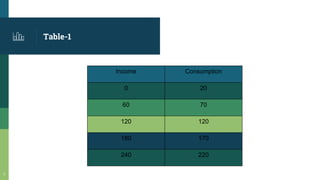
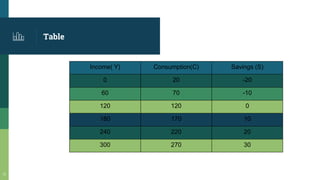
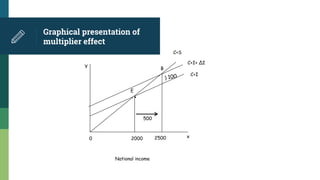
This document provides an introduction to consumption functions, the multiplier effect, and the accelerator principle in economics. It defines key terms like the consumption schedule, average propensity to consume, marginal propensity to consume, and the investment multiplier. It presents examples to illustrate how increases in consumption or investment can lead to multiplied increases in total national income through repeated rounds of spending. The size of the multiplier depends on the marginal propensity to consume. The accelerator principle is also explained as how increased consumption demand can lead to increased investment in capital goods.