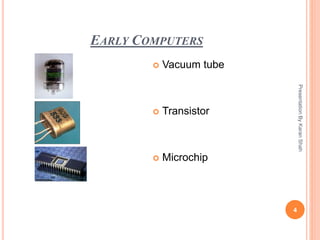
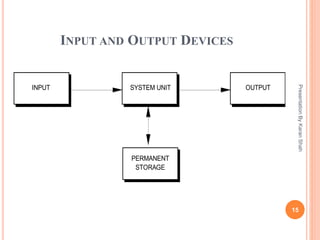
Computers are digital devices that can process information. Early computing devices included the abacus and Pascal's mechanical calculator. The first modern computers used vacuum tubes, then transistors were developed in the 1940s-50s leading to integrated circuits and microchips. Personal computers emerged in the 1970s-80s with the IBM PC and Apple Macintosh. Computers have hardware components like processors, memory and storage as well as software programs that perform tasks. Operating systems control the hardware and allow use of application software. Common operating systems include Windows, MacOS, Linux and mobile OSs. Computers provide benefits like fast processing, data storage, and entertainment.