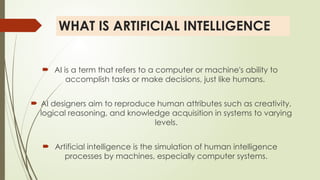
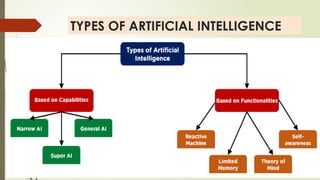
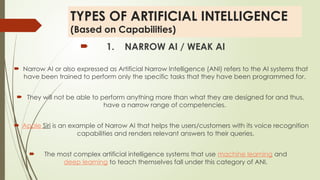
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), defining it as the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, and categorizing it into three main types based on capabilities: narrow AI, general AI, and super AI. It explores various sub-disciplines of AI, including machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing, highlighting their applications across different industries like healthcare, finance, and education. Additionally, the document discusses the benefits and risks associated with AI, including job displacement, loss of privacy, and ethical concerns.