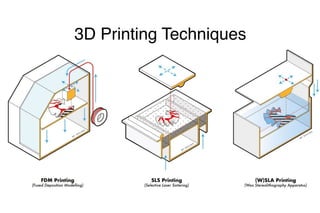
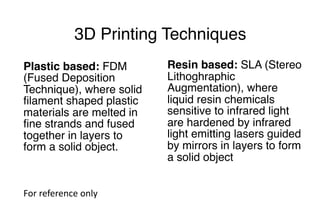
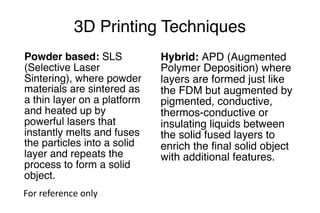
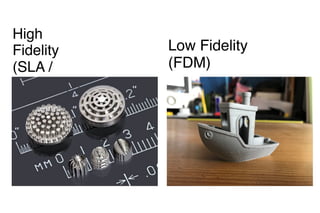
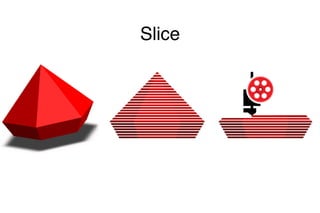
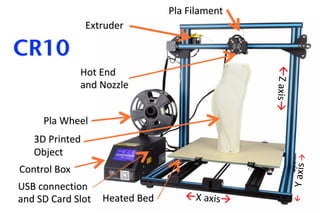
The document discusses 3D printing techniques such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and describes the 3D printing process which involves designing a 3D model, slicing it to generate G-code instructions, and printing the model using the G-code sent to a 3D printer. It also outlines some common applications of 3D printing such as producing low-fidelity prototypes and models or high-fidelity industrial parts and medical devices.