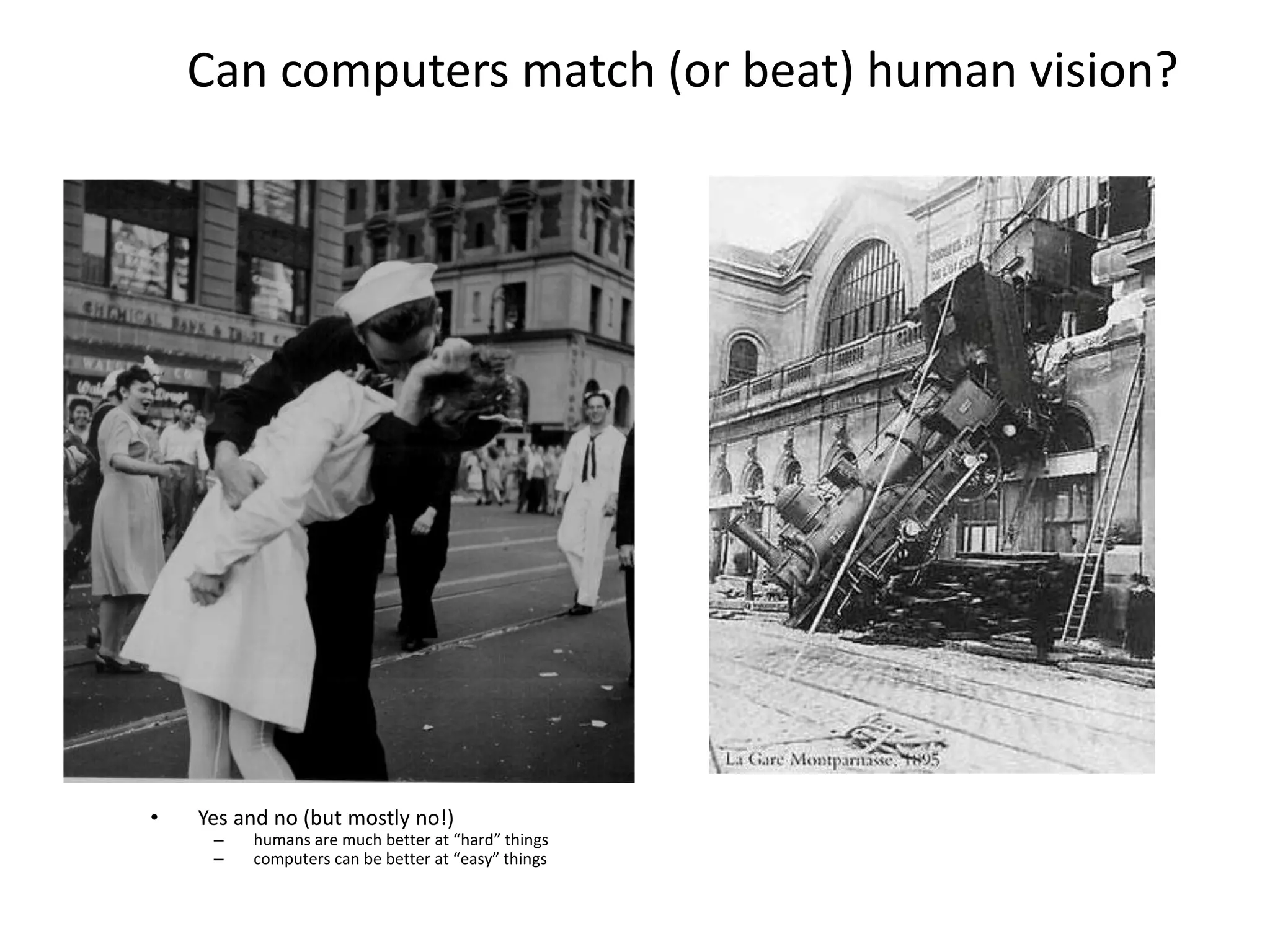
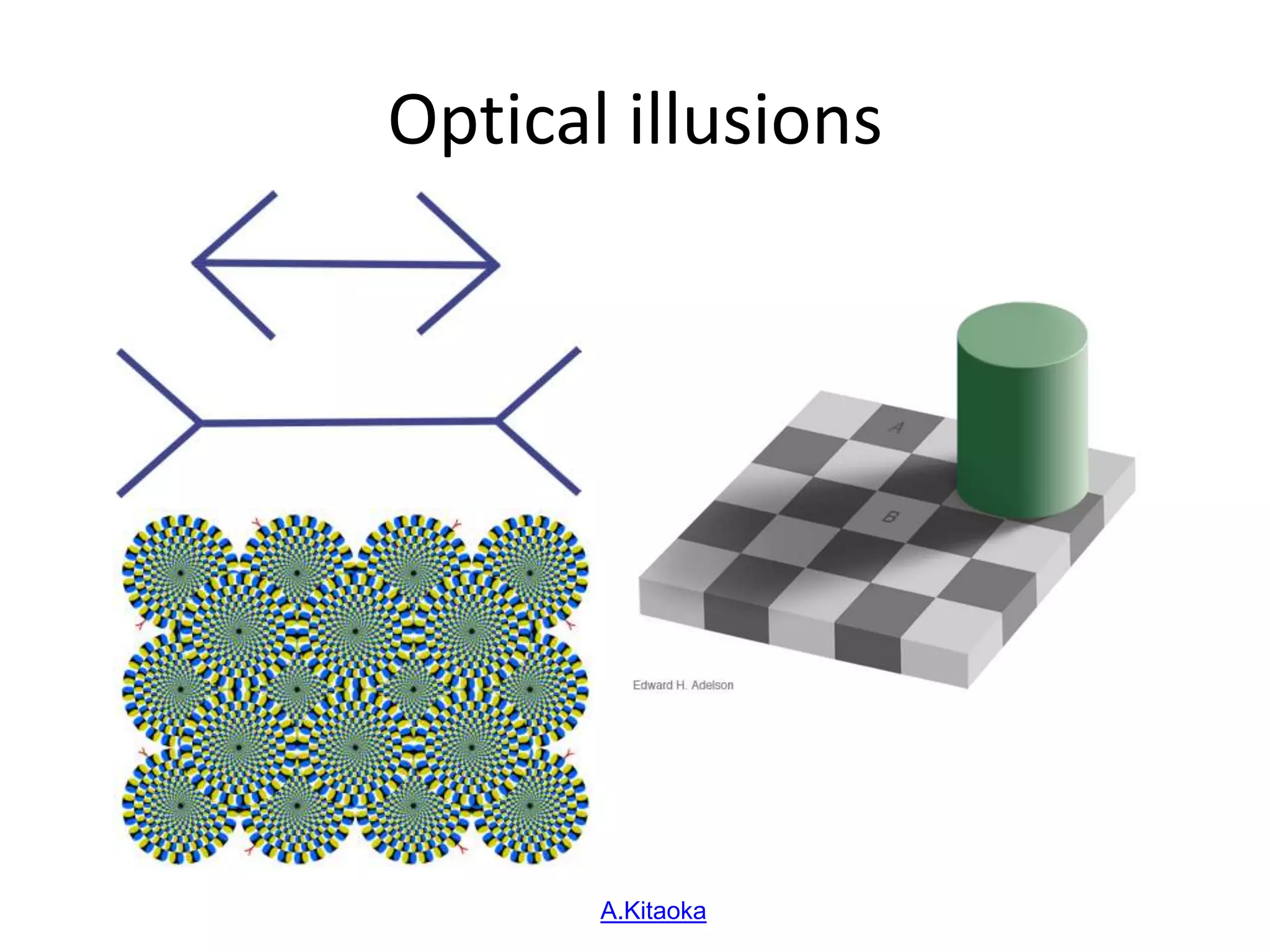
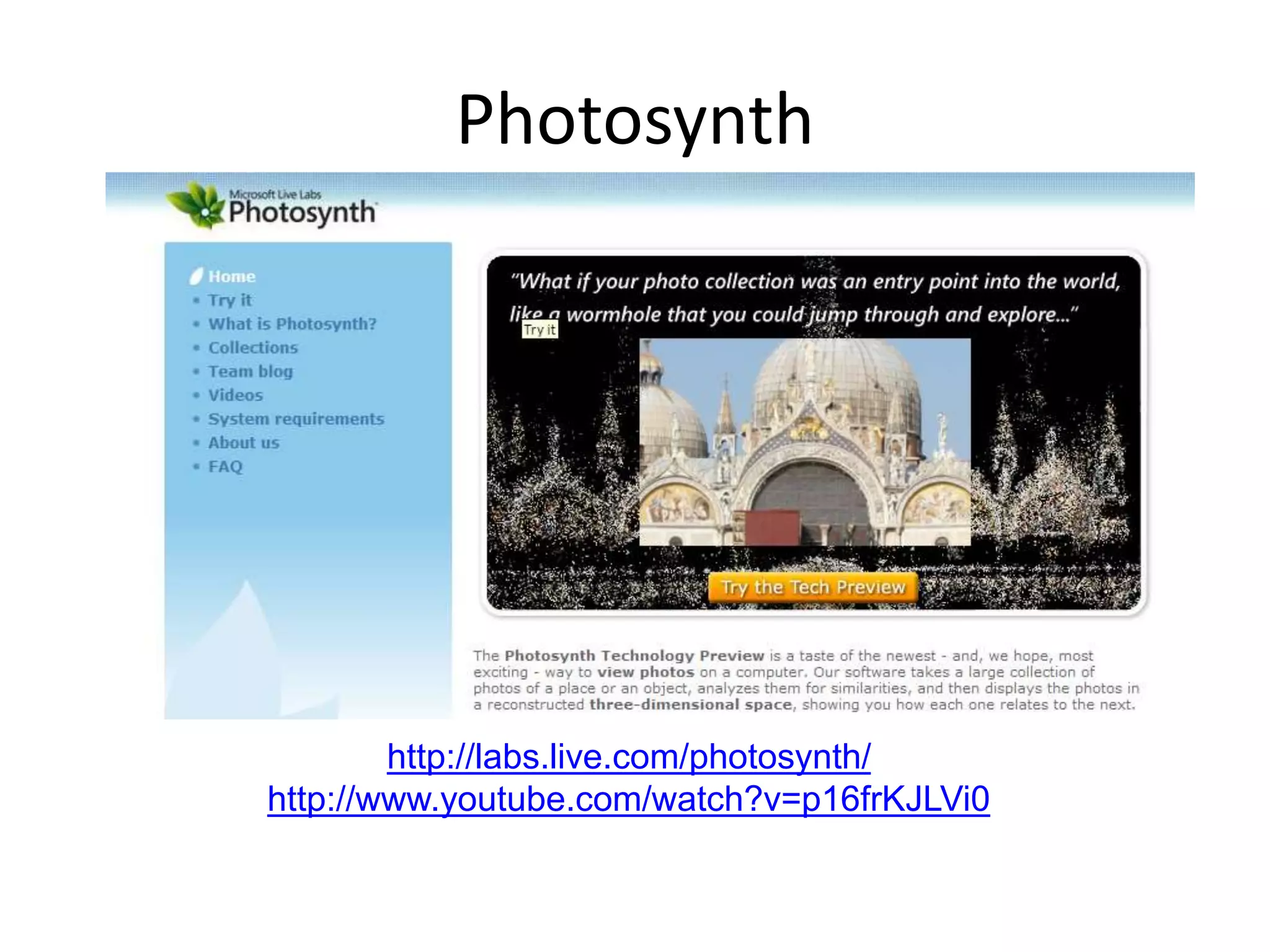
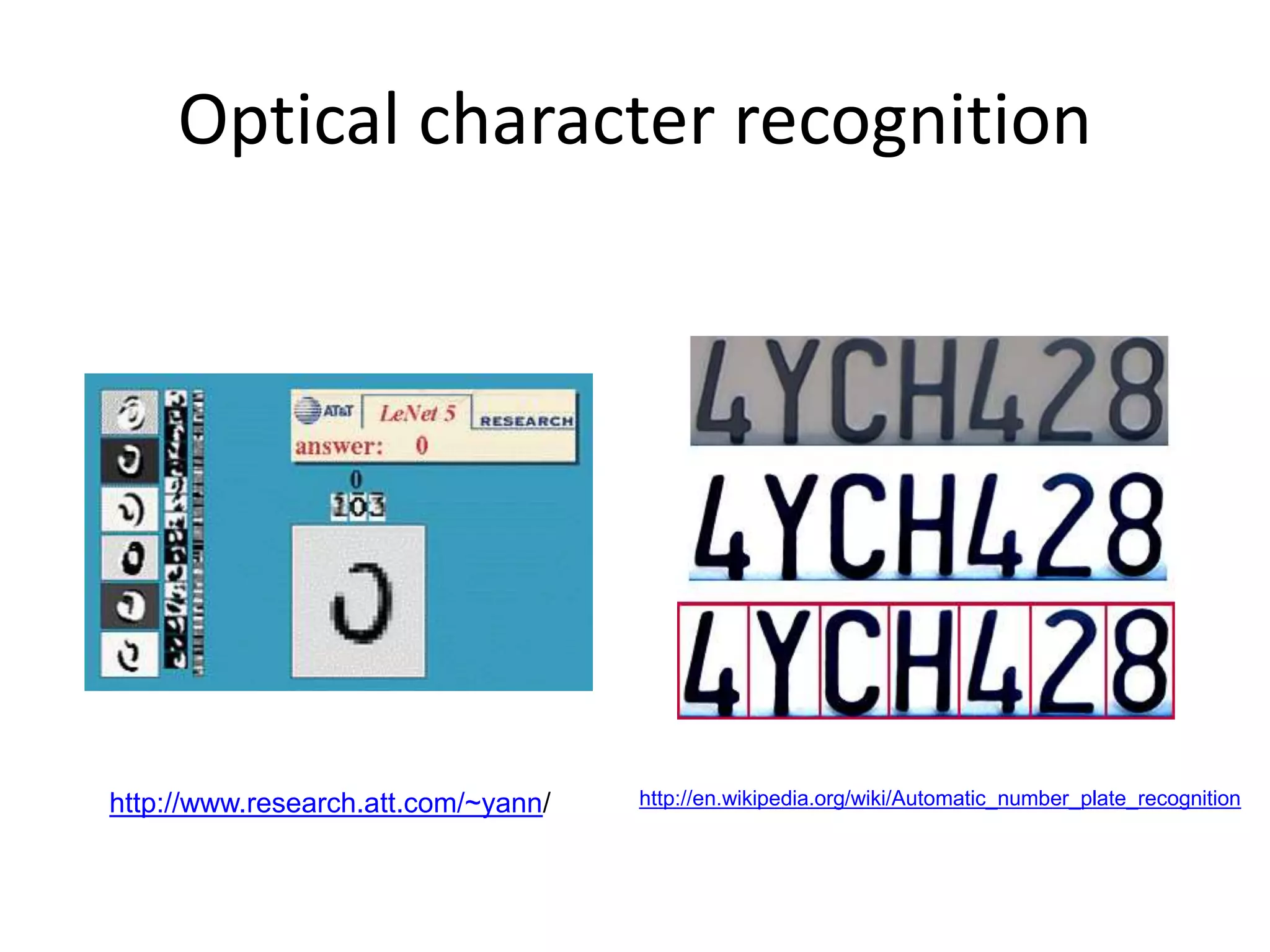
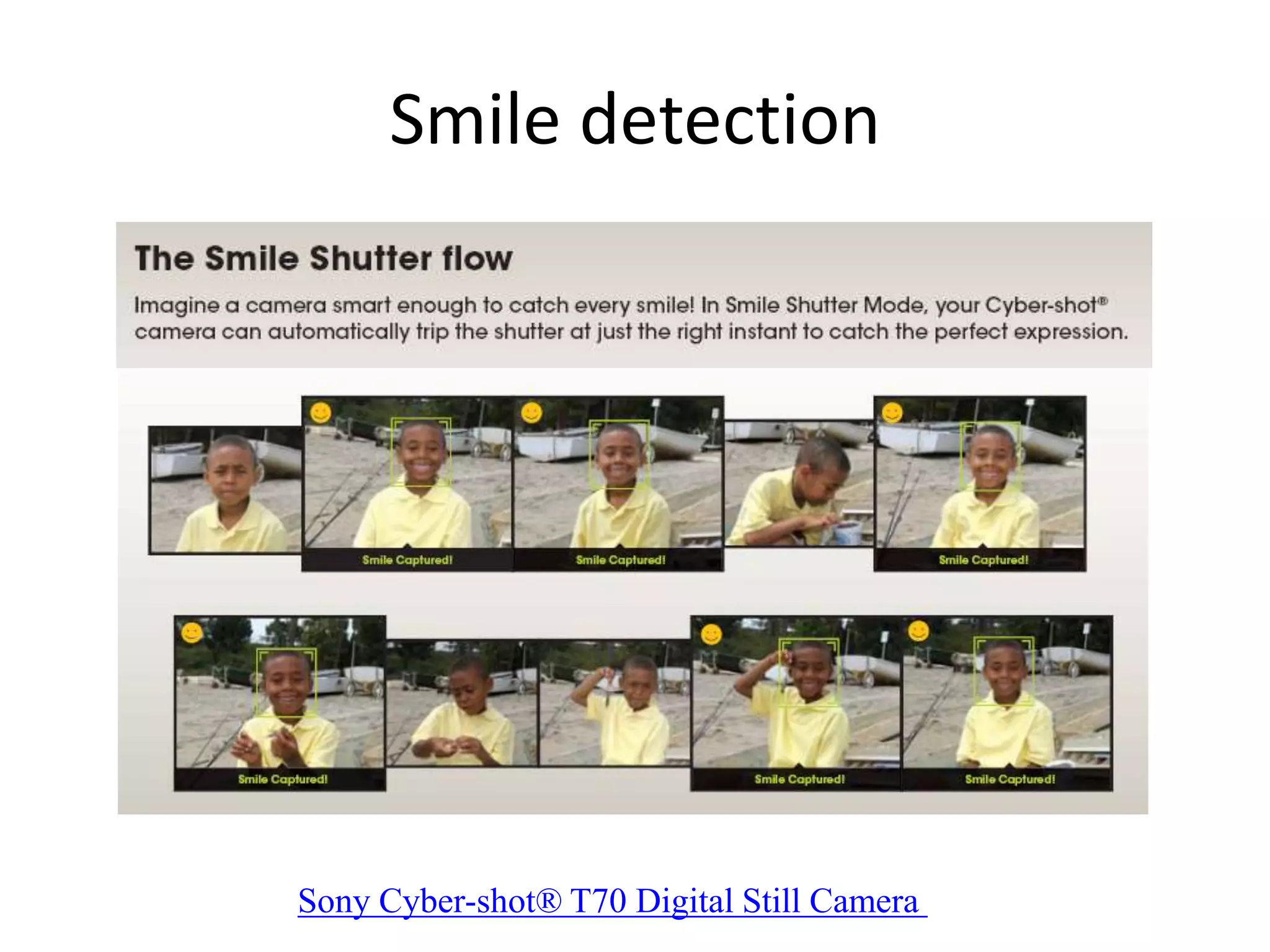
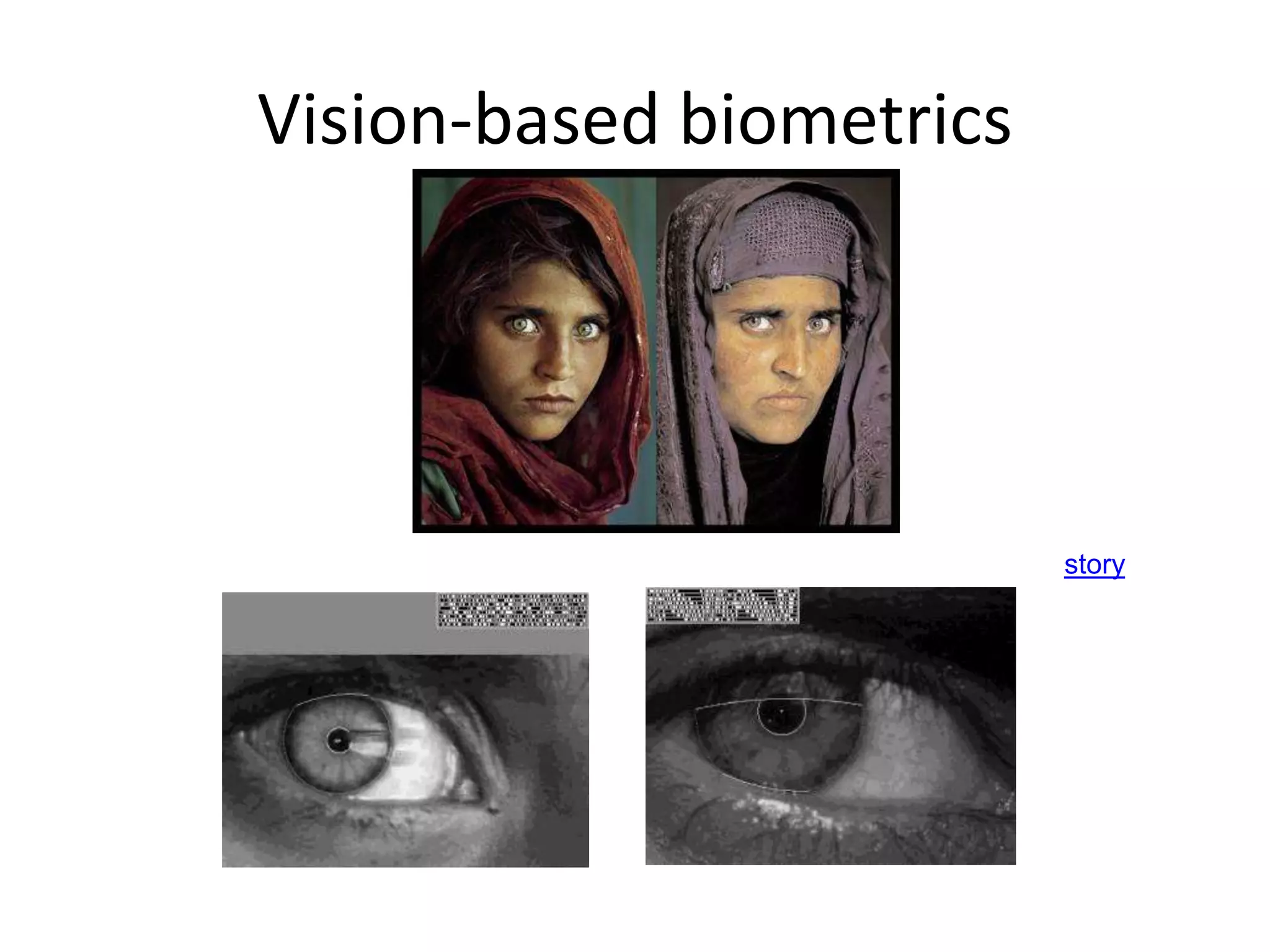
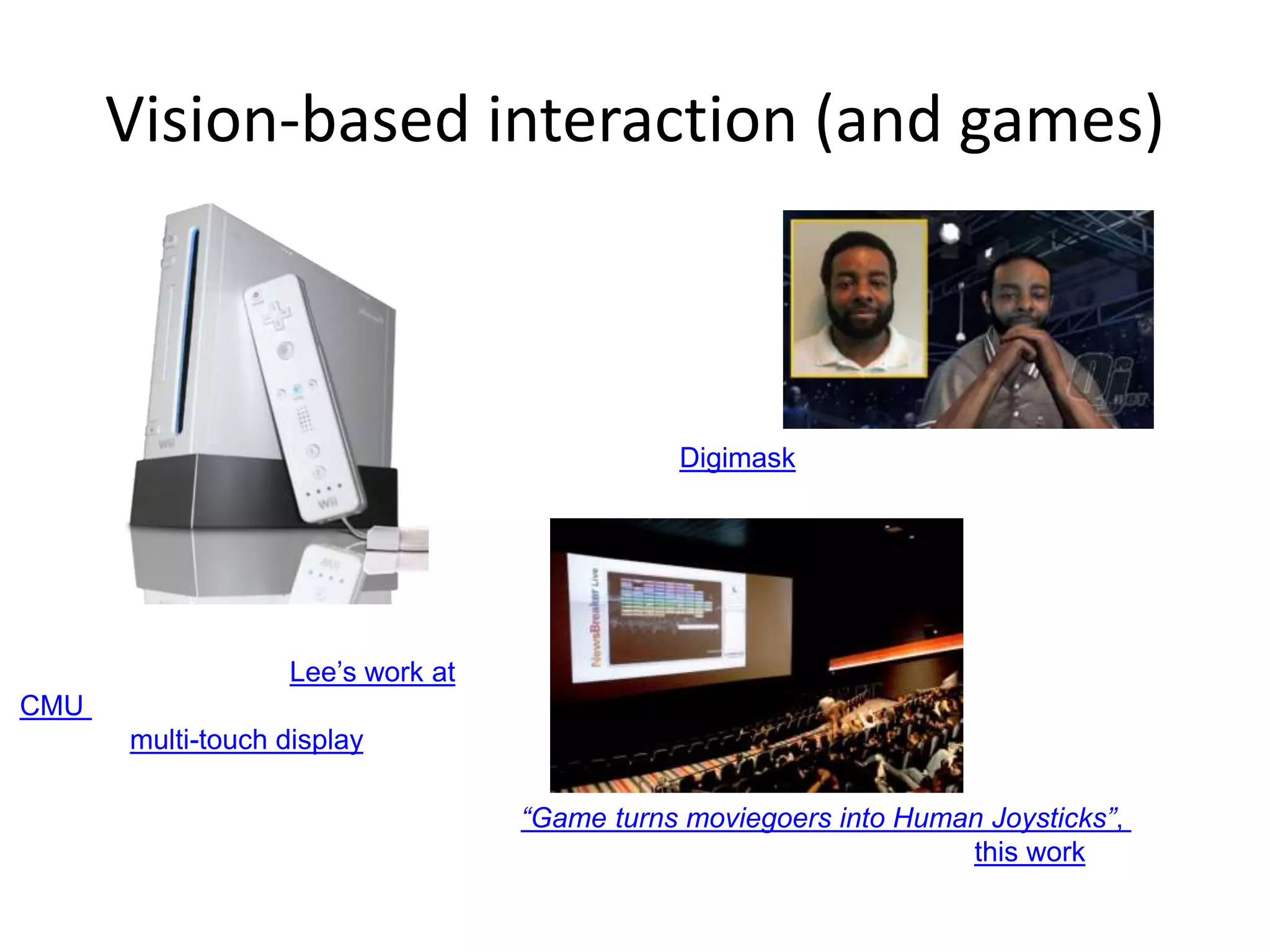
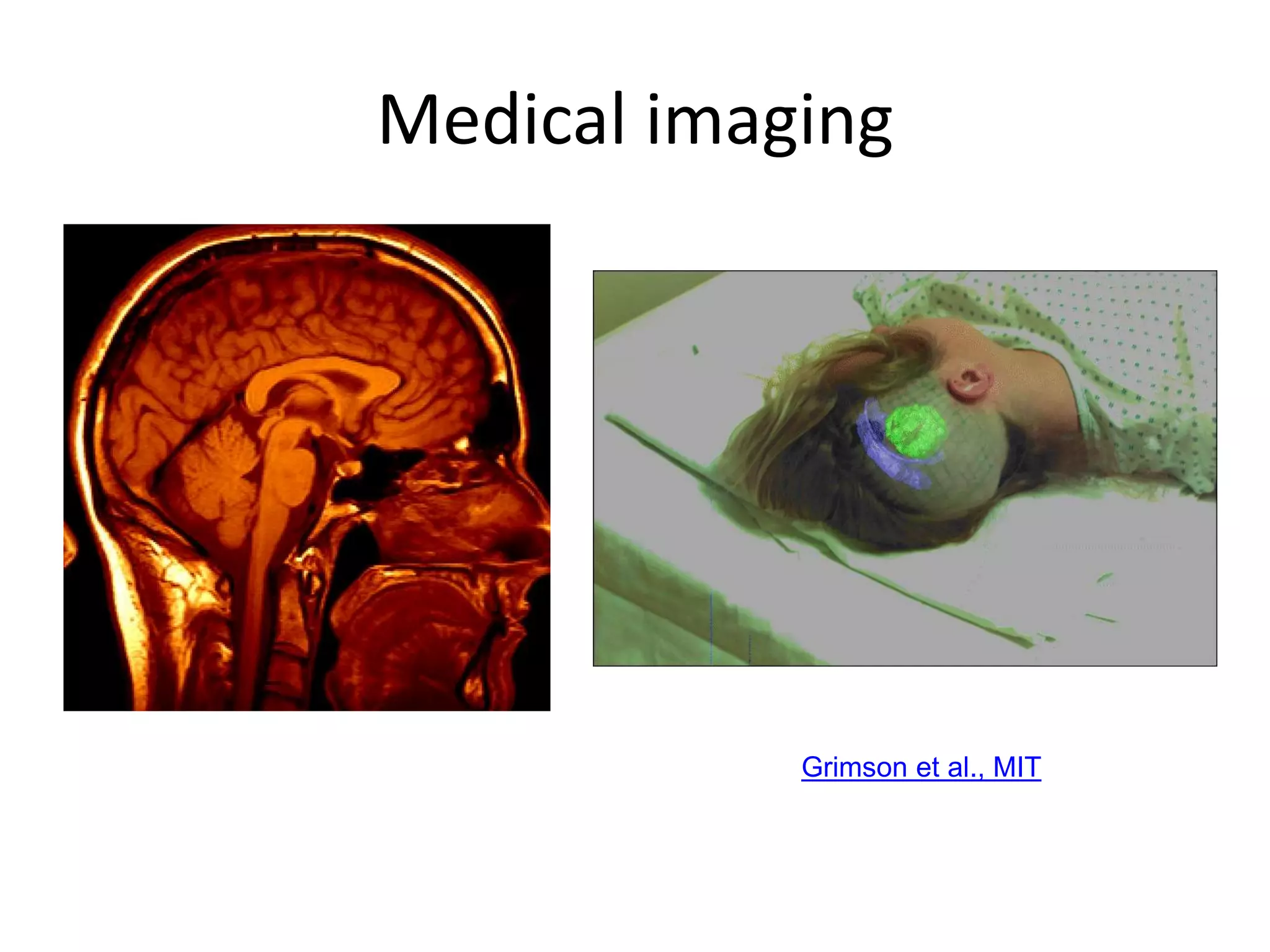
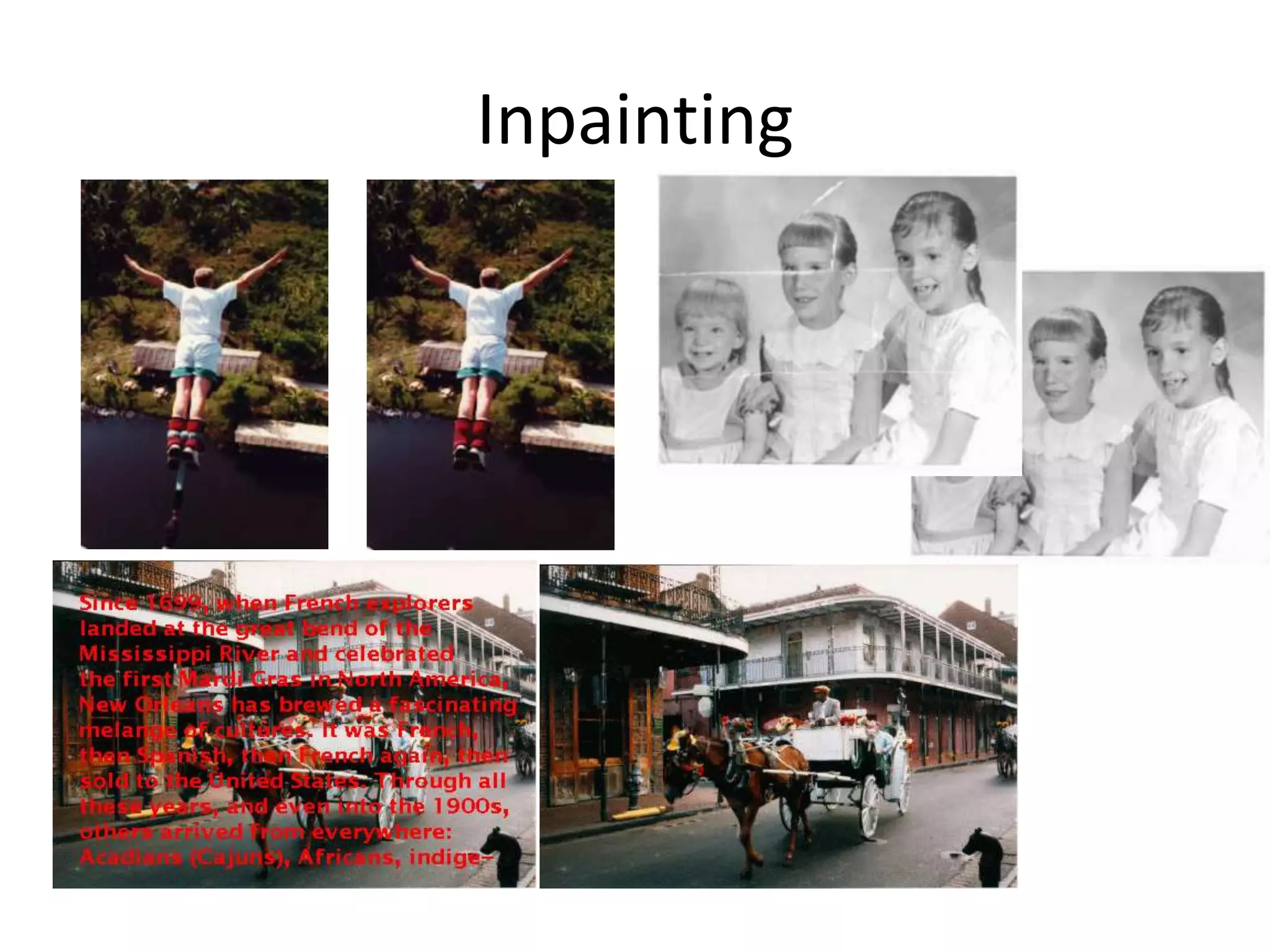
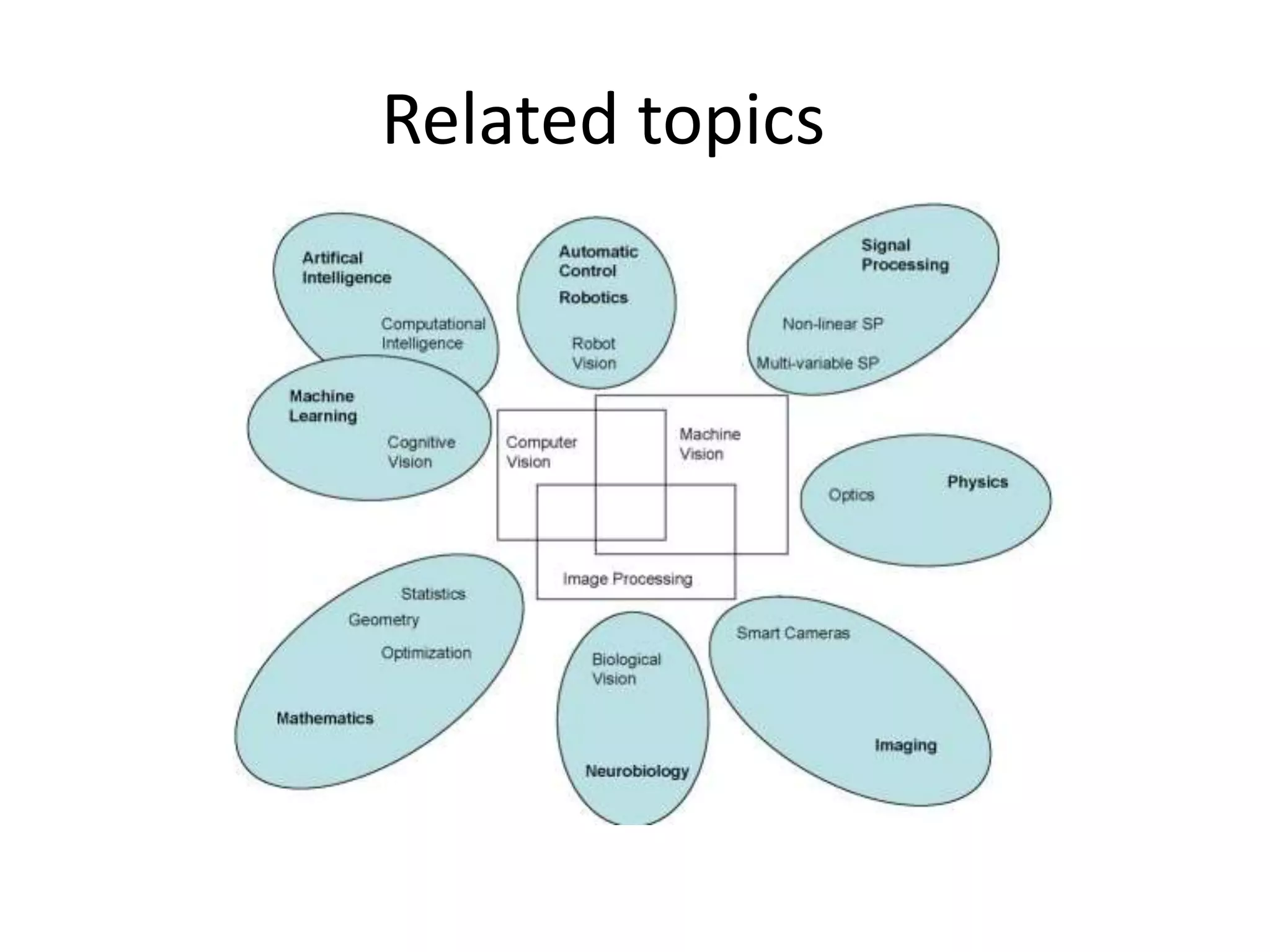
Computer vision aims to program computers to interpret and understand images in the way humans do. While humans are better at complex visual tasks, computers excel at simpler problems. Computer vision is challenging due to issues like noise, variation, and its inverse and ill-posed nature. Examples of computer vision applications discussed include image search, facial recognition, medical imaging, robotics, and self-driving cars. The field involves algorithms for early vision tasks like segmentation and recognition, as well as hardware like cameras. It is an active area of research with many emerging applications over the next 5 years.