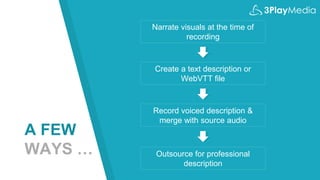
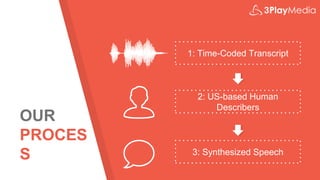
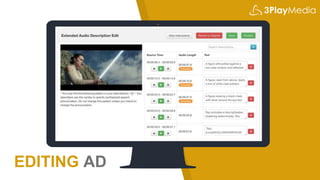
The webinar discusses audio description, its creation, benefits, and legal requirements, highlighting its importance for accessibility, particularly for the visually impaired. It also outlines various publishing methods and technologies, including synthesized speech, and presents 3Play Media's role in providing these services. Legal cases emphasize the necessity of compliance with accessibility laws related to audio description in media.