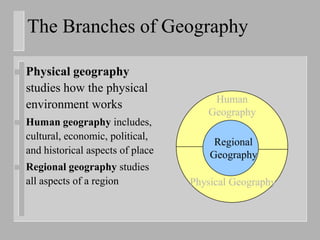
The document provides an introduction to a physical geography course, explaining what physical geography is, the different branches of geography, and how physical geography examines human impacts on the environment and natural hazards. It gives an overview of the course topics, assignments, and resources for students to use for studying.