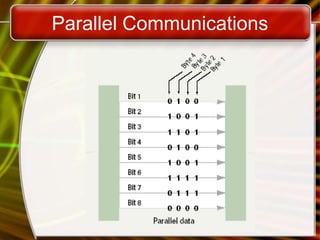
This document discusses modern CPUs and how they can be extended. It covers CPU architecture, manufacturers like Intel and AMD, comparing processor features, and ports/buses that expand processing power. These include serial/parallel ports, SCSI, USB, FireWire, expansion slots, and PC Cards. Plug and play allows automatic installation of new hardware.