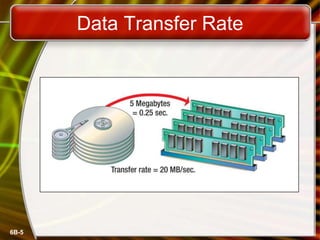
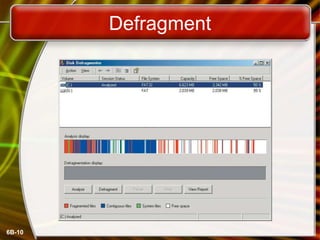
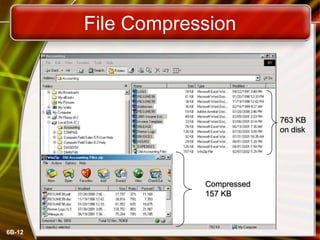
This document discusses measuring and improving drive performance. It describes average access time and data transfer rates for different types of drives like hard drives, CDs, and floppies. It recommends optimizing drive performance through disk maintenance like cleaning unnecessary files, scanning for errors, defragmenting disks, and compressing files. The document also outlines different drive interface standards including EIDE, SCSI, USB, and FireWire and how they determine transfer rates and number of connectable devices.