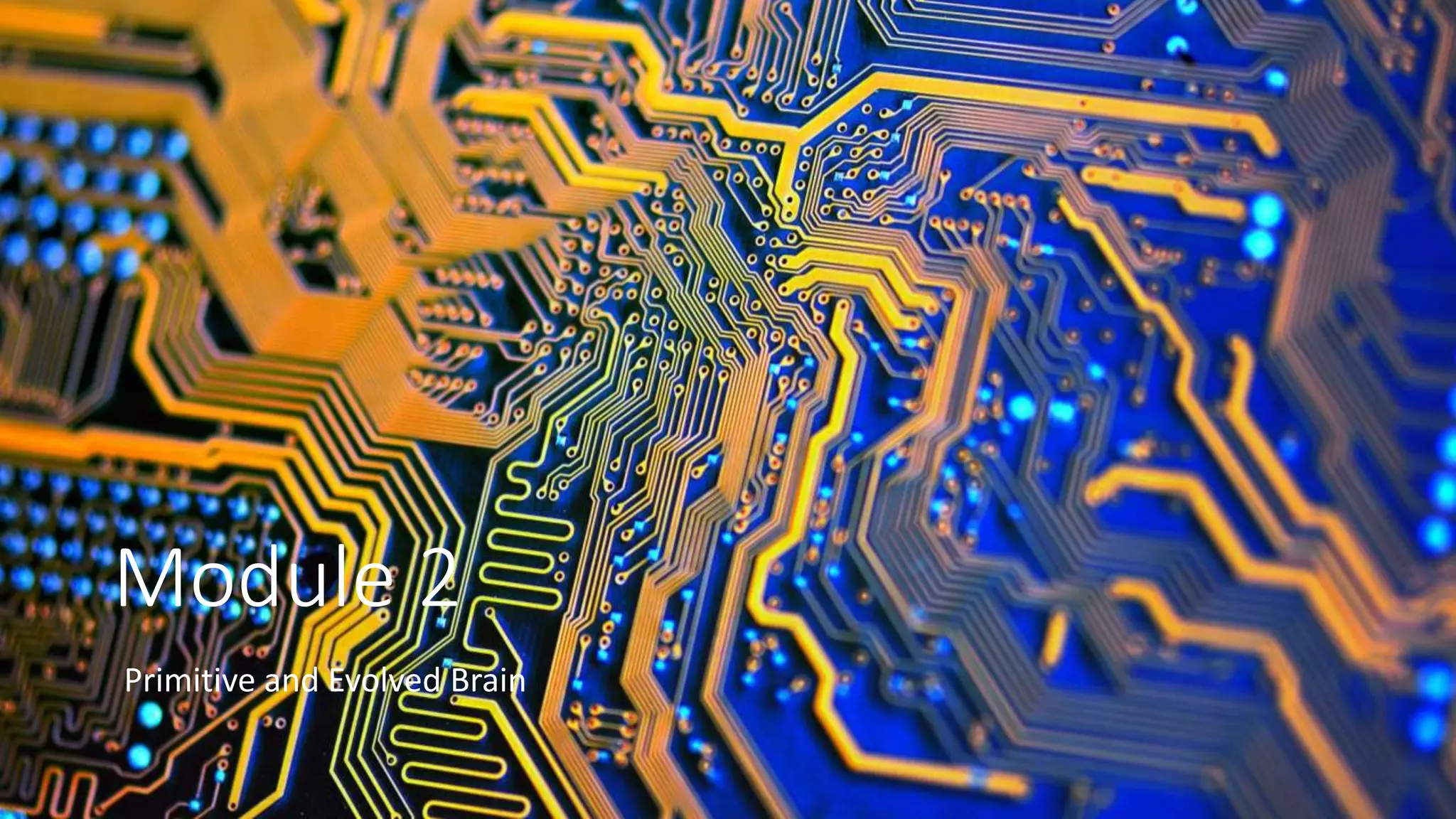
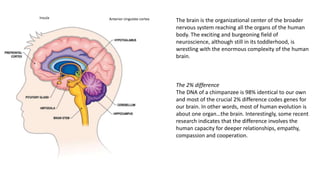
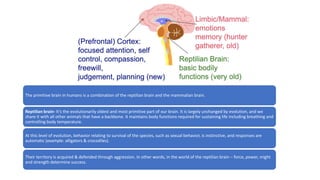
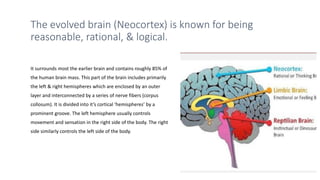
The document summarizes information about the primitive, mammalian, and evolved parts of the human brain. It discusses how the primitive brain, including the reptilian brain, controls basic survival functions like breathing and temperature regulation. The mammalian brain allows for more complex functions and basic emotions. The evolved neocortex, which makes up 85% of the human brain, is responsible for rational and logical thought. It also discusses how early parts of the brain can still influence behaviors and emotions like anger when activated by stress, and how mindfulness can strengthen neuronal connections in the evolved brain.