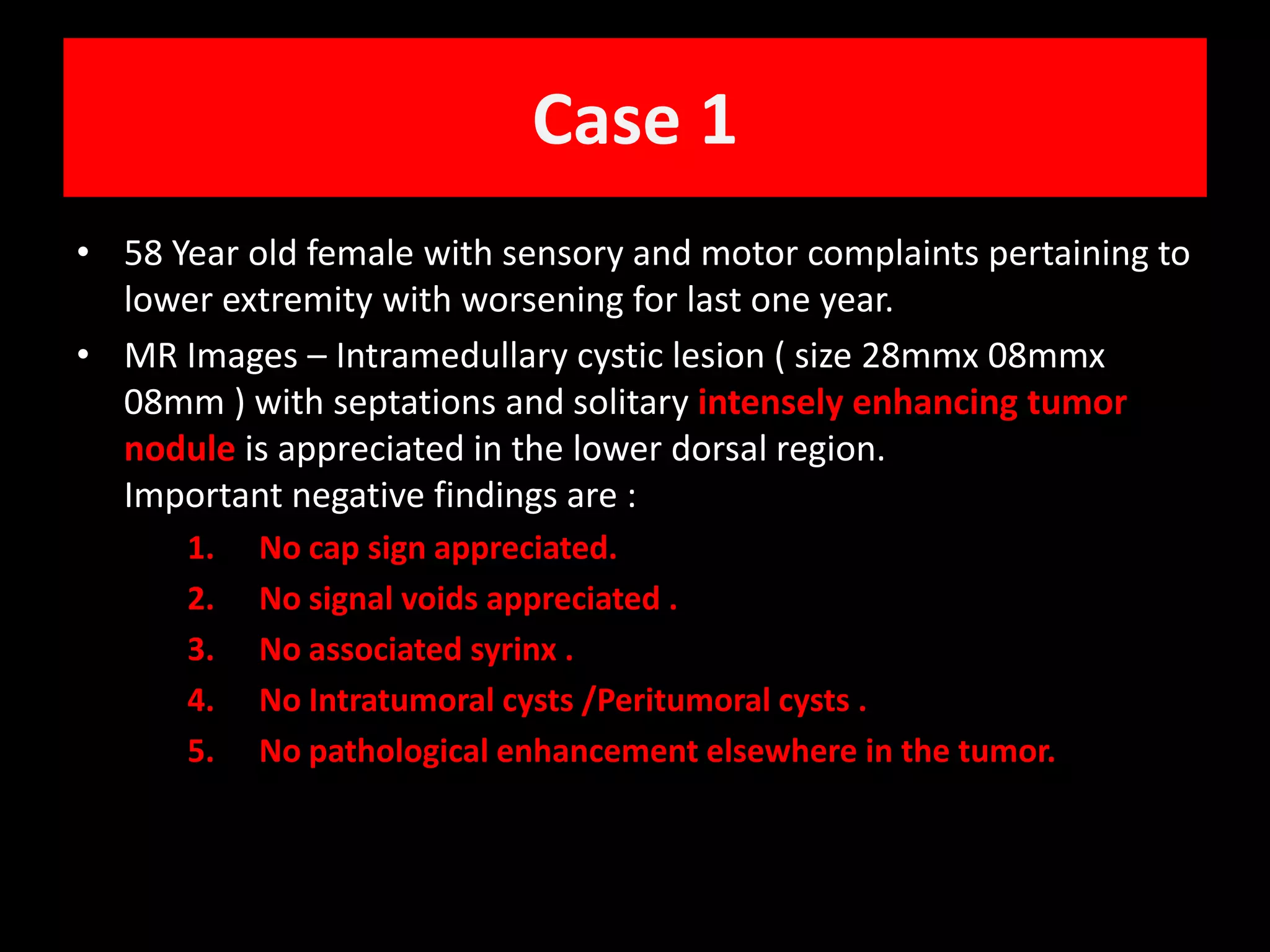
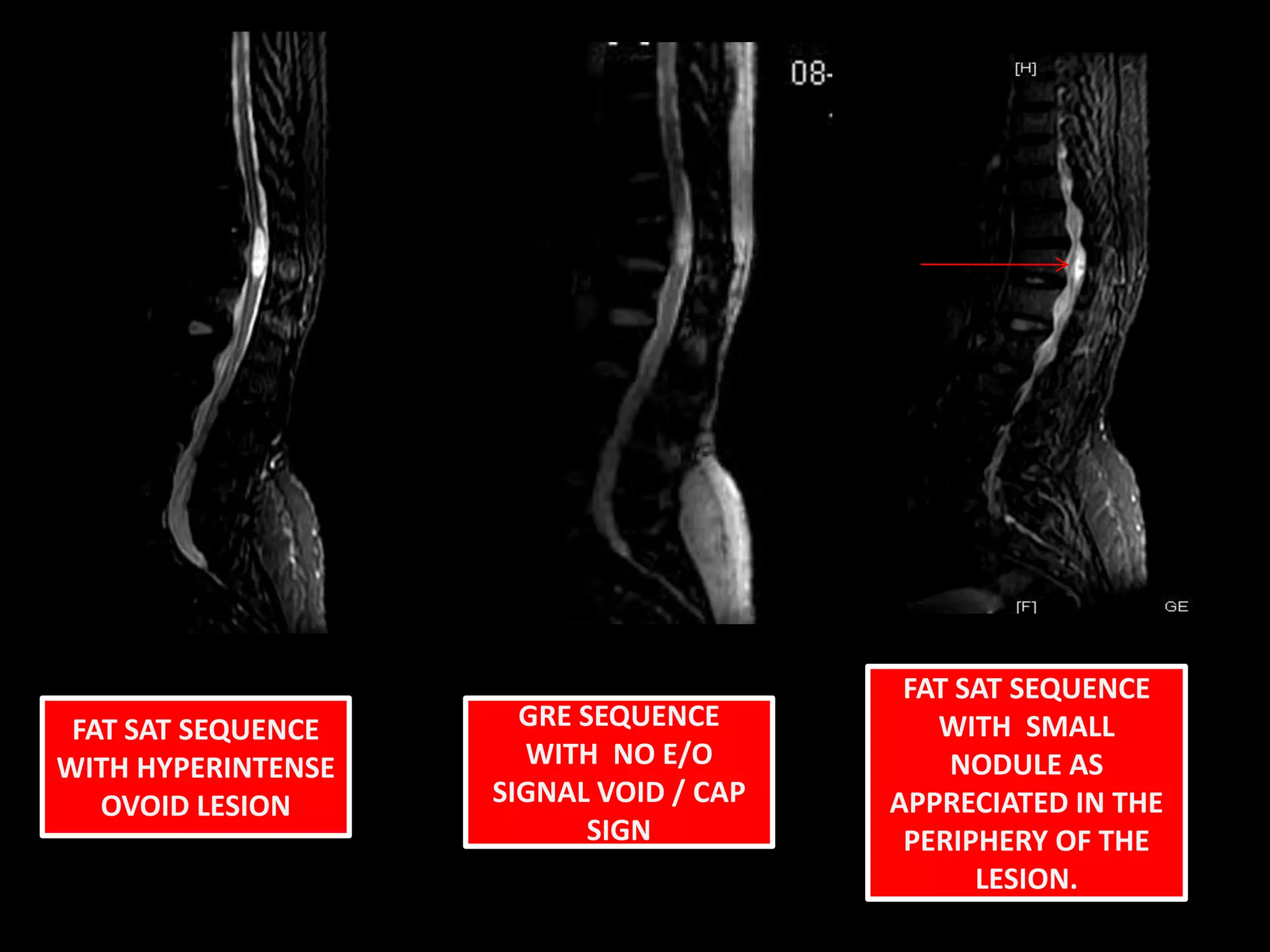
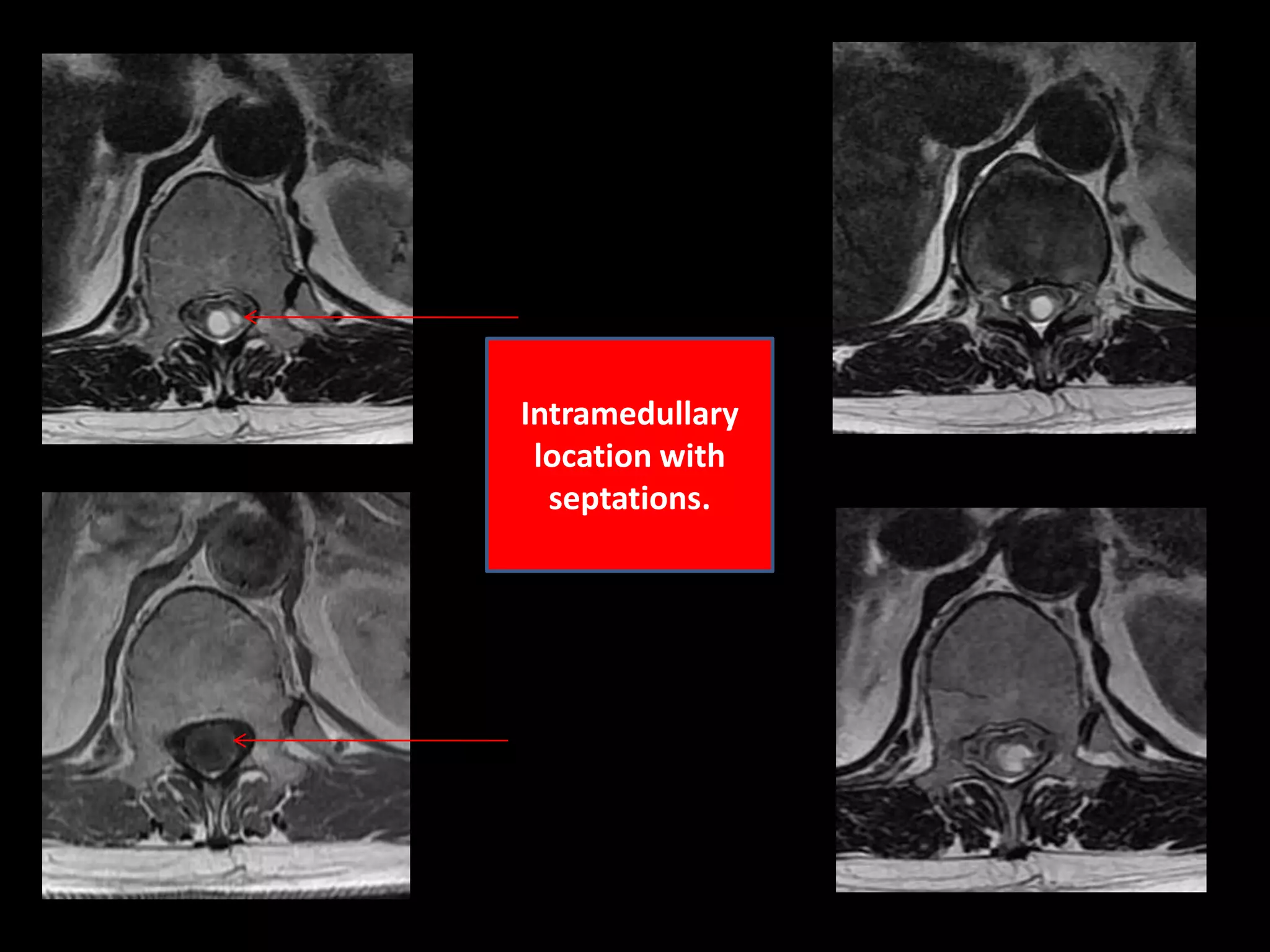
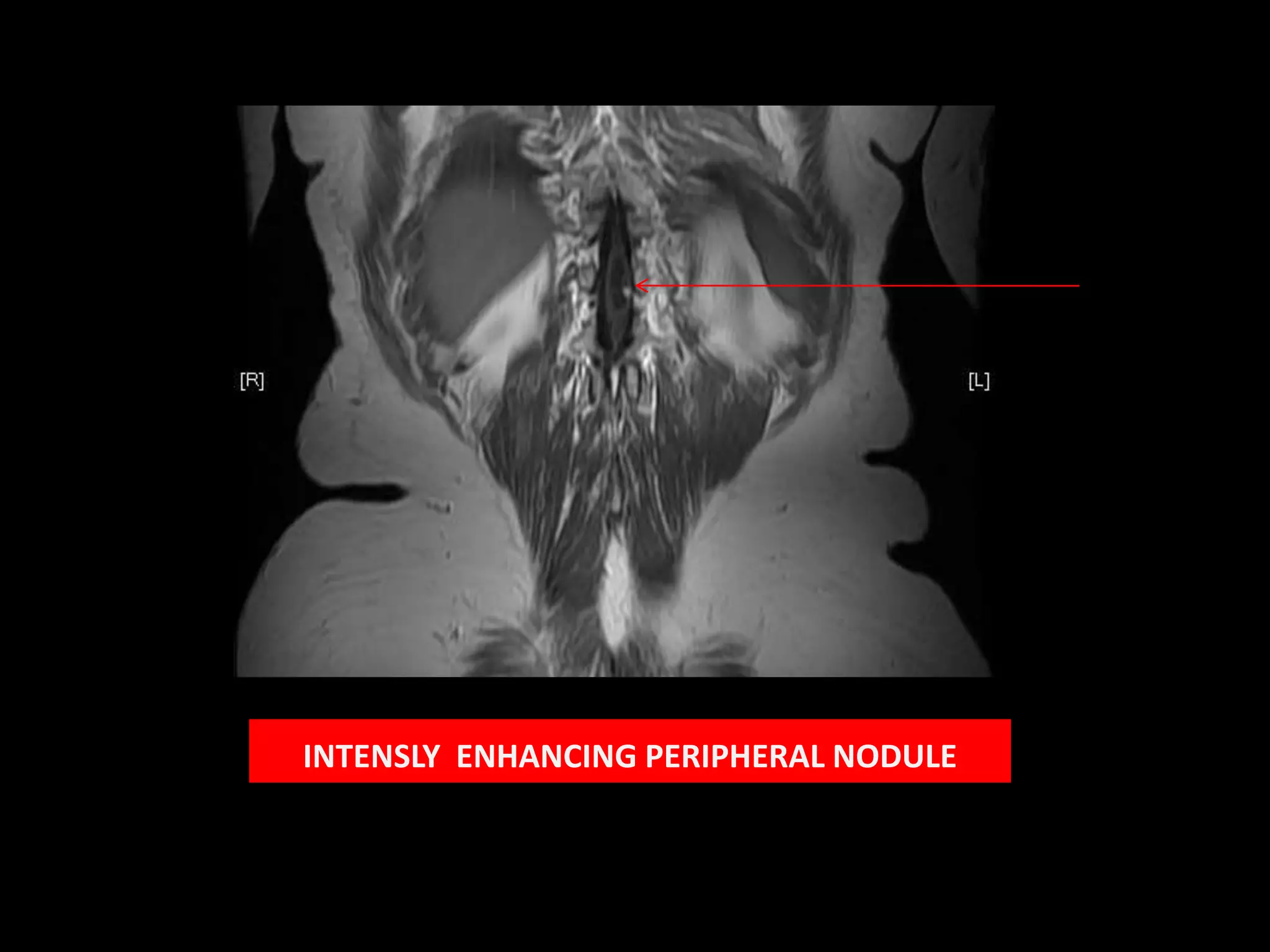
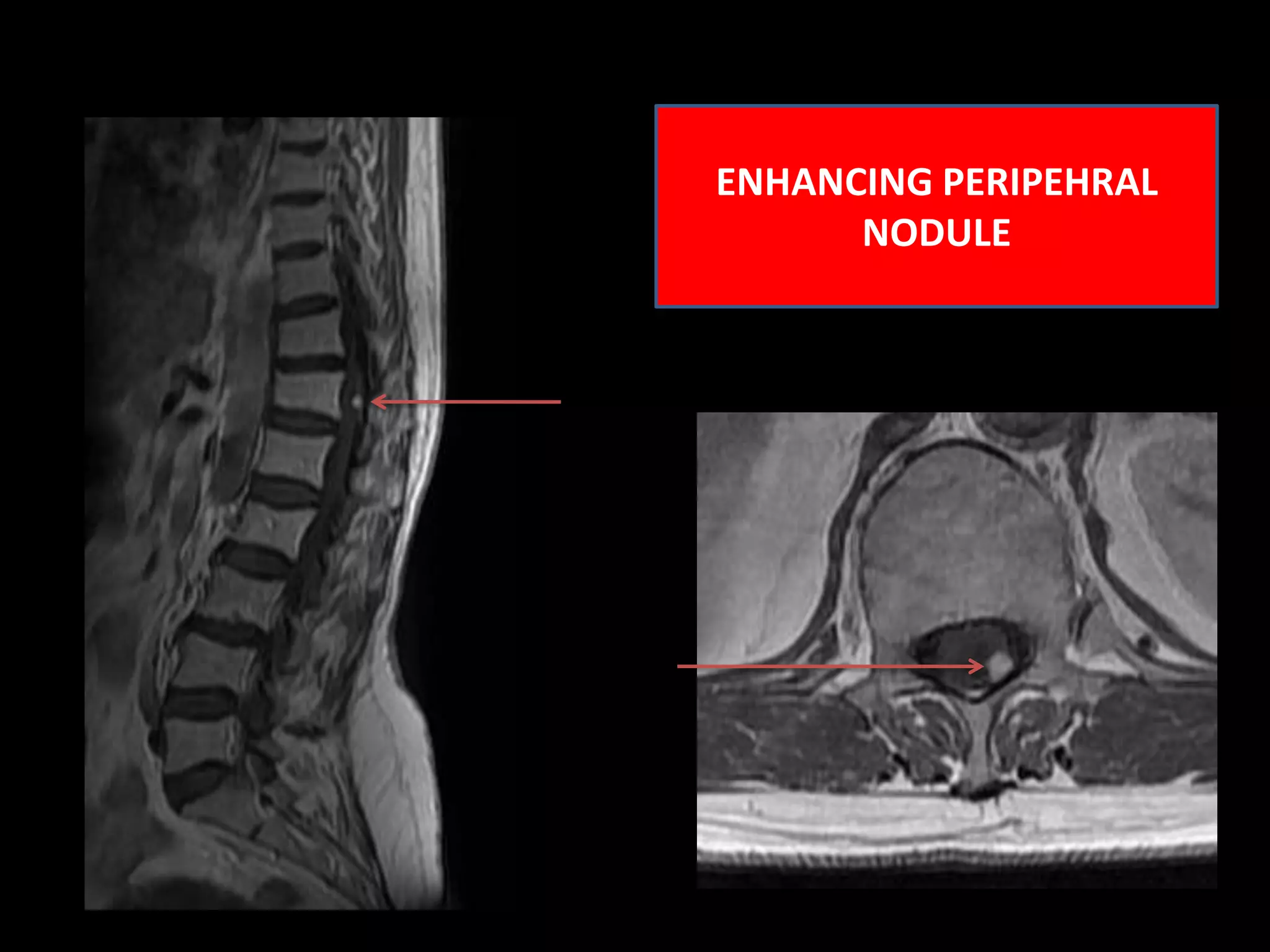
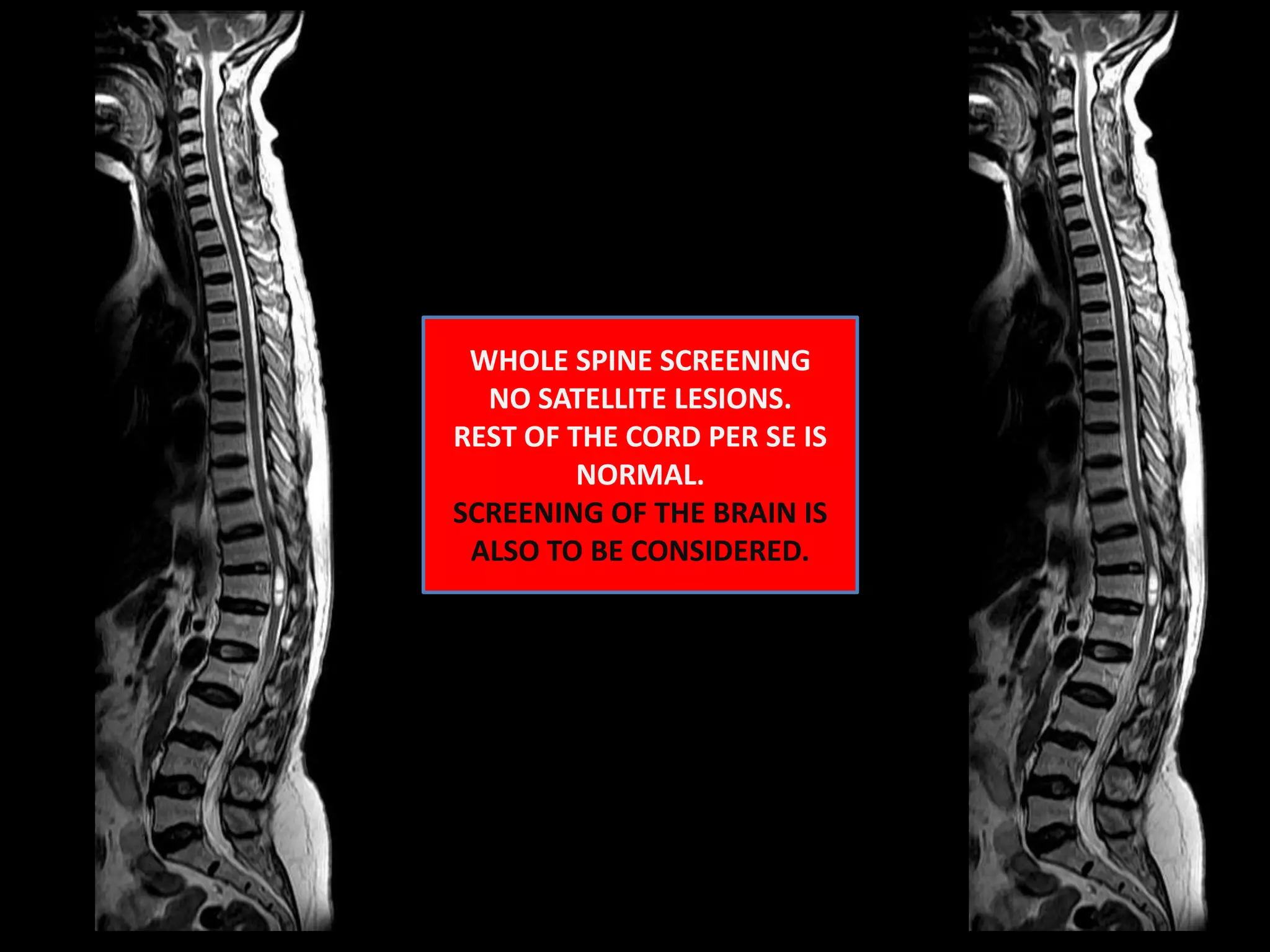
1) A 58-year-old female presented with lower extremity sensory and motor symptoms. MRI showed a 28mm x 8mm x 8mm cystic intramedullary lesion in the lower dorsal spine with septations and a solitary intensely enhancing nodule.
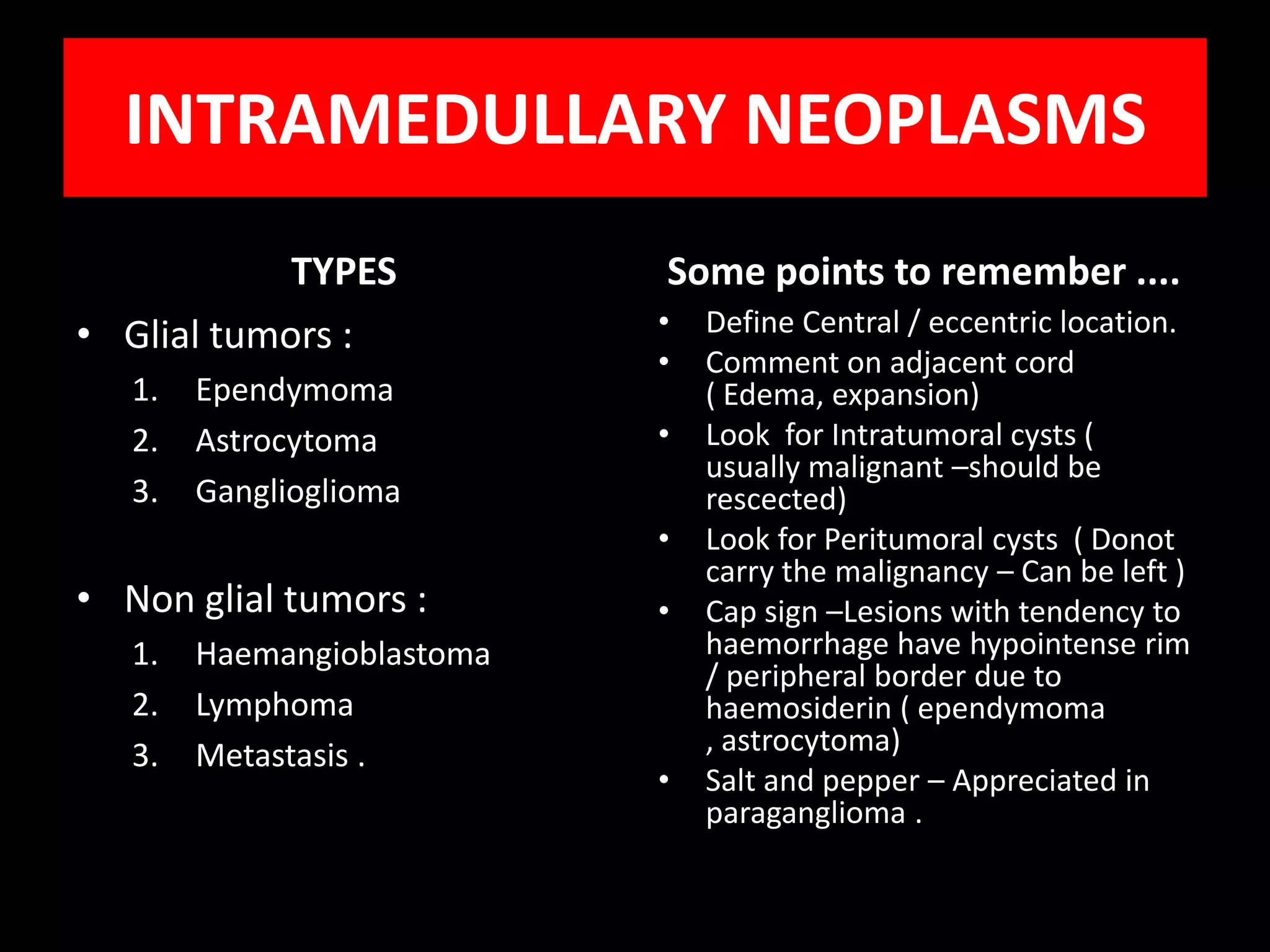
2) Haemangioblastomas are highly vascular tumors that can present as intramedullary or intradural/extradural lesions in the dorsal spine. They often enhance intensely and contain signal voids.
3) The enhancing peripheral nodule and lack of other findings make haemangioblastoma the most likely diagnosis in this case.