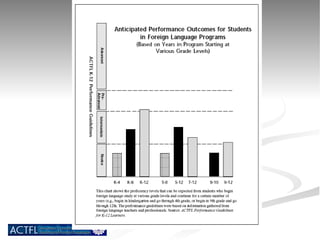
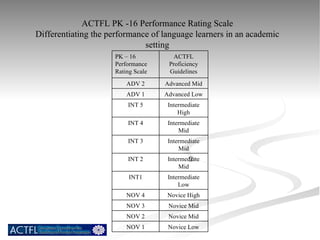
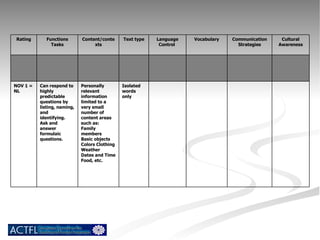
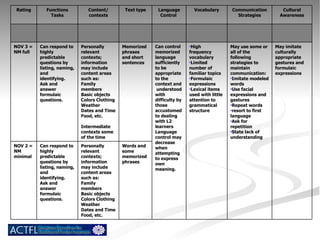
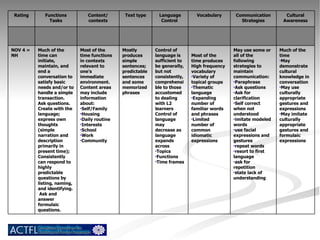
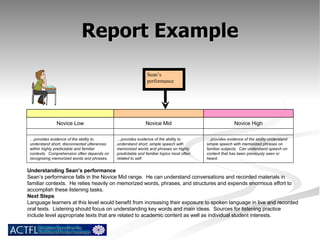
The document summarizes benchmarks for student progress in learning Chinese as a foreign language. It outlines the major proficiency levels from novice to advanced based on the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages guidelines. It then provides examples of tasks and ratings associated with different proficiency levels to assess students' communication skills in interpreting, presenting, and interacting in the target language.