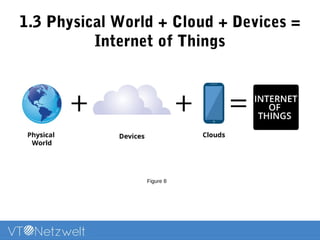
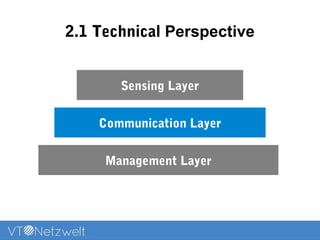
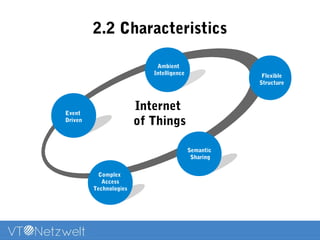
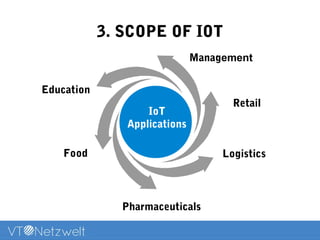
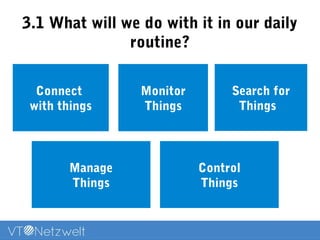
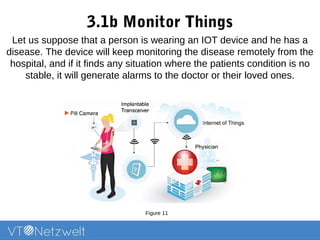
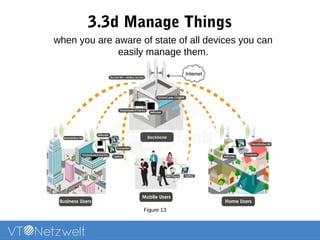
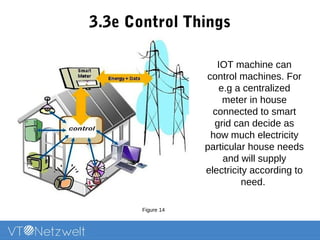
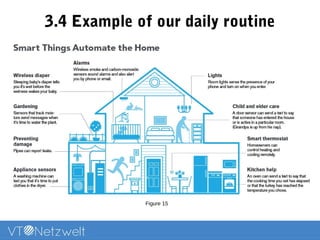
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of uniquely identifiable objects that can transfer data without human intervention, evolving from a blend of wireless technologies and the internet. It encompasses various applications and allows for connectivity, monitoring, management, and control of everyday items, while facing challenges related to security, privacy, and resource efficiency. The document provides an overview of IoT's functionality, scope in daily routines, and the technological and societal issues it encounters.