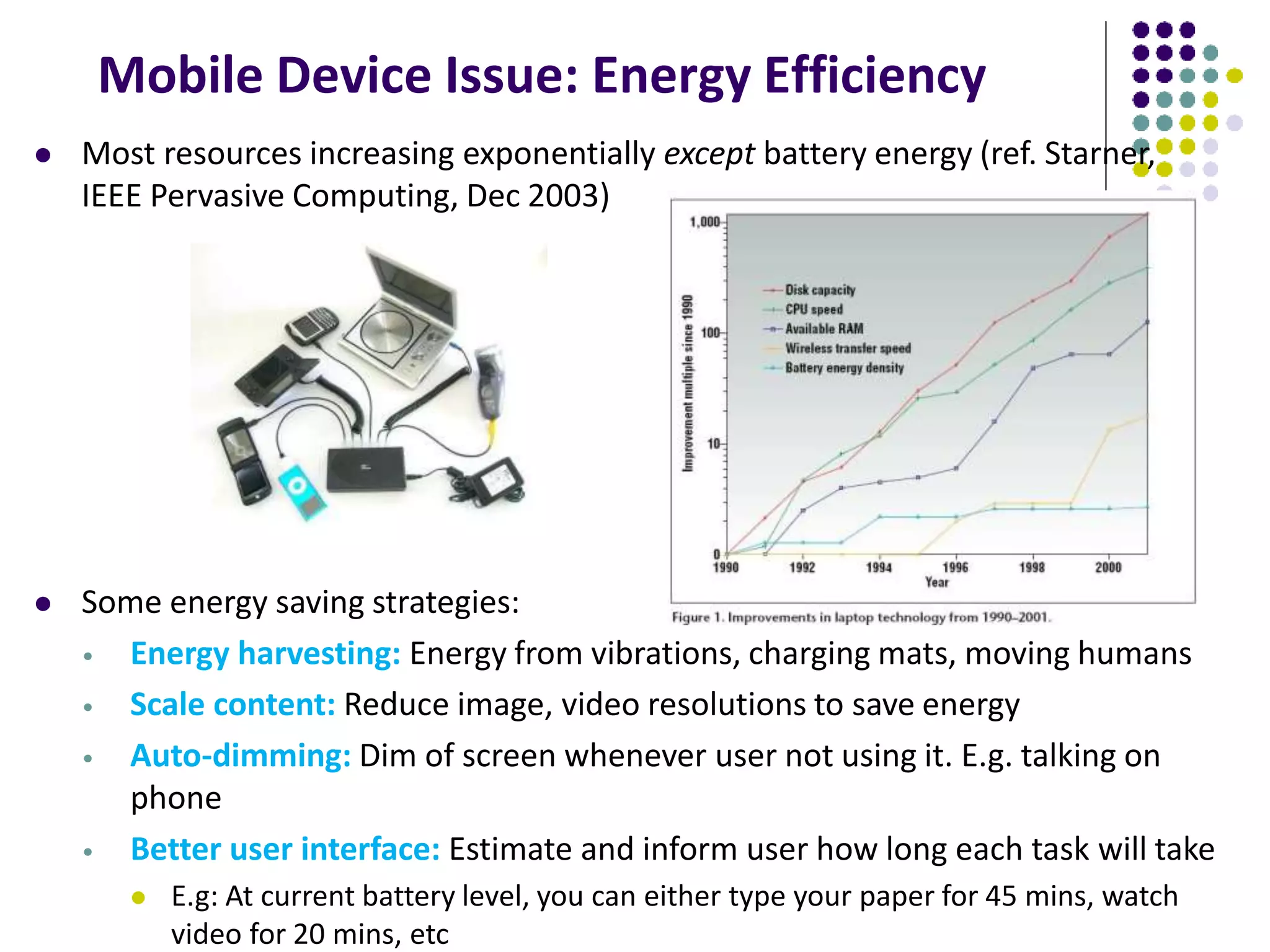
1. The document provides an introduction to mobile and ubiquitous computing, covering topics like mobile devices, wireless networks, mobile computing concepts, and ubiquitous computing applications.
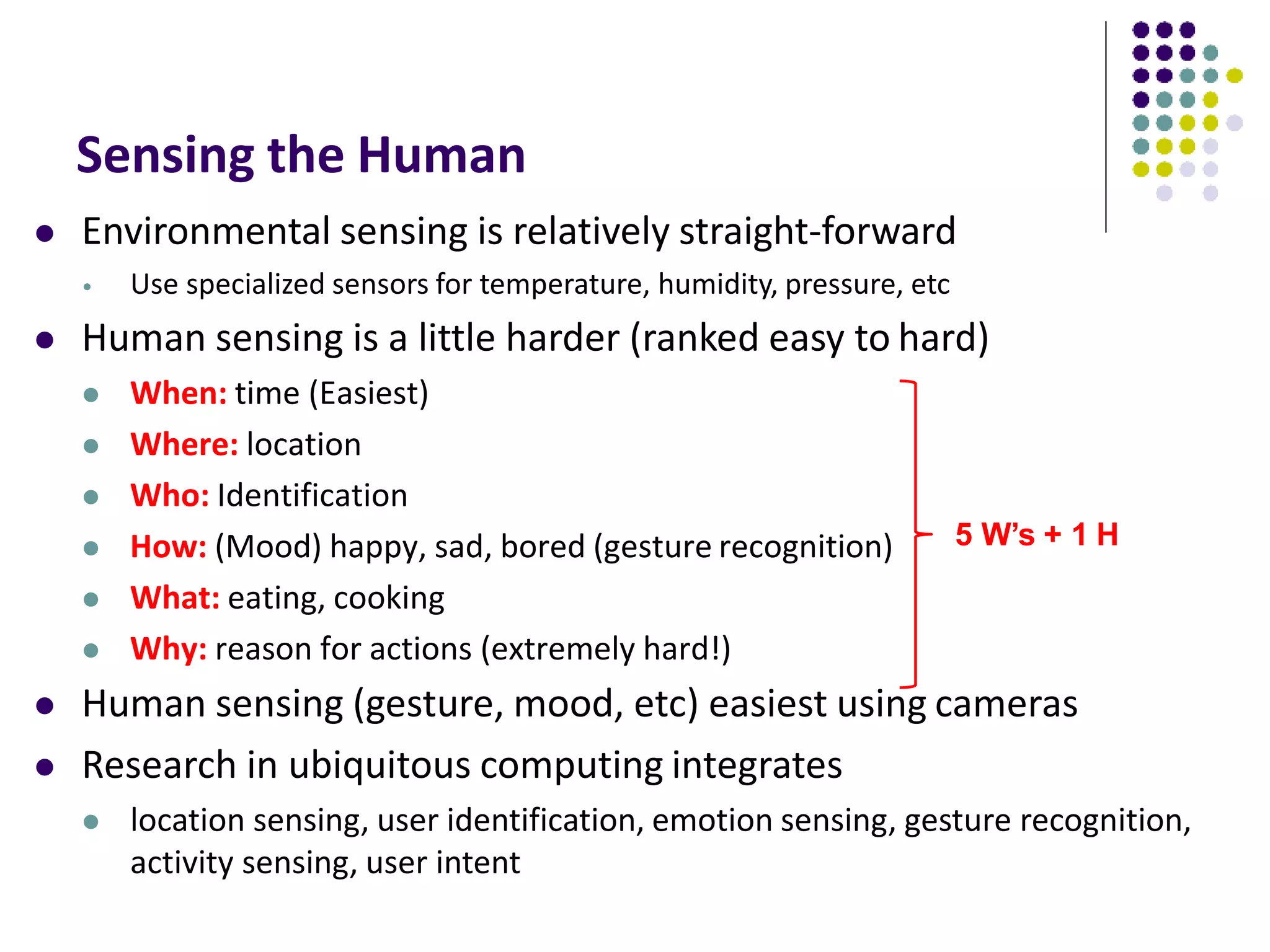
2. It discusses how ubiquitous computing uses sensors and context awareness to create intelligent systems that can actively assist users based on their environment and intentions.
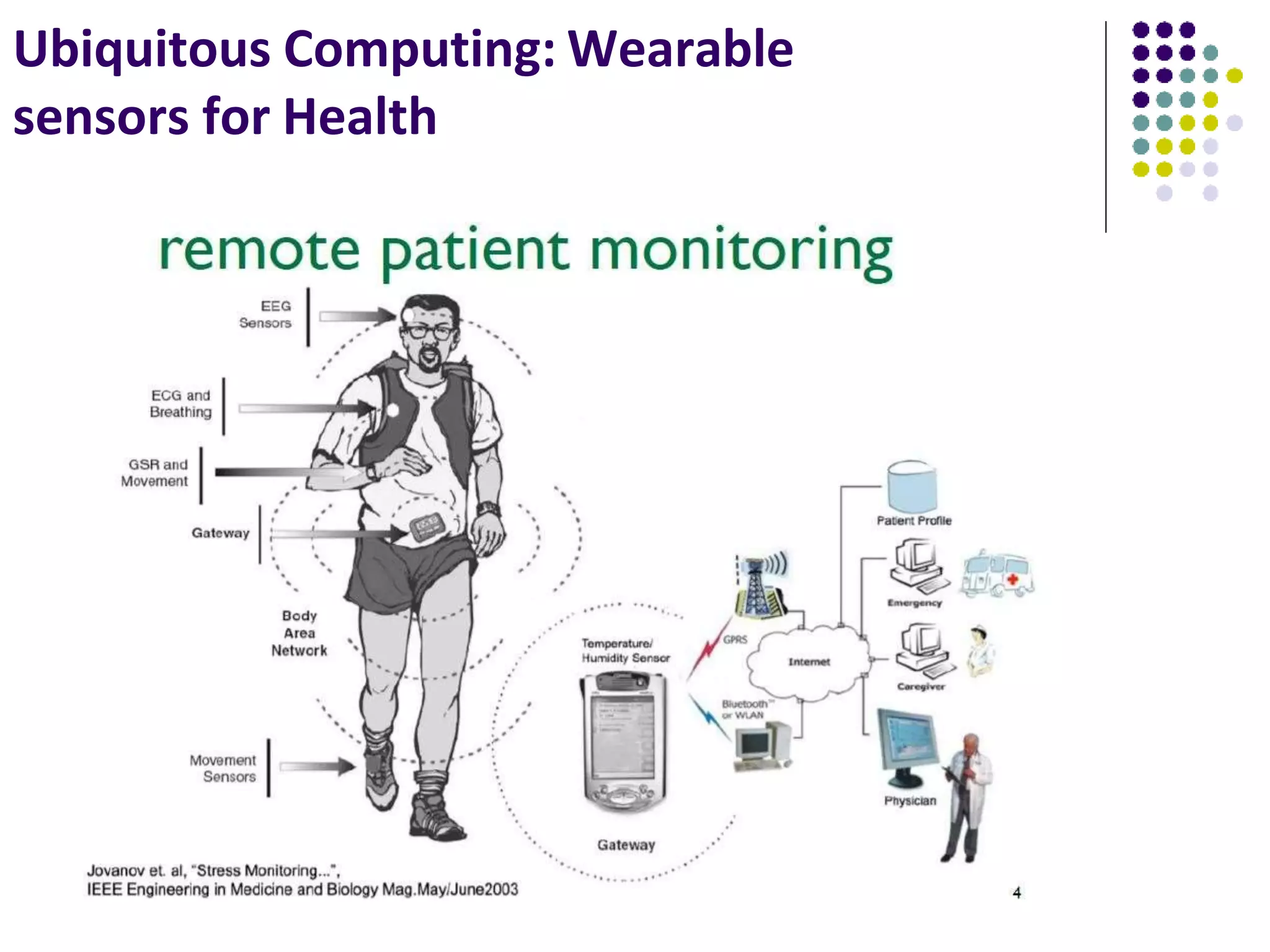
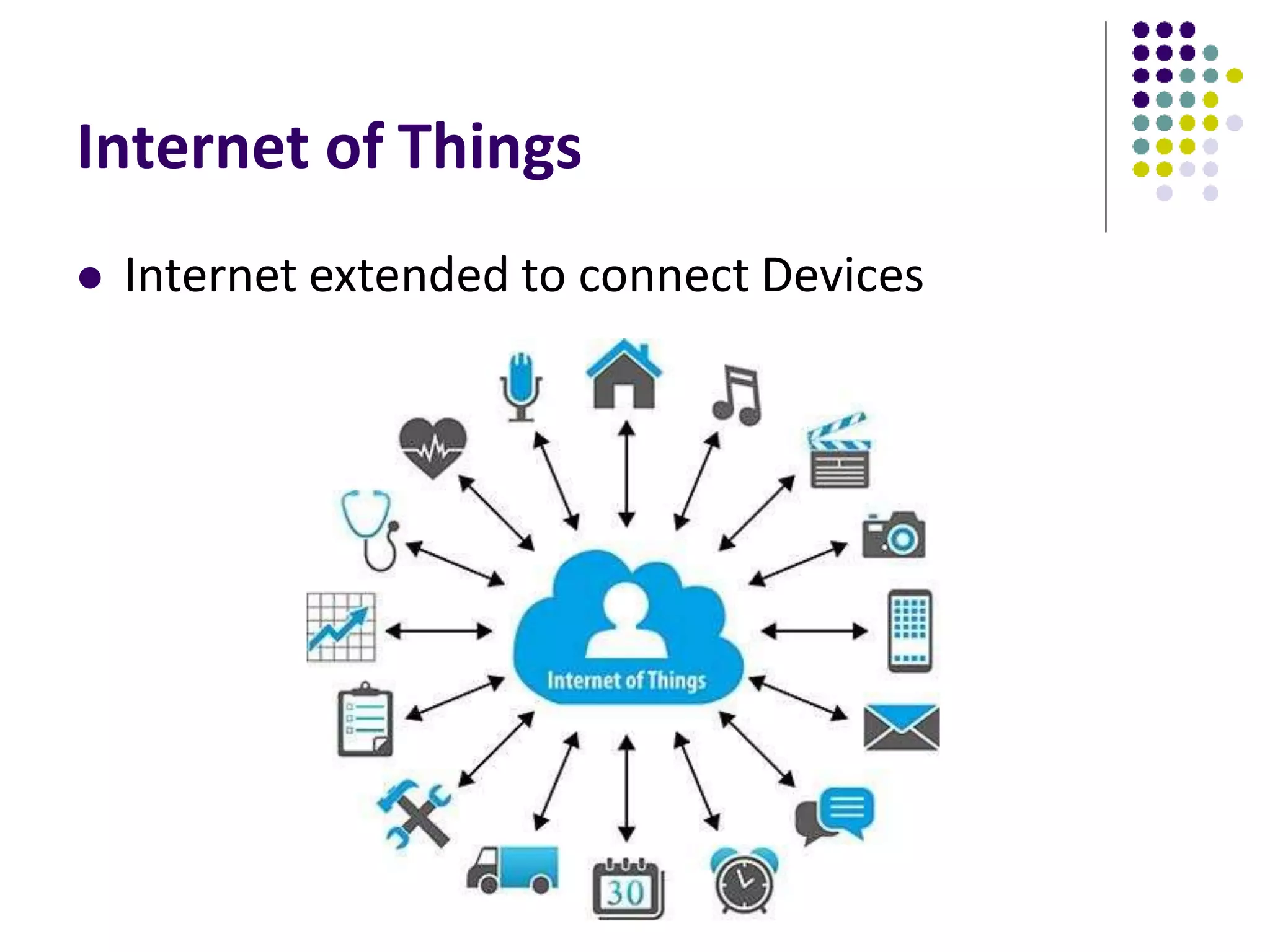
3. The rise of wearable devices and the Internet of Things is extending ubiquitous computing beyond mobile devices by embedding sensors into everyday objects to sense and interact with the physical world.