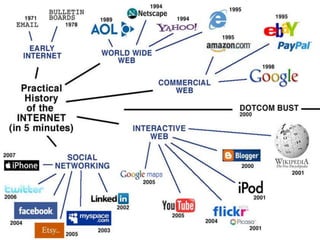
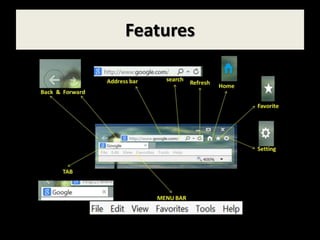
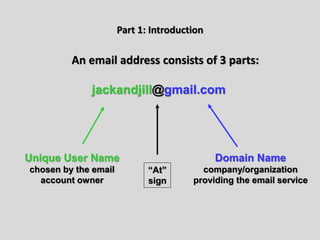
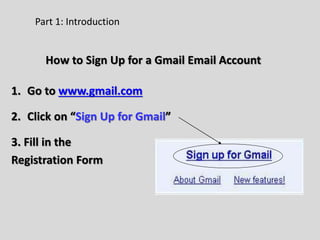
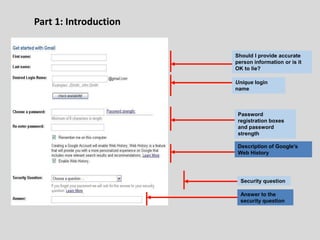
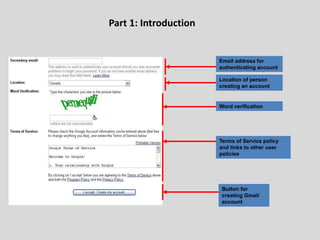
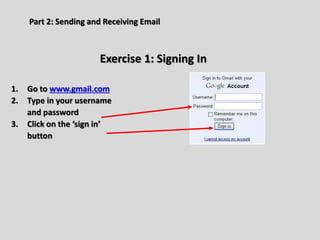
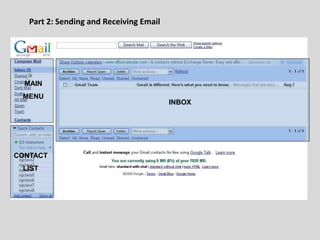
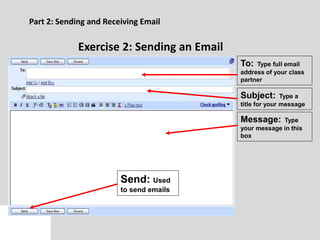
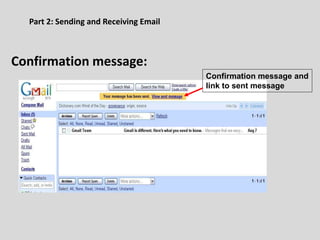
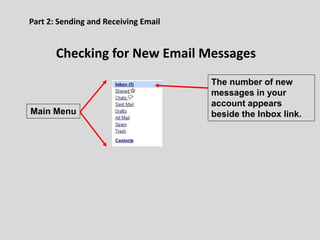
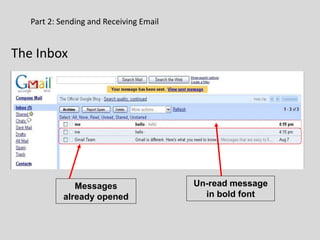
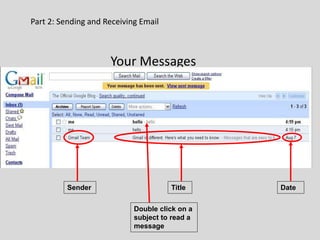
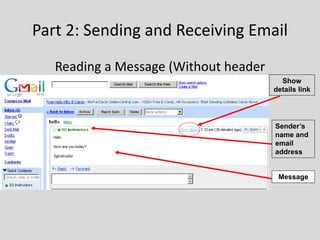
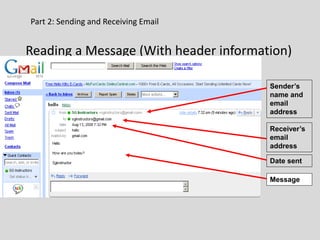
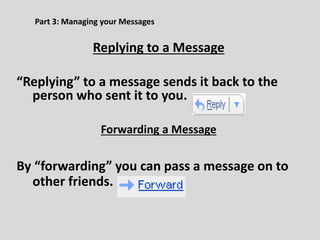
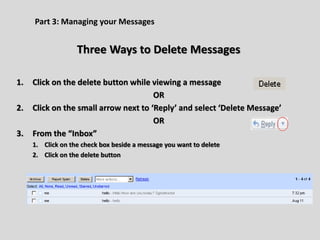
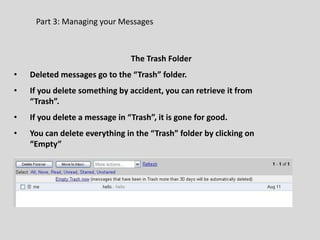
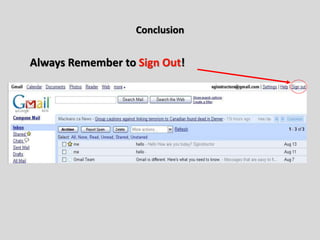
This document provides an overview of email and how it works. It discusses the components of an email address, popular email providers like Gmail and Hotmail, and how to sign up for a free email account. It also describes how to send, receive and manage emails, including composing, replying, forwarding, and deleting messages. Basic email security tips are also covered, such as signing out of email accounts and avoiding phishing scams. The document concludes by providing contact information for any additional email training questions.