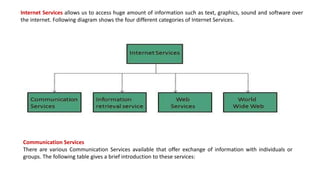
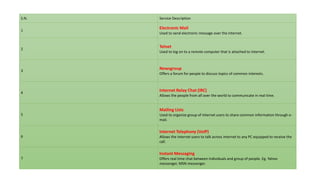
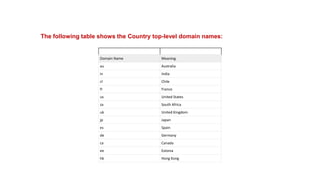
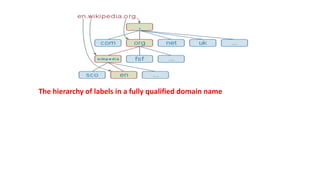
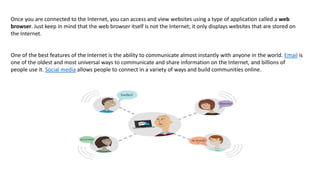
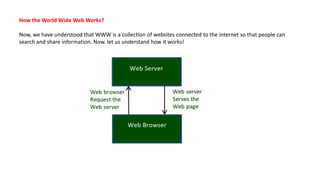
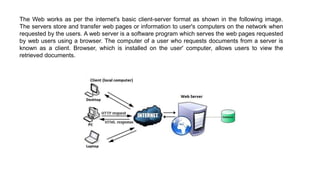
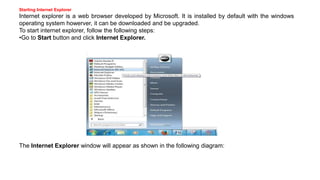
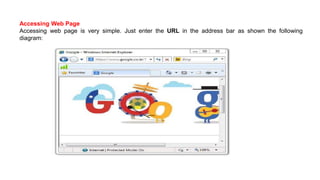
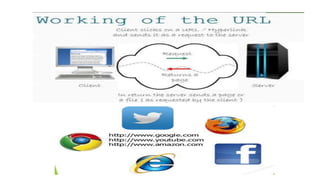
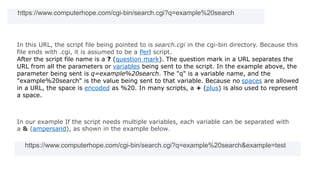
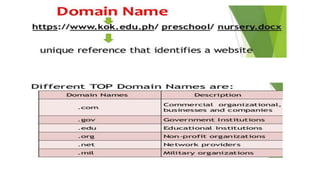
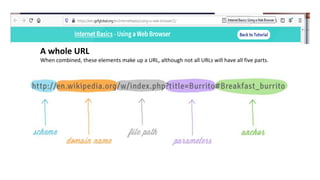
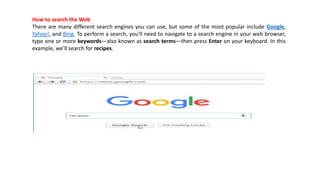
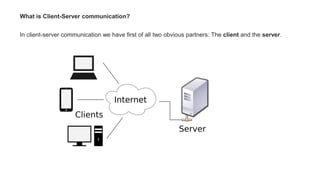
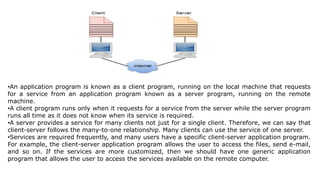
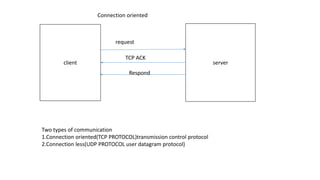
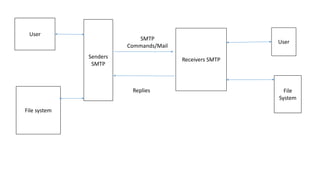
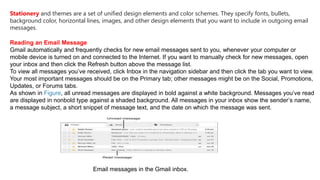
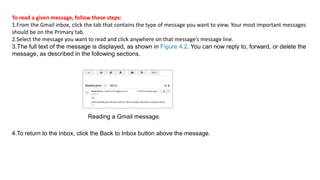
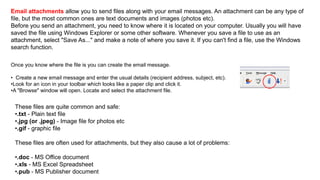
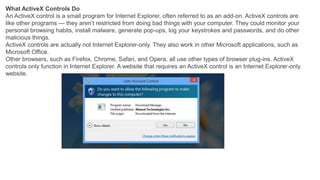
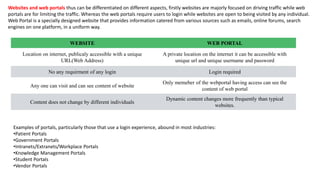
The document provides an overview of the internet and its services, explaining its significance in daily life and various functionalities such as communication, information retrieval, and online interactions. It describes elements like IP addresses, domain names, and the World Wide Web (WWW), detailing their structures and functions. Additionally, it outlines the history and evolution of the web, emphasizing its role in facilitating global connectivity and commerce.