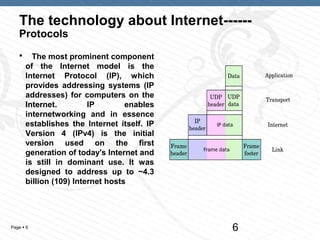
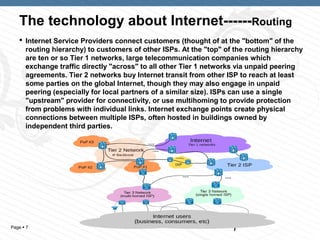
The document discusses the history and technology of the Internet. It began as a project by ARPA and the U.S. Department of Defense in 1983 to develop protocols like TCP/IP to connect heterogeneous networks. The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use standards like TCP/IP to serve billions of users worldwide. It uses protocols like IP to provide addressing and enable internetworking between millions of private, public, academic, business and government networks. Internet service providers and routing hierarchies allow networks and users to connect globally through peering agreements and transit. The Internet is now tied to over 160 countries and considered the prototype of the future global information highway.