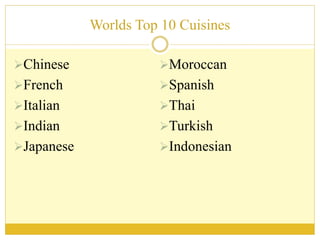
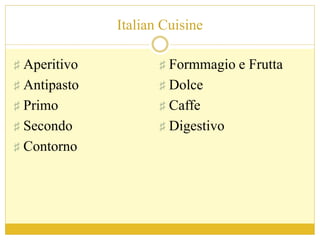
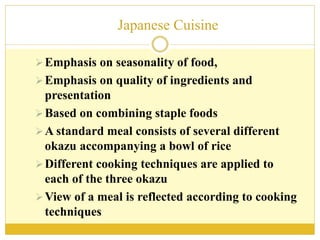
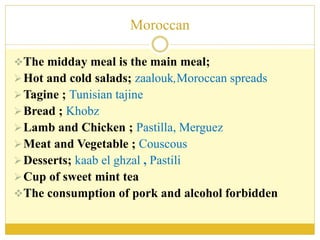
The document discusses the top 10 world cuisines including Chinese, French, Italian, Indian, Japanese, Moroccan, Spanish, Thai, Turkish, and Indonesian cuisine. It provides an overview of each cuisine including popular dishes, cooking techniques, and regional variations within countries. Key ingredients and cultural customs associated with meals are also summarized for each cuisine.