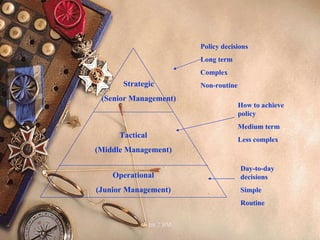
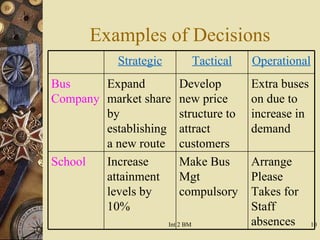
This document discusses business enterprise decision making. It outlines the objectives and strategies that managers use to determine where the business is currently and where it wants to go. Strategic decisions are long term and made by senior management. Tactical decisions are short term and made by middle managers. Operational decisions are day to day and made by low level managers. The types and examples of strategic, tactical, and operational decisions are provided.