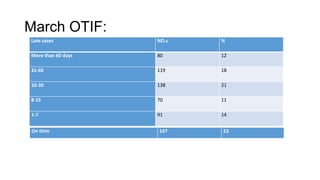
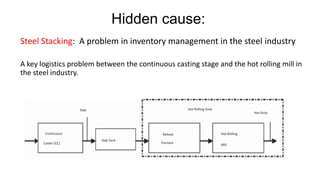
The document discusses customer service level improvements in Vardhman Special Steels' supply chain, emphasizing the importance of delivery performance indicators such as Order Fulfilment Rate (FFCOFR) and On Time In Full (OTIF). OTIF is crucial for measuring efficiency and accuracy in deliveries, requiring correct order entries and timely execution across the company's operations. It identifies root causes of delivery failures, such as internal miscommunication and inventory management issues, and suggests solutions including improved planning and communication among departments.