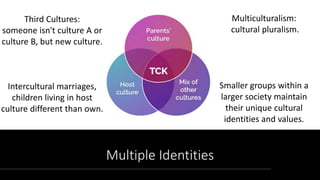
This document discusses intercultural communication competence, which refers to the ability to communicate effectively with people from other cultures. It identifies several skill areas important for intercultural communication, including personality strength, communication skills, psychological adjustment, and cultural awareness. The document also discusses concepts like third cultures, multiculturalism, post-ethnic cultures, ethics in intercultural communication, barriers to intercultural communication, and more.